-
 @ infognomics
2025-05-01 08:19:56
@ infognomics
2025-05-01 08:19:56In the heart of Romania’s 2024 presidential election, a seismic shock rattled the foundations of its democracy. Just days before the final runoff, the Constitutional Court made an unprecedented move: it annulled the entire election, citing evidence of Russian interference that propelled a far-right nationalist, Călin Georgescu, to a surprise lead. Was this a bold reflex to safeguard democratic integrity against foreign manipulation, or a chilling cancellation of the people’s voice, silencing millions who had cast their ballots? As Romania grapples with this historic decision, the line between protecting democracy and undermining it has never been blurrier, leaving citizens and observers alike questioning the true cost of this electoral upheaval.
In this article, I will explore Romania’s 2024 presidential election annulment chronologically, tracing the rise of far-right candidate Călin Georgescu, the Constitutional Court’s decision to cancel the vote on December 6, and the resulting protests and probes into foreign interference. This timeline will clarify whether the move was a democratic safeguard or an undemocratic suppression of the people’s will.
October 15, 2024
Judges booted candidate Diana Șoșoacă, leader of the ultra-nationalist party S.O.S Romania, from the race because she threatened Bucharest’s place in the EU and NATO. But her rivals are saying the court overstepped its remit.
The unprecedented ruling by the Constitutional Court of Romania (CCR) sparked criticism from Șoșoacă’s rivals across the political spectrum, encompassing socialists, liberals and academics — with one figure even pointing to how it echoes the Kremlin’s electoral governance.
November 22, 2024
The final major poll before Romania’s 2024 presidential election, released on the eve of the vote, painted a starkly different picture from the eventual outcome. Prime Minister Marcel Ciolacu led with 23.7%, followed by Elena Lasconi at 17.8%, George Simion at 16.9%, and Nicolae Ciucă at 14.3%. Astonishingly, Călin Georgescu, who would later surge to a stunning first-round victory, languished in fifth place with just 8.1%, a staggering underestimation that would soon fuel suspicions of manipulation and upend the nation’s electoral process.

November 24, 2024
In a stunning upset, Călin Georgescu won Romania’s 2024 presidential election with 22.94% of the vote, dominating the first round despite trailing in pre-election polls. George Simion, often labeled the country’s “hard right chief” by Western media, lagged behind in fourth place with just 13.8%. No credible evidence suggests vote tampering; Georgescu’s victory reflected a genuine surge of voter support, particularly among the diaspora, where he won overwhelmingly—except in Moldova, where he secured only 3.11% amid a large pro-Russian population that had narrowly passed a pro-EU referendum a month earlier.
As regards Georgescu himself, by CV, appearance and speaking style he comes across as the ideal candidate. He studied agronomy, has a PhD in soil science and is a university lecturer; has worked at senior levels in government – including in the Ministry of Foreign Affairs – as well as at the UN and other NGOs, with a focus on sustainable development; and he speaks four foreign languages. He projects a professional, clean-cut image of a determined, experienced 62 year-old nationalist at the apex of his powers, speaking very simply and clearly in a calm, confident manner. Strictly by these superficial PR metrics, on paper, he is, at first glance, perfectly suited for the role.
Nor is he unknown in Romanian politics; but he is – or has been – a very fringe figure. His name was floated several times in recent years, in nationalist-populist circles, as a potential alternative for prime minister. He nearly became honorary president of Romania’s main nationalist conservative party, AUR, before the deal fell through when past comments came to light in which he had called the country’s Second World War leader and Axis ally, Marshal Antonescu – who is considered responsible for the Romanian Holocaust – a “hero”.
Georgescu had conducted a persuasive online campaign, primarily on TikTok, focusing on the importance of an autochthon economy, the inherent superiority of rural life in Romania, and essentially claiming that just like a national poet from the 19th century, he is a divine messenger. The campaign consisted of thousands of TikTok profiles distributing ten-second videos about him, with many influencers suggesting in the past weeks that they would vote for him. According to Georgescu, he didn’t spend any money on the campaign, but the scale and the professionalism in which it was conducted suggest otherwise.
November 25, 2024
Politico comes to remind us why EU is so interested about Romania. According to this article, Romania has been a steadfast ally in the West’s support for Ukraine, leveraging the Port of Constanța as a critical lifeline for exporting Ukrainian grain and funneling military supplies into the conflict zone. The war has also elevated the strategic significance of the Mihail Kogălniceanu air base on the Black Sea, poised to become NATO’s largest. However, Călin Georgescu’s unexpected electoral triumph raises alarms across Europe, as his leadership could pivot Romania away from this pro-Western stance, potentially disrupting these vital geopolitical roles. This prospect underscores why European leaders are deeply invested in ensuring Romania remains in “reliable” hands, aligned with NATO and EU priorities.
