-
 @ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-11 16:17:44You can learn about what we’re doing at lava on our website: [lava.xyz](http://lava.xyz). We recommend you take a thorough look through everything before applying. Not an immediate fit? Lava has an open referral bounty. If you refer someone to us and we hire them, we will pay you $5k for an in-person NYC full-time hire and $1k for non-NYC full time hires. Send referrals to [hello@lava.xyz](mailto:hello@lava.xyz) We are looking for a designer to join our team at Lava. In this role, you will be responsible for leading the design of all of our products. **What you will do** - Drive and execute on an ambitious design vision for Lava - Communicate with engineering teams to make sure designs are implemented properly - Talk to users, analyze user feedback, and identify areas for improvement **What we look for in you** - You align with the guidelines and values we use to decide who we hire and how we operate: https://www.lava.xyz/onepager - Expertise as a designer - You are a great communicator (written and verbal). - You are extremely organized. - You learn fast. - You work hard. - You get shit done quickly. - You live in NYC, or you’re willing to relocate to NYC. If you feel that the above describes you, we’d love to hear from you! Please fill out this form: https://forms.gle/cJFsuP3tXgSknPJ8A Job Description: [https://lavaxyz.notion.site/Founding-Designer-78c91e29f4a44d0b8cb32e33ff40c167?pvs=4](https://www.notion.so/Founding-Designer-78c91e29f4a44d0b8cb32e33ff40c167?pvs=21) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/910384
@ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-11 16:17:44You can learn about what we’re doing at lava on our website: [lava.xyz](http://lava.xyz). We recommend you take a thorough look through everything before applying. Not an immediate fit? Lava has an open referral bounty. If you refer someone to us and we hire them, we will pay you $5k for an in-person NYC full-time hire and $1k for non-NYC full time hires. Send referrals to [hello@lava.xyz](mailto:hello@lava.xyz) We are looking for a designer to join our team at Lava. In this role, you will be responsible for leading the design of all of our products. **What you will do** - Drive and execute on an ambitious design vision for Lava - Communicate with engineering teams to make sure designs are implemented properly - Talk to users, analyze user feedback, and identify areas for improvement **What we look for in you** - You align with the guidelines and values we use to decide who we hire and how we operate: https://www.lava.xyz/onepager - Expertise as a designer - You are a great communicator (written and verbal). - You are extremely organized. - You learn fast. - You work hard. - You get shit done quickly. - You live in NYC, or you’re willing to relocate to NYC. If you feel that the above describes you, we’d love to hear from you! Please fill out this form: https://forms.gle/cJFsuP3tXgSknPJ8A Job Description: [https://lavaxyz.notion.site/Founding-Designer-78c91e29f4a44d0b8cb32e33ff40c167?pvs=4](https://www.notion.so/Founding-Designer-78c91e29f4a44d0b8cb32e33ff40c167?pvs=21) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/910384 -
 @ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-11 13:32:15`Remote only` `Part Time` Estamos em busca de um profissional para aprimorar a experiência dos usuários em nossos produtos ramblyn.app. Você trabalhará remotamente com um time pequeno e ágil, colaborando diretamente no design de interfaces. Não nos preocupamos com diplomas, buscamos alguém criativo, organizado e capaz de aprimorar e implementar processos em sua área. **Requisitos:** - Experiência com desenvolvimento web e web design. - Ser uma pessoa organizada, com habilidade para documentar processos. - Experiência prévia com atendimento ao cliente (diferencial). - Conhecimento sobre Bitcoin e Lightning Network (diferencial). - Capacidade de criar interfaces intuitivas e otimizadas para a melhor experiência do usuário. [APPLY](https://t.me/RamblynHelp) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/910158
@ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-11 13:32:15`Remote only` `Part Time` Estamos em busca de um profissional para aprimorar a experiência dos usuários em nossos produtos ramblyn.app. Você trabalhará remotamente com um time pequeno e ágil, colaborando diretamente no design de interfaces. Não nos preocupamos com diplomas, buscamos alguém criativo, organizado e capaz de aprimorar e implementar processos em sua área. **Requisitos:** - Experiência com desenvolvimento web e web design. - Ser uma pessoa organizada, com habilidade para documentar processos. - Experiência prévia com atendimento ao cliente (diferencial). - Conhecimento sobre Bitcoin e Lightning Network (diferencial). - Capacidade de criar interfaces intuitivas e otimizadas para a melhor experiência do usuário. [APPLY](https://t.me/RamblynHelp) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/910158 -
