-
 @ Cryptape
2025-04-25 02:00:02
@ Cryptape
2025-04-25 02:00:02Crypto Insights
1 BTC Quantum Cracking Challenge Called a Joke
Quantum computing research organization Project Eleven launched “Q-Day Challenge,” announcing a 1 BTC reward to the first team that can crack an ECC (elliptic curve cryptography) key using Shor’s algorithm on a quantum computer before April 5, 2026. Project Eleven considers this an extremely difficult task, stating that even recovering a few private keys would be big news.
However, Shinobi from Bitcoin Magazine called the bounty a joke, arguing it provides no serious incentive for several reasons:
- Even highly optimistic forecasts place the feasibility of such a quantum breakthrough at least 5–10 years away.
- At Bitcoin’s current price of $80,000, the bounty is insufficient compensation for such a demanding task.
- A quantum computer could be used for much more lucrative exploits—eavesdropping on internet connections regardless of TLS, breaking encrypted private communications, or compromising the certificate authority hierarchy of the DNS system.
New BIP Proposal to Redefine Bitcoin’s Smallest Unit
A new BIP draft proposes redefining the term “Bitcoin” to refer to the smallest indivisible unit in the system—currently “sat” (Satoshi). The goal is to make transaction amounts more readable and reduce user error. For example, someone with 851 sats would simply see “851 bitcoin” instead of “0.00000851 BTC.” Only the display and interpretation of amounts would change—the protocol remains untouched.
Previously, BIP 176 attempted to improve readability by introducing “bits” (100 sats), but it introduced a new denomination users had to learn and switch between.
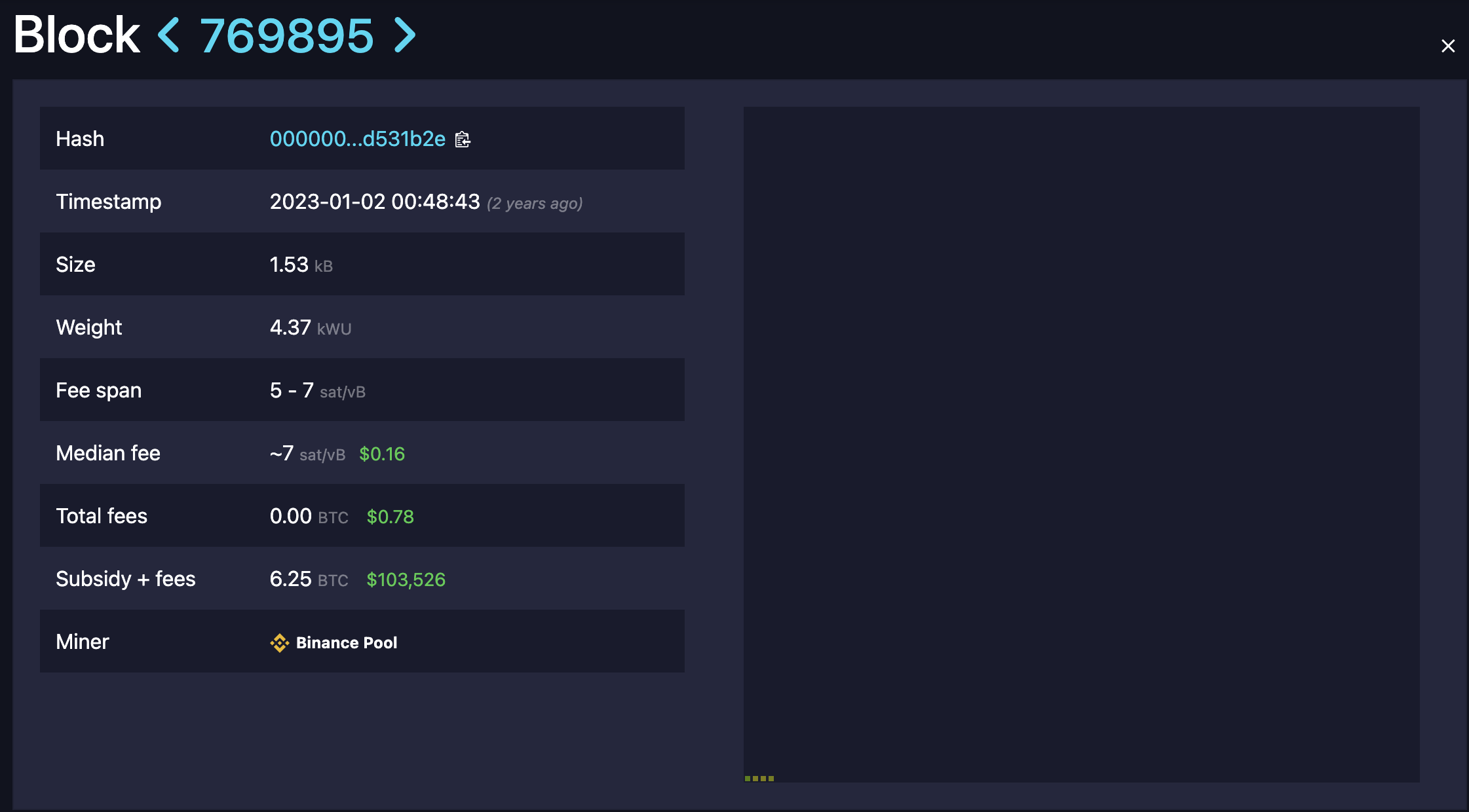
Sparse Bitcoin Block Contains Only 7 Transactions
Bitcoin transaction activity has slumped to its lowest in over two years. Recently, top mining pool Foundry mined a sparse block—Block 890466—containing only 7 transactions and weighing 5,369 weight units.

The last time a block was sparser was in January 2023, when Binance Pool mined Block 769895, which included just 4 transactions and weighed 4,370 weight units.
Over 95% of Bitcoin Blocks Mined by Just 6 Pools