November 26, 2024
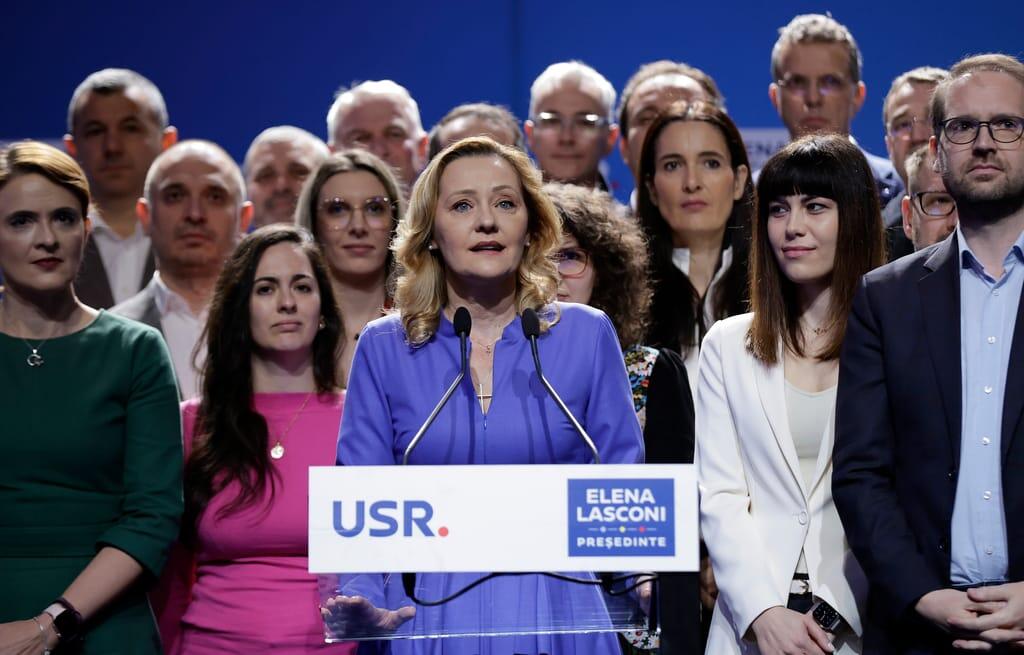
Reformist Elena Lasconi, who was going to face Georgescu in the runoff on Dec. 8, was directly warning that Romanians must now rally together to stop the country falling back under the thrall of Russia, which occupied it after World War II. She urged a crowd in Bucharest not to let frustration with the current establishment “become a vulnerability exploited by Russia.”

November 28, 2024
The official claim of Russian meddling rested directly and exclusively on a specific set of intelligence documents on the matter, first submitted in a closed National Security Council meeting on 28 November. Romania’s Constitutional Court asked the country’s top election authority to recount and check again all ballots from Sunday’s presidential election first round.
November 30, 2024
Elena Lasconi, who narrowly secured a runoff spot by edging out PSD Prime Minister Marcel Ciolacu by just 2,700 votes, has firmly rejected allegations of electoral misconduct. Lasconi and her party, USR, accuse the PSD and center-right PNL of undermining the people’s will through the annulment push. In a passionate statement, she urged, “I appeal to all state institutions: Don’t destroy democracy in Romania,” highlighting the high stakes for the nation’s democratic integrity.
December 4, 2024
The set of intelligence documents on the matter, first submitted in a closed National Security Council meeting on 28 November and then hastily declassified on 4 December by the sitting President in order to “inform” the Constitutional Court’s decision. But the reports contained no actual evidence of the sort.

The documents alleged that 800 TikTok accounts had been activated just before the election and that they had supported Călin Georgescu’s campaign.
Albeit these reports did not definitely say that the meddling effort managed to actually sway the election in Georgescu’s favour, they suggested it.
I ve translated the declassified documents using the AI tools: Grok and ChatGPT. I can assure you that the following summary from "Brussels Signal" is accurate. I will quote the summary because of the key importance on the subject:
The documents provide no concrete evidence of Russian state interference in Romania’s presidential elections or any links between presidential candidate Calin Georgescu and Russia.
The most important and explosive term used in these documents (by SRI) is “state actor.” The documents offer no evidence or analytical explanation for the use of this term, rendering it an unsupported claim.
On the contrary, to the extent that they shed light on anything, the documents indicate that Georgescu’s campaign simply employed highly effective digital marketing techniques, giving him a “comparative exponential” advantage (according to SRI).
The documents offer only disparate, circumstantial, and often trivial information presented in a way that leaves plenty of room for wide-ranging interpretations. Their tone and terminology appear designed to fuel an anti-Georgescu narrative in the public sphere.
As intelligence products, the documents are sloppy and of very poor quality by Allied standards. They include contradictions, errors, and blatant inaccuracies. The language is often vague, and key terms remain undefined (e.g., various uses of the word “network”). For the most part, the documents are full only of useless platitudes, with the majority of the information already having been circulating in the public domain in the days after 24 November (the date of the first voting round).
The documents are merely “Briefing Notes” (note informative, in Romanian), not assessments – thus lacking clear and definitive analytical conclusions or interpretations. They make isolated claims (mostly unsupported), with no discussion of sources or evidence. This is likely a method for the intelligence services to protect themselves politically. Subsequent interpretations of these documents by the media are not, therefore, based on conclusions of the Romanian state.
The documents are also redacted in key parts. It is therefore important to understand that the information in these documents was only partially declassified – despite the media narrative suggesting the documents were declassified in their entirety. It is also important to understand that the redacted passages may alter the meaning of the text.
The SIE Briefing Note has not actually been declassified. The President only published an “unclassified excerpt” from it. The SIE Note itself remains classified, likely because it contradicts the Notes submitted by the other agencies.
The documents do point to potential irregularities in Georgescu’s campaign finance statements. However, such issues are common in campaigns worldwide and, moreover, should be investigated with respect to all the other candidates as well, in the same way. In any case, the documents make no suggestion of foreign funding, let alone from Russia.
The only concrete elements noted in the documents as being specifically identified as of 24 November (the day of the vote in the first round) are: 100 TikTok influencer accounts paid to distribute content using 3 (three) hashtags that do not even mention Calin Georgescu; 797 accounts created before (!) the launch of TikTok itself, under this brand name; 1,088 users in a “coordination” group on Telegram (which, again, is standard in all political campaigns); and $381,000 paid to some “influencers”.
Conclusion: The CSAT documents declassified by the President provide absolutely no real, concrete basis for the public narratives about a “Russian attack” on Romania or of links between Georgescu’s campaign and Russia. These documents, by themselves, cannot rationally be used as arguments against this candidate because they prove nothing.
Shortly after the vote in a televised address President Iohannis claimed that the ‘campaign was illegally supported from outside Romania’ and that it is a ‘matter of national security’.