 @ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-11 10:28:08## The Role Our team brings deep expertise across electric power markets, project development, and software development, positioning us as trusted experts in this rapidly evolving market. We are seeking an experienced Software Product Manager to lead the planning, development, and execution of our software products. You will play a key role in defining the product vision, roadmap, and strategy, and you will collaborate closely with cross-functional teams to ensure successful product launches and iterations. The ideal candidate will have an energy background, a deep understanding of user needs, and the ability to balance technical requirements with business objectives. ## Your Day-to-Day - Product Vision and Strategy: You will define and effectively communicate the product vision, strategy, and roadmap to internal teams and key stakeholders, ensuring alignment between our goals and our customers’ needs to drive product decisions and adoption. To do this, you will need to stay informed on industry trends, emerging technologies, and competition to ensure our product remains innovative and competitive. - End-to-End Product Development: You will lead the product development process from concept to launch, ensuring timely delivery of features that meet both quality standards and customer expectations. You will gather, prioritize, and articulate product requirements based on user feedback, market trends, and business goals. You will maintain clear and thorough documentation for product features, workflows, and technical specifications. You will - Performance Analysis and Improvement: You will continuously monitor product performance using key metrics and user feedback to refine and iterate on the product, driving ongoing enhancements. You will advocate for user needs throughout the product development cycle to create products that truly resonate with them and a product experience that provides outsized value. - Stakeholder Communication and Collaboration: You will synthesize and communicate results, insights, and actionable recommendations to the leadership team and all relevant stakeholders, and you will collaborate cross functionally to remove bottlenecks and be a force multiplier for our team. [APPLY](https://apply.workable.com/satoshi-energy/j/ba09aa8693/?utm_source=stackernews) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/910029
@ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-11 10:28:08## The Role Our team brings deep expertise across electric power markets, project development, and software development, positioning us as trusted experts in this rapidly evolving market. We are seeking an experienced Software Product Manager to lead the planning, development, and execution of our software products. You will play a key role in defining the product vision, roadmap, and strategy, and you will collaborate closely with cross-functional teams to ensure successful product launches and iterations. The ideal candidate will have an energy background, a deep understanding of user needs, and the ability to balance technical requirements with business objectives. ## Your Day-to-Day - Product Vision and Strategy: You will define and effectively communicate the product vision, strategy, and roadmap to internal teams and key stakeholders, ensuring alignment between our goals and our customers’ needs to drive product decisions and adoption. To do this, you will need to stay informed on industry trends, emerging technologies, and competition to ensure our product remains innovative and competitive. - End-to-End Product Development: You will lead the product development process from concept to launch, ensuring timely delivery of features that meet both quality standards and customer expectations. You will gather, prioritize, and articulate product requirements based on user feedback, market trends, and business goals. You will maintain clear and thorough documentation for product features, workflows, and technical specifications. You will - Performance Analysis and Improvement: You will continuously monitor product performance using key metrics and user feedback to refine and iterate on the product, driving ongoing enhancements. You will advocate for user needs throughout the product development cycle to create products that truly resonate with them and a product experience that provides outsized value. - Stakeholder Communication and Collaboration: You will synthesize and communicate results, insights, and actionable recommendations to the leadership team and all relevant stakeholders, and you will collaborate cross functionally to remove bottlenecks and be a force multiplier for our team. [APPLY](https://apply.workable.com/satoshi-energy/j/ba09aa8693/?utm_source=stackernews) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/910029 -
 @ a95c6243:d345522c