A recent investigation by b10c analyzed the hash rate shares of Bitcoin’s five largest mining pools to examine centralization trends in 2025. Part one looked at mining pool information in coinbase transactions. Part two considered the assumed potential proxy pools. Both parts revealed a high concentration of mining activity. The conclusion: over 95% of recent blocks were mined by just six pools.
Bitcoin Hashrate Projections Through 2027
Valentin Rousseau in collaboration with Blockspace published hashrate forecast, covering:
- Hashrate forecasts for 2025, 2026, and 2027
- How current Bitcoin mining economics may influence the hashrate trajectory
- Hashrate expansion schedules for public miners, plus probability of completion
- Sensitivity tables for hashrate growth under various Bitcoin prices
Using VLS for Non-Custodial Lightning Integration
VLS (Validating Lightning Signer) is a library and reference implementation for a signer module to secure Lightning nodes. It separates Lightning private keys and security rule validation from the node, moving them to a dedicated signing device, thereby reducing the attack surface and enhancing security.
Before VLS, it was nearly impossible to securely manage Lightning private keys in a hosted environment without taking custody of user funds. Blockstream’s Greenlight demonstrates in this case study how VLS enables developers to seamlessly integrate non-custodial Lightning payments into their apps, with minimal overhead, while ensuring users retain full control of their funds.
How CTV+CSFS improves BitVM bridges
Robin Linus elaborates on how input-committing covenants can be used to build more efficient and secure bridges in the BitVM ecosystem. By using CTV (CHECKTEMPLATEVERIFY) and CSFS (CHECKSIGFROMSTACK), the need for presigning committees is eliminated and transaction size is significantly reduced. This simplifies bridge architecture, enhances operational efficiency, and aims towards trust-minimized Bitcoin interoperability, though challenges such as potential censorship in the peg-in process remain.
RISC Zero Launches R0VM 2.0 with Performance and Security Gains
RISC Zero introduced R0VM 2.0, a major upgrade to its zkVM focused on performance and scalability. Enhancements include:
- Ethereum block validation and execution time cut from 35 minutes to 44 seconds;
- Validity proof costs reduced 5x, with batch sizes of 25 bringing per-block costs down from $1.355 to $0.2747; for larger batches, as low as $0.0012.