December 6, 2024
Romania’s top constitutional court dramatically cancelled high-stakes presidential elections after security services warned Russia was mounting “aggressive” hybrid attacks against the country. Călin Georgescu was accused to benefit from a TikTok campaign that was similar to influence operations allegedly run by the Kremlin in Ukraine and Moldova. The files said Moscow was targeting Romania as an enemy state, using “aggressive hybrid action,” a view backed by the United States, at that time.
Running as an independent, Georgescu was due to face liberal Elena Lasconi of the Save Romania Union (USR) in a Dec. 8 runoff. Suspicious of the two old parties, she is also calling on the court not to meddle with Romanian democracy. According to Radio Romania Actualitati, she said: ‘Today is the moment when the Romanian state has trampled on democracy,’ adding: ‘We should have gone ahead with the vote. We should have respected the will of the Romanian people, whether we like it or not; legally and legitimately, nine million Romanian citizens, both at home and in the diaspora, have expressed their preference for a particular candidate by voting. We cannot ignore their will.’
Elena Lasconi, a liberal—by Western standards, however, she might not be considered a typical liberal, as she openly expresses patriotism, displays the Romanian flag alongside the EU flag, and occasionally wears traditional folk costumes—former TV journalist. Lasconi, like Georgescu, is an anti-establishment figure, vocal in her criticism of the current political elite and adept at channelling voter discontent and frustration with mainstream parties. It is no surprise, then, that both the Social Democratic Party (PSD) and the National Liberal Party (PNL)—Romania’s two largest establishment parties—reacted with dismay to the performances of Georgescu and Lasconi. This discontent was amplified by the fact that neither party’s candidate came close to qualifying for a potential second round. Politicians from both the far right as well as liberal reformists Save Romania Union (USR) party view an annulment as an attempt by the widely distrusted old establishment parties — the Social Democratic Party (PSD) and the center-right National Liberal Party (PNL) — to hold on to power by pulling strings within the judiciary. Elena Lasconi, a liberal former TV journalist who was set to stand against Georgescu in the second round, was mortified by what she saw as a hijacking of the electoral process.
The court canceled the process completely, leaving voters bemused as they turned up to cast their ballots. In a defiant video released on Friday night, Georgescu accused the court of launching “practically a formalized coup d’état” and told his supporters to show they are “brave” and not to give up.
In fact, Georgescu was leading with as much as 77 per cent against Lasconi’s 23 per cent in the diaspora when Romania’s Constitutional Court decided to annul the elections.
The President, at that time, Klaus Iohannis was due to end his term on Dec. 21. But in an address to the nation Friday evening, he announced that he was going to stay on until the next president was about to sworn in.
Nicolae Ciucă, the head of the Romanian senate and the National Liberal Party’s presidential candidate in the first round said that The decision to cancel the vote was “without precedent in Romania’s democratic history,” he said, adding “the current situation is a difficult test for our democratic institutions.”
According to the press's findings, behind Georgescu there appears to have been an entire “network” of volunteers – often organised via Telegram – running thousands of co-ordinated TikTok accounts designed to boost each other’s posts – i.e. Georgescu’s short promo videos. TikTok has only relatively recently caught on in Romania; certainly it wasn’t a factor at the last election. This might explain why a strong TikTok campaign would not have registered properly in political analysis, and why it might’ve had an outsized effect on voting intentions. It is also a warning for the future of the very idea of democratic politics, as it shows that it is possible for candidates to completely side-step the traditional “public square”, avoid any major real-world debates or campaigning, and win elections exclusively online.
Still, there is a great deal of mystery over exactly how all this worked. Georgescu’s TikTok metrics are inferior to his three key adversaries for example: there were 145 million views this year for Georgescu’s main hashtags compared to 396 million for Simion’s, 328 million for Ciolacu and 202 million for Lasconi. One difference is that the bulk of Georgescu’s TikTok views and followers accrued within the past two months. Coupled with other indicators, it seems rather clear that so-called “troll farms” have been at work on his behalf, to spread his message; but it is not clear whether this practice is unique to Georgescu or whether it has been used – to varying degrees – by his opponents as well.
As Georgescu is perceived to be “pro-Russia” – an imprecise term to boot – suspicion in this regard is directed towards the Kremlin. But hard evidence is lacking; there is no smoking gun, so far. Russian actors are involved in virtually every election in the West, but their exact role in swinging the result is hardly ever clear. In the US a Congressional investigation – eventually known as the “Russia Hoax”, for good reason – failed to prove alleged collusion between Trump’s 2016 campaign and Moscow, despite widespread belief in this story from those shocked that “orange man” could ever win because his message was more effective.
The reaction from the EU and Washington was particularly alarming, though hardly surprising. ‘The integrity of Romania’s elections is paramount for Romanians’ hard-earned democracy. It is the choice of the Romanian people whom they elect. No other country or foreign actor has that right,’ the US State Department said in a statement. The contradiction is glaring, isn’t it? It’s supposedly the Romanians’ choice who they elect, yet if a candidate not favoured by the Americans wins, the election results are annulled.
Moscow denied meddling into the Romanian democratic process.
December 20, 2024
According to a Snoop (investigative journalist organization) investigation, Georgescu’s alleged financing would have been done by the PNL. ** All this, so that Georgescu’s message would spread and more people could vote for him so that George Simion would not make it to the second round. ** In fact, the ANAF (National Agency for Tax Administration) discovered that the PNL paid for a campaign massively promoting Călin Georgescu on TikTok, published on 20 December 2024.