2025-03-11 10:22:36**«Wir brauchen eine digitale Brandmauer gegen den Faschismus»,** [schreibt](https://www.ccc.de/de/updates/2025/ccc-fordert-digitale-brandmauer) der Chaos Computer Club (CCC) auf seiner Website. Unter diesem Motto präsentierte er letzte Woche einen Forderungskatalog, mit dem sich 24 Organisationen an die kommende Bundesregierung wenden. Der Koalitionsvertrag müsse sich daran messen lassen, verlangen sie. **In den drei Kategorien «Bekenntnis gegen Überwachung»,** «Schutz und Sicherheit für alle» sowie «Demokratie im digitalen Raum» stellen die [Unterzeichner](https://d-64.org/digitale-brandmauer/), zu denen auch Amnesty International und Das NETTZ gehören, unter anderem die folgenden «Mindestanforderungen»: * Verbot biometrischer Massenüberwachung des öffentlichen Raums sowie der ungezielten biometrischen Auswertung des Internets. * Anlasslose und massenhafte Vorratsdatenspeicherung wird abgelehnt. * Automatisierte Datenanalysen der Informationsbestände der Strafverfolgungsbehörden sowie jede Form von Predictive Policing oder automatisiertes Profiling von Menschen werden abgelehnt. * Einführung eines Rechts auf Verschlüsselung. Die Bundesregierung soll sich dafür einsetzen, die Chatkontrolle auf europäischer Ebene zu verhindern. * Anonyme und pseudonyme Nutzung des Internets soll geschützt und ermöglicht werden. * Bekämpfung «privaten Machtmissbrauchs von Big-Tech-Unternehmen» durch durchsetzungsstarke, unabhängige und grundsätzlich föderale Aufsichtsstrukturen. * Einführung eines digitalen Gewaltschutzgesetzes, unter Berücksichtigung «gruppenbezogener digitaler Gewalt» und die Förderung von Beratungsangeboten. * Ein umfassendes Förderprogramm für digitale öffentliche Räume, die dezentral organisiert und quelloffen programmiert sind, soll aufgelegt werden. **Es sei ein Irrglaube, dass zunehmende Überwachung einen Zugewinn an Sicherheit darstelle,** ist eines der Argumente der Initiatoren. Sicherheit erfordere auch, dass Menschen anonym und vertraulich kommunizieren können und ihre Privatsphäre geschützt wird. **Gesunde digitale Räume lebten auch von einem demokratischen Diskurs,** lesen wir in dem Papier. Es sei Aufgabe des Staates, Grundrechte zu schützen. Dazu gehöre auch, Menschenrechte und demokratische Werte, insbesondere Freiheit, Gleichheit und Solidarität zu fördern sowie den Missbrauch von Maßnahmen, Befugnissen und Infrastrukturen durch «die Feinde der Demokratie» zu verhindern. **Man ist geneigt zu fragen, wo denn die Autoren «den Faschismus» sehen,** den es zu bekämpfen gelte. Die meisten der vorgetragenen Forderungen und Argumente finden sicher breite Unterstützung, denn sie beschreiben offenkundig gängige, kritikwürdige Praxis. Die Aushebelung der Privatsphäre, der Redefreiheit und anderer Grundrechte im Namen der Sicherheit wird bereits jetzt massiv durch die aktuellen «demokratischen Institutionen» und ihre «durchsetzungsstarken Aufsichtsstrukturen» betrieben. **Ist «der Faschismus» also die EU und ihre Mitgliedsstaaten?** Nein, die «faschistische Gefahr», gegen die man eine digitale Brandmauer will, kommt nach Ansicht des CCC und seiner Partner aus den Vereinigten Staaten. Private Überwachung und Machtkonzentration sind dabei weltweit schon lange Realität, jetzt endlich müssen sie jedoch bekämpft werden. In dem Papier heißt es: > «Die willkürliche und antidemokratische Machtausübung der Tech-Oligarchen um Präsident Trump erfordert einen Paradigmenwechsel in der deutschen Digitalpolitik. (...) Die aktuellen Geschehnisse in den USA zeigen auf, wie Datensammlungen und -analyse genutzt werden können, um einen Staat handstreichartig zu übernehmen, seine Strukturen nachhaltig zu beschädigen, Widerstand zu unterbinden und marginalisierte Gruppen zu verfolgen.» **Wer auf der anderen Seite dieser Brandmauer stehen soll, ist also klar.** Es sind die gleichen «Feinde unserer Demokratie», die seit Jahren in diese Ecke gedrängt werden. Es sind die gleichen Andersdenkenden, Regierungskritiker und Friedensforderer, die unter dem großzügigen Dach des Bundesprogramms «Demokratie leben» einem «kontinuierlichen Echt- und Langzeitmonitoring» wegen der Etikettierung [«digitaler Hass»](https://bag-gegen-hass.net/) unterzogen werden. **Dass die 24 Organisationen praktisch auch die Bekämpfung von Google,** Microsoft, Apple, Amazon und anderen fordern, entbehrt nicht der Komik. Diese fallen aber sicher unter das Stichwort «Machtmissbrauch von Big-Tech-Unternehmen». Gleichzeitig verlangen die Lobbyisten implizit zum Beispiel die Förderung des [Nostr](https://reason.com/video/2024/09/17/is-nostr-an-antidote-to-social-media-censorship/)-Netzwerks, denn hier finden wir dezentral organisierte und quelloffen programmierte digitale Räume par excellence, obendrein zensurresistent. Das wiederum dürfte in der Politik weniger gut ankommen. *\[Titelbild:* *[Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/de/illustrations/uns-ihnen-stammes-wettbewerb-1767691/)]* *** Dieser Beitrag ist zuerst auf ***[Transition News](https://transition-news.org/digitale-brandmauer-gegen-den-faschismus-von-der-kunftigen-bundesregierung)*** erschienen.