On the security side, formal verification is a key focus of R0VM 2.0. The Keccak circuit’s determinism has been fully verified, and 122 of the 123 components in the v2 RISC-V core circuit have also been confirmed deterministic.
Bitcoin Soft Forks Could Improve BitVMX
BitVMX is a platform for optimistic verification of Bitcoin smart contracts. In this article, Fairgate Labs outlines various potential Bitcoin upgrades and how they could benefit BitVMX. The article argues that new opcodes introduced via soft forks could improve efficiency, reduce on-chain costs, simplify scripting, and promote decentralization.
Ethereum Execution Layer to Replace EVM with RISC-V
Vitalik announced a long-term proposal to replace the EVM in Ethereum’s execution layer with RISC-V as the virtual machine for smart contracts. This aims to significantly improve execution efficiency and address key scalability bottlenecks, while also simplifying the execution layer.
Additionally, Cardano’s Charles Hoskinson mentioned that their project is also using RISC-V in BitVMX, stating: “RISC-V is the future.”
Top Reads on Blockchains and Beyond
Viewing a Clown World Through Bitcoin: Responsibility, Freedom, and Self-Reflection
The book Bitcoin: The Inverse of Clown World critiques a modern society filled with “clowns”—obsessed with false political narratives and meaningless social issues, such as excessive focus on “political correctness” and climate change. The author argues that the root of absurdity is a lack of personal responsibility, and that when money breaks down, everything becomes political theater.
Beyond exposing and criticizing these absurdities, the book promotes Bitcoin as a means to succeed by providing value. It emphasizes the importance of protecting one’s time and mind in an era of information overload and encourages readers to reflect on their lifestyles and contribute to making a better world—with Bitcoin as a foundation for that change.
The book review by Bitcoin Magazine.
GPU Proof-of-Work: Redefining Energy, Computation, and Money in the AI Age
The author envisions a future where GPU-based Proof-of-Work (GPU PoW) plays a pivotal role in an AI-driven world. GPU PoW can secure cryptocurrencies, train AI models, balance energy loads, and help build a global compute marketplace. Unlike ASICs, which are limited to mining, GPUs are versatile and can dynamically shift workloads for optimal economic return.
By coordinating local data centers, superclusters, and middleware, GPU PoW can improve energy and compute efficiency without sacrificing decentralization. This gives rise to a new utility-based economic system. PoW is no longer just about mining—it becomes infrastructure supporting the convergence of AI, energy systems, and monetary networks.
DahLIAS:First Cryptographic Protocol for Fully Cross-Input Signature Aggregation Compatible with Secp256k1
Blockstream’s research team has introduced DahLIAS, the first cryptographic protocol that enables full cross-input signature aggregation, while remaining compatible with Bitcoin's existing secp256k1 elliptic curve.
An interactive aggregate signature scheme allows n signers—each with their own (sk, pk) key pair and message m—to jointly produce a short signature that proves each m was signed under its corresponding pk. While such schemes can offer massive space and verification savings—two critical bottlenecks for blockchain like Bitcoin—aggregate signatures have received less attention compared to other multisig schemes like MuSig2 or FROST.
DahLIAS is the first such scheme built on discrete logarithms in pairing-free groups, with constant-size signatures that look just like standard Schnorr signatures. DahLIAS also addresses real-world use cases. In addition to its savings in space and time, it supports key tweaking—a common Bitcoin technique used in hierarchical deterministic wallets to derive keys and enhance on-chain privacy.
Read the full paper.
Thunderbolt: A Formally Verified Protocol for Off-Chain Bitcoin Transfers
Bitcoin Thunderbolt is a novel off-chain protocol for asynchronous, secure transfer of Bitcoin UTXOs between uncoordinated users. Unlike prior solutions such as payment channels or the Lightning Network, Bitcoin Thunderbolt requires no prior trust, direct interaction, or continuous connectivity between sender and receiver.
At its core, Bitcoin Thunderbolt employs a Byzantine fault-tolerant committee to manage threshold Schnorr signatures, enabling secure ownership delegation and on-chain finalization.
Read the full paper.