December 22, 2024
Subsequent investigations by the National Agency for Fiscal Administration (ANAF), Romania’s tax authority, uncovered the origins of Călin Georgescu’s successful TikTok campaign: the PNL. The centre-right party’s campaign initially employed the hashtag #echilibrusiseriozitate to promote European values and pro-EU positions. Kensington Communication, the company responsible for the campaign, also targeted Georgescu’s content, aiming to counter his EU-critical rhetoric. However, the hashtag #echilibrusiseriozitate, designed to create an unfavourable environment for non-liberal presidential candidates on TikTok, was replaced by #echilibrusiverticalitate on the FameUP platform—a free automated platform that amplifies marketing campaigns. Interestingly, this new hashtag was ultimately adopted and used by Georgescu’s supporters, transforming its purpose and amplifying his campaign’s visibility. The Romanian government proposed 4 May as the date for a new presidential election. However, no formal decision was made since. Călin Georgescu has since challenged the Constitutional Court’s decision at a local appeals court and lodged a complaint with the European Court of Human Rights. ‘I will take our cause to the heart of Europe, to the highest courts. Each of us is doing our part in this historic mission to defend our democracy,’ he declared.
January 5, 2025
Recent polls show that Călin Georgescu remains the most popular presidential candidate, with some surveys suggesting that the ultranationalist contender could garner close to 40 per cent support.
January 8, 2025
The court is considering disqualifying Georgescu for undeclared campaign funding.
The leaders of the ruling coalition made up of the Social Democrats (PSD), Liberals (PNL), the Democratic Alliance of Hungarians (UDMR), and the minorities' group decided on the new dates for the presidential elections. According to the agreed election schedule, the first round would have taken place on May 4, followed by the runoff on May 18.
At the beginning of the government meeting, prime minister Marcel Ciolacu announced the introduction of sanctions against social media networks that favor candidates, according to Europa Libera Romania.
Georgescu’s appeal against the constitutional court’s decision to nullify the election was rejected, so he lodged a complaint to the European Court of Human Rights.
In fact, even the Venice Commission (the officially European Commission for Democracy through Law) stated that, regarding what had happened in Romania, evidence must be given: ‘An election annulment must be based on transparent evidence, not classified information.’