@ a95c6243:d345522c
2025-03-11 10:22:36**«Wir brauchen eine digitale Brandmauer gegen den Faschismus»,** [schreibt](https://www.ccc.de/de/updates/2025/ccc-fordert-digitale-brandmauer) der Chaos Computer Club (CCC) auf seiner Website. Unter diesem Motto präsentierte er letzte Woche einen Forderungskatalog, mit dem sich 24 Organisationen an die kommende Bundesregierung wenden. Der Koalitionsvertrag müsse sich daran messen lassen, verlangen sie. **In den drei Kategorien «Bekenntnis gegen Überwachung»,** «Schutz und Sicherheit für alle» sowie «Demokratie im digitalen Raum» stellen die [Unterzeichner](https://d-64.org/digitale-brandmauer/), zu denen auch Amnesty International und Das NETTZ gehören, unter anderem die folgenden «Mindestanforderungen»: * Verbot biometrischer Massenüberwachung des öffentlichen Raums sowie der ungezielten biometrischen Auswertung des Internets. * Anlasslose und massenhafte Vorratsdatenspeicherung wird abgelehnt. * Automatisierte Datenanalysen der Informationsbestände der Strafverfolgungsbehörden sowie jede Form von Predictive Policing oder automatisiertes Profiling von Menschen werden abgelehnt. * Einführung eines Rechts auf Verschlüsselung. Die Bundesregierung soll sich dafür einsetzen, die Chatkontrolle auf europäischer Ebene zu verhindern. * Anonyme und pseudonyme Nutzung des Internets soll geschützt und ermöglicht werden. * Bekämpfung «privaten Machtmissbrauchs von Big-Tech-Unternehmen» durch durchsetzungsstarke, unabhängige und grundsätzlich föderale Aufsichtsstrukturen. * Einführung eines digitalen Gewaltschutzgesetzes, unter Berücksichtigung «gruppenbezogener digitaler Gewalt» und die Förderung von Beratungsangeboten. * Ein umfassendes Förderprogramm für digitale öffentliche Räume, die dezentral organisiert und quelloffen programmiert sind, soll aufgelegt werden. **Es sei ein Irrglaube, dass zunehmende Überwachung einen Zugewinn an Sicherheit darstelle,** ist eines der Argumente der Initiatoren. Sicherheit erfordere auch, dass Menschen anonym und vertraulich kommunizieren können und ihre Privatsphäre geschützt wird. **Gesunde digitale Räume lebten auch von einem demokratischen Diskurs,** lesen wir in dem Papier. Es sei Aufgabe des Staates, Grundrechte zu schützen. Dazu gehöre auch, Menschenrechte und demokratische Werte, insbesondere Freiheit, Gleichheit und Solidarität zu fördern sowie den Missbrauch von Maßnahmen, Befugnissen und Infrastrukturen durch «die Feinde der Demokratie» zu verhindern. **Man ist geneigt zu fragen, wo denn die Autoren «den Faschismus» sehen,** den es zu bekämpfen gelte. Die meisten der vorgetragenen Forderungen und Argumente finden sicher breite Unterstützung, denn sie beschreiben offenkundig gängige, kritikwürdige Praxis. Die Aushebelung der Privatsphäre, der Redefreiheit und anderer Grundrechte im Namen der Sicherheit wird bereits jetzt massiv durch die aktuellen «demokratischen Institutionen» und ihre «durchsetzungsstarken Aufsichtsstrukturen» betrieben. **Ist «der Faschismus» also die EU und ihre Mitgliedsstaaten?** Nein, die «faschistische Gefahr», gegen die man eine digitale Brandmauer will, kommt nach Ansicht des CCC und seiner Partner aus den Vereinigten Staaten. Private Überwachung und Machtkonzentration sind dabei weltweit schon lange Realität, jetzt endlich müssen sie jedoch bekämpft werden. In dem Papier heißt es: > «Die willkürliche und antidemokratische Machtausübung der Tech-Oligarchen um Präsident Trump erfordert einen Paradigmenwechsel in der deutschen Digitalpolitik. (...) Die aktuellen Geschehnisse in den USA zeigen auf, wie Datensammlungen und -analyse genutzt werden können, um einen Staat handstreichartig zu übernehmen, seine Strukturen nachhaltig zu beschädigen, Widerstand zu unterbinden und marginalisierte Gruppen zu verfolgen.» **Wer auf der anderen Seite dieser Brandmauer stehen soll, ist also klar.