January 10, 2025
Former European commissioner Thierry Breton assured that the European Union has mechanisms to overturn an eventual AfD victory:
We did it in Romania and obviously we will do it in Germany if necessary.

This was widely seen as a clear admission of their true intentions, as if they had dropped all pretenses and fully revealed themselves.
They tell you to your face that they can suspend elections and that absolutely nothing happens, then they have the cheek to declare themselves the ‘democrats’ and ‘tolerant’, when it is them who are the main enemies of democracy and freedom of expression!
January 12, 2025
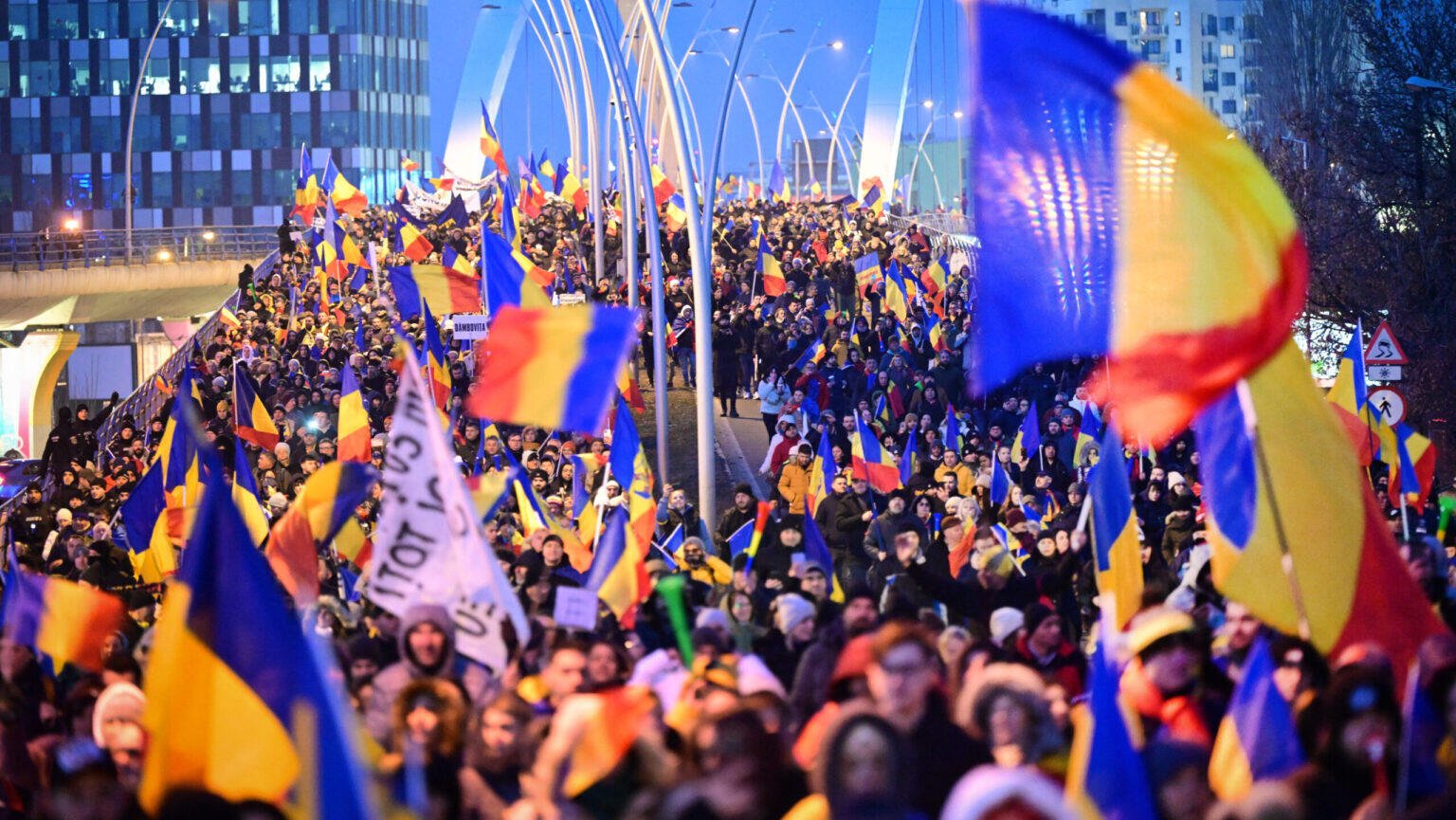
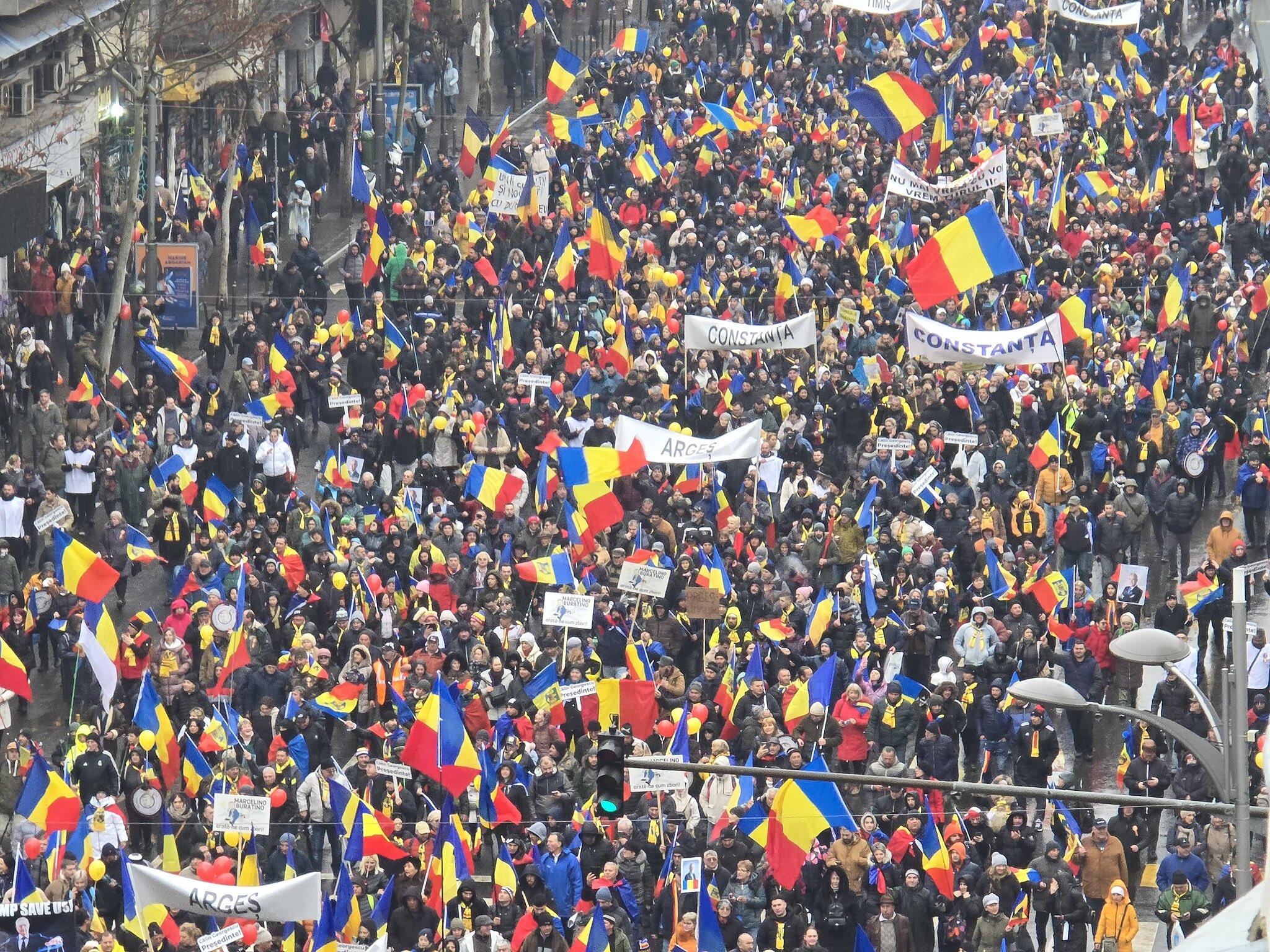
Tens of thousands of supporters of Romanian presidential candidate Călin Georgescu took to the streets in Bucharest on Sunday to protest the annulment of the presidential election. With no concrete evidence emerging to substantiate the allegations of Russian interference, it has become increasingly evident that the progressive elite will go to any lengths to remain in power.

February 1, 2025 According to the last polls, Georgescu would be around 50 per cent; specifically, according to the last one published by România TV, he would obtain 47 per cent.
February 10, 2025
Romanian President Klaus Iohannis announced his resignation before his possible forced dismissal from parliament. Iohannis, echoing Joe Biden, made sure to pardon his family and the judges who suspended the presidential election before leaving, for reasons of precaution.
Once the court cancelled the elections—so no new president was elected—, it also decided to lengthen the current president’s term in office until a new vote in May 2025. Iohannis faced raising opposition, however, as some viewed his lengthened mandate as illegitimate. On the one hand, the Romanian constitution states that a presidential term is five years, and the president remains in office until their successor takes over. On the other hand, it also makes clear that the presidency can be extended only in case of war or catastrophe. Protests also took place against the decision of him remaining in office, and the legislature initiated his removal as well. **Preventing a successful impeachment procedure, Klaus Iohannis stepped down. ** In his resignation speech he highlighted that Romania’s western partners will not understand the reason why he was forced to step down, and that his departure will damage Bucharest’s relationship with its allies. The country’s interim president will be the Senate’s president, Ilie Bolojan.
February 15, 2025
The Constitutional Court of Romania is accused of canceling elections without evidence, allegedly to suppress votes against the EU-aligned political establishment. Claims suggest court judges are linked to Soros-funded NGOs. A network of "independent" NGOs and media, funded by hundreds of millions from the EU and USAID, is said to promote left-wing globalist agendas, manipulate public opinion, and counter conservative values. EU grants and a secret 130 million euro contract to a French agency, tied to corruption, allegedly fueled pro-EU media campaigns, undermining independent journalism and labeling critics as pro-Russia. Independent journalist, Iosefina Pascal, talks thoroughly about this case.
February 19, 2025 Renowned journalist and X (formerly Twitter) personality Mario Nawfal interviews Georgescu, with clear expressions of support for Trump and Musk, alongside a strong critical stance toward George Soros.
February 26, 2025 Romania’s presidential candidate, Calin Georgescu was arrested while en route to Bucharest to announce his new presidential campaign. Georgescu’s campaign team has confirmed that Georgescu was picked up by the police and detained in the middle of traffic for questioning at the attorney general’s office.
Georgescu was declared the winner of that election round, but an arrest warrant was issued against him on February 26, as reported by the Romanian press.
Romanian prosecutors have initiated criminal proceedings against the right-wing politician and candidate for the 2024 presidential election, Călin Georgescu, on six charges. These include allegations of engaging in unconstitutional activities and providing inaccurate financial disclosures, according to official sources.
March 1, 2025
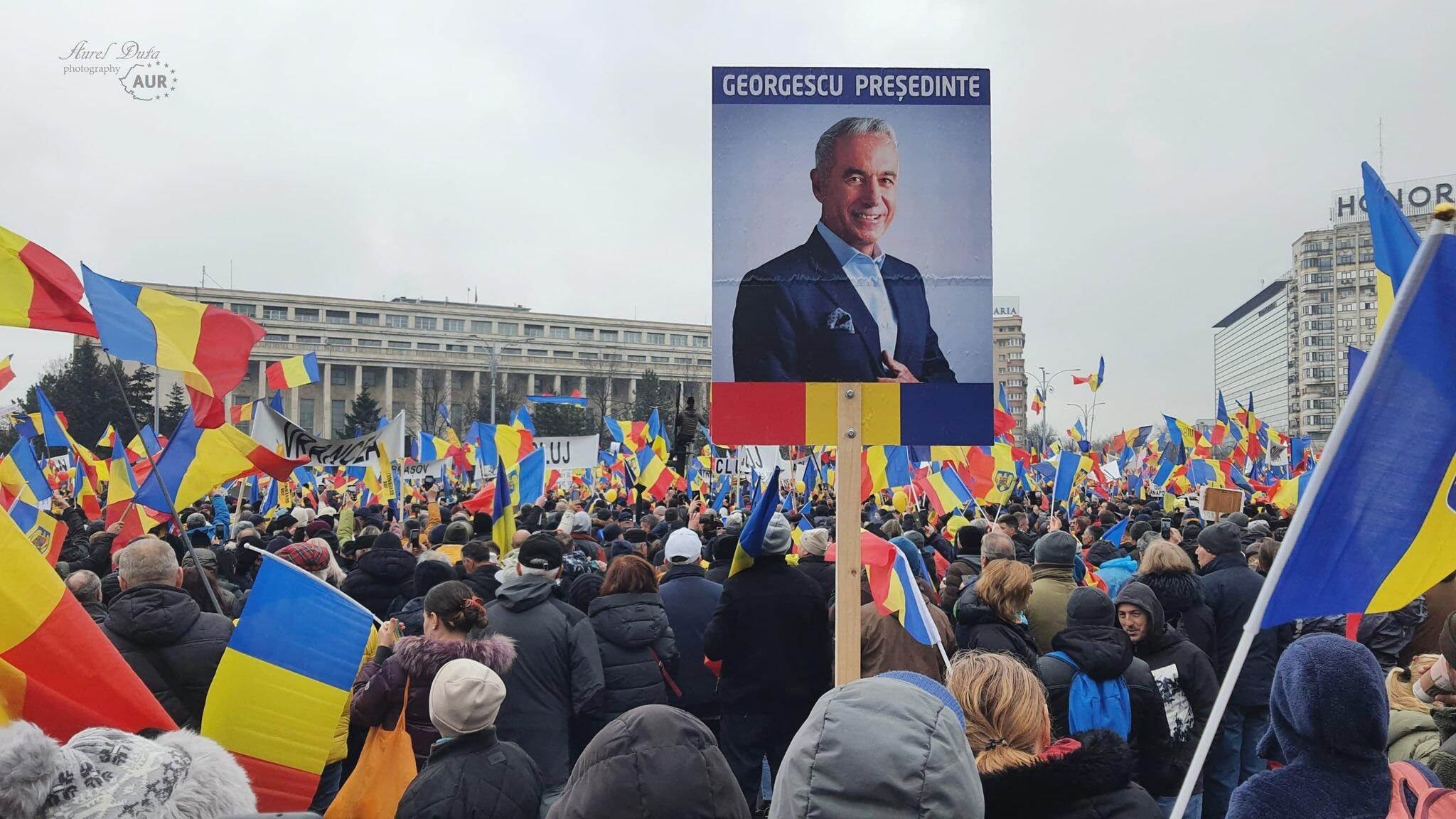
Thousands march for freedom in Romania. Over 200,000 Romanians flood streets for Georgescu. Anti-Soros feelings are everywhere.


March 6, 2025
The Romanian opposition – denied a likely victory – took their case to the European Court of Human Rights.
The ECHR (The European Convention on Human Rights, a supranational convention to protect human rights and political freedoms in Europe) threw the case out without even hearing it. Apparently, the Romanian courts were perfectly within their rights to simply indefinitely postpone their election on the basis of unproven allegations.
Romania is moving toward its strictest censorship law since 1989, granting authorities the power to block websites and social media posts without independent review.
The Emergency Ordinance (OUG) would allow the government to shut down content deemed “false information,” “manipulation,” or a “threat to national security,” with no clear definitions or court approval required.
The Romanian Intelligence Service (SRI), military, cybersecurity agencies, and electoral authorities would have sweeping powers to remove posts and block platforms, while internet providers refusing to comply could face massive daily fines.
This law could be used to silence journalists and political opponents, as there is no independent oversight and no clear standard for what counts as “false information.”
The government claims the measure is meant to combat foreign election interference, but it will actually be weaponized against free speech.
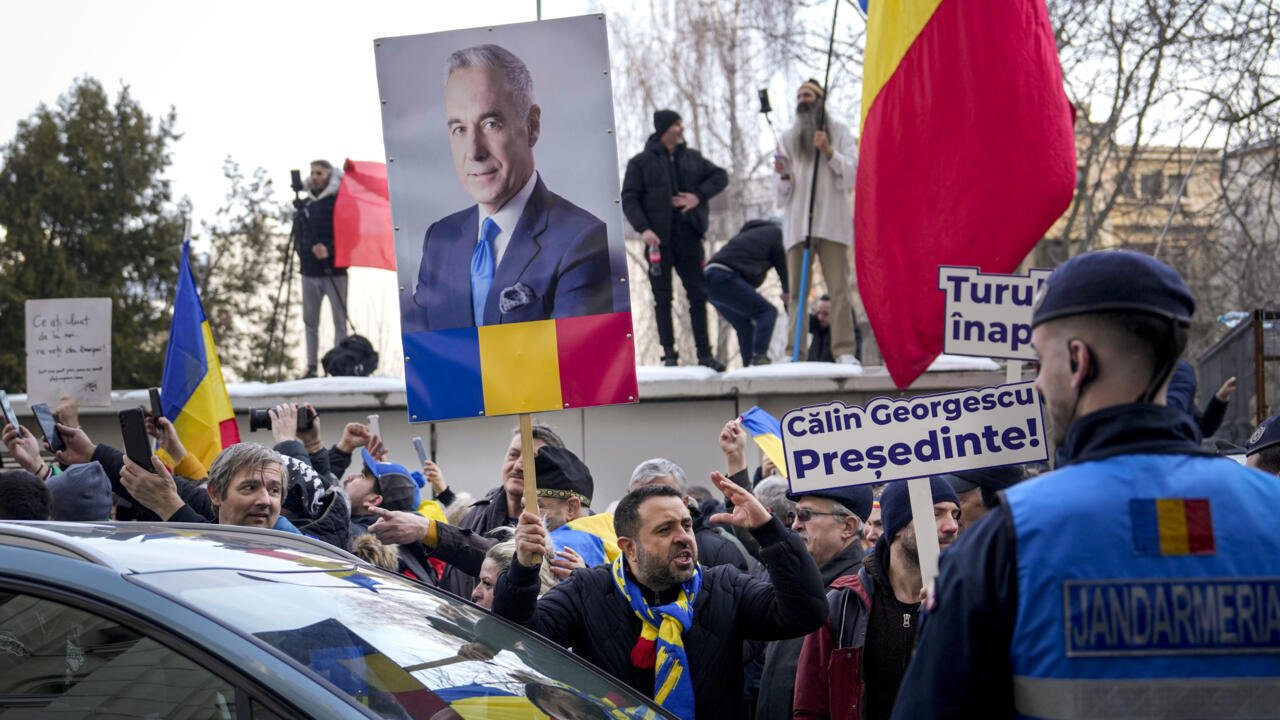
March 7, 2025 Călin Georgescu, the people’s choice in Romania’s annulled election, has officially submitted his candidacy for the upcoming presidential race, backed by over 324,000 signatures.
The Constitutional Court will decide this month or early April if his candidacy is approved, assuming, of course, that he doesn't get arrested again this time.


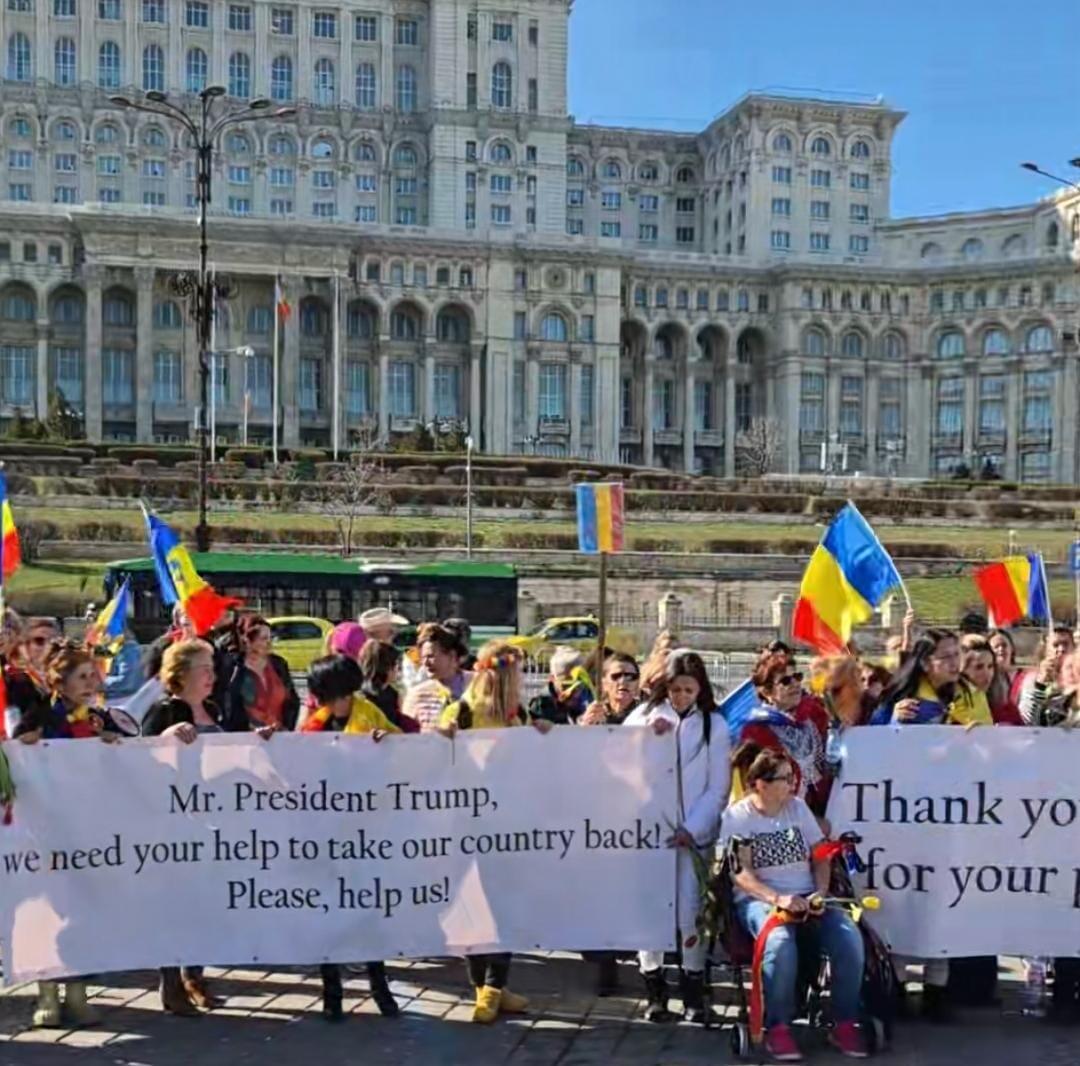
March 8, 2025
Demonstrators gathered in front of Romania’s Palace of Parliament, holding banners thanking Tulsi Gabbard and urging Trump to “help take our country back!”

Romania’s Constitutional Court has unanimously rejected 4 appeals attempting to block Călin Georgescu from the presidential race. The challenges, filed by minor candidates Sebastian Popescu and Cristian Terheș, accused him of failing to disclose campaign funding and alleged foreign financial ties. The court dismissed the claims as inadmissible, citing procedural failures and lack of legal merit.
Allegedly Soros-linked activists flood Romanian Electoral Bureau with 1,000 identical appeals against CĂLIN GEORGESCU
Over 1,000 copy-paste appeals were filed against Călin Georgescu’s candidacy, organized by Soros-backed activists trying to block him.
But the Electoral Bureau (BEC) is set to reject them all—the challenges were filed before his candidacy was even validated, making them invalid.
March 9, 2025
Calin Georgescu’s presidential candidacy has been officially rejected, sparking outrage among his supporters, who attempted to breach the Bureau of Electoral Control (BEC).
The candidacy was rejected with 10 votes in favor and 4 against.
Romania’s Electoral Office bypassed the Constitutional Court, which had approved his candidacy in December, and shut him down directly instead.
George Simion, president of the AUR stated in viral video:
Georgescu put his candidacy at the Central Electoral Bureau and by 10 members to 4, it was rejected without any reason. All the papers were in good order. They just said they voted through their conscience. We live in a dictatorship. Please help us. Please be on our side to restore democracy in Romania.




March 11, 2025
Romanian presidential candidate Călin Georgescu cannot run in the Presidential Election. Călin Georgescu’s appeal against the invalidation of his presidential candidacy has been rejected by the Constitutional Court.
March 27, 2025
The National Authority for Administration and Regulation in Communications (ANCOM), coordinator of digital services in Romania held an exercise to test the capacity to respond to challenges that may emerge in the online environment, in view of the presidential elections in May.
This initiative takes its root from the Rapid Response Mechanism (RRM), which ironically, was established during the G7 Charlevoix Summit in June 2018, meant to enhance cooperation among nations in addressing ‘crisis’ moments and perceived threats to western democracy.
Ahead of Romania’s new presidential election, the European Commission has launched its ‘RRM’ as a proactive strategy which the EC presents as a means to tackle potential electoral law violations on social media in member states holding elections. In effect, a similar simulation was reportedly held before the February elections in Germany. Coincidentally, a call for proposals to manage the new project described as a “Media Freedom Rapid Response Mechanism” was issued by the European Commission on Oct 24, 2024, under the cross-sectoral strand of the Creative Europe Programme. This CFP was launched to allegedly promote an independent and pluralistic media environment through an independent Europe-wide rapid response mechanism.
Subsequently, the Romanian government is now drafting an emergency ordinance to empower authorities to eliminate illegal (or inconvenient) online content, which they argue is essential for protecting the electoral process. However, some interpret this as a sign of a democratic crisis, with the current administration struggling to maintain power and resorting to emergency measures to suppress opposition and their freedom of speech. Recent polls suggest that Călin Georgescu could win the presidency in a single round, a situation complicated by the exclusion of the right-wing conservative candidate from the May 2025 elections. Other talks about possible corruption surrounding the construction of the multi-billion classified secret service contract for the Realization of the infrastructure of NATO 57th Air Base Mihail Kogălniceanu, located only 30 kilometres from the Black Sea and anticipated to be NATO’s largest base in Europe upon completion.