** Es sind die gleichen «Feinde unserer Demokratie», die seit Jahren in diese Ecke gedrängt werden. Es sind die gleichen Andersdenkenden, Regierungskritiker und Friedensforderer, die unter dem großzügigen Dach des Bundesprogramms «Demokratie leben» einem «kontinuierlichen Echt- und Langzeitmonitoring» wegen der Etikettierung [«digitaler Hass»](https://bag-gegen-hass.net/) unterzogen werden. **Dass die 24 Organisationen praktisch auch die Bekämpfung von Google,** Microsoft, Apple, Amazon und anderen fordern, entbehrt nicht der Komik. Diese fallen aber sicher unter das Stichwort «Machtmissbrauch von Big-Tech-Unternehmen». Gleichzeitig verlangen die Lobbyisten implizit zum Beispiel die Förderung des [Nostr](https://reason.com/video/2024/09/17/is-nostr-an-antidote-to-social-media-censorship/)-Netzwerks, denn hier finden wir dezentral organisierte und quelloffen programmierte digitale Räume par excellence, obendrein zensurresistent. Das wiederum dürfte in der Politik weniger gut ankommen. *\[Titelbild:* *[Pixabay](https://pixabay.com/de/illustrations/uns-ihnen-stammes-wettbewerb-1767691/)]* *** Dieser Beitrag ist zuerst auf ***[Transition News](https://transition-news.org/digitale-brandmauer-gegen-den-faschismus-von-der-kunftigen-bundesregierung)*** erschienen. -
 @ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-10 23:31:30Bitcoin has always been rooted in freedom and resistance to authority. I get that many of you are conflicted about the US Government stacking but by design we cannot stop anyone from using bitcoin. Many have asked me for my thoughts on the matter, so let’s rip it. **Concern** One of the most glaring issues with the strategic bitcoin reserve is its foundation, built on stolen bitcoin. For those of us who value private property this is an obvious betrayal of our core principles. Rather than proof of work, the bitcoin that seeds this reserve has been taken by force. The US Government should return the bitcoin stolen from Bitfinex and the Silk Road. Usually stolen bitcoin for the reserve creates a perverse incentive. If governments see a bitcoin as a valuable asset, they will ramp up efforts to confiscate more bitcoin. The precedent is a major concern, and I stand strongly against it, but it should be also noted that governments were already seizing coin before the reserve so this is not really a change in policy. Ideally all seized bitcoin should be burned, by law. This would align incentives properly and make it less likely for the government to actively increase coin seizures. Due to the truly scarce properties of bitcoin, all burned bitcoin helps existing holders through increased purchasing power regardless. This change would be unlikely but those of us in policy circles should push for it regardless. It would be best case scenario for American bitcoiners and would create a strong foundation for the next century of American leadership. **Optimism** The entire point of bitcoin is that we can spend or save it without permission. That said, it is a massive benefit to not have one of the strongest governments in human history actively trying to ruin our lives. Since the beginning, bitcoiners have faced horrible regulatory trends. KYC, surveillance, and legal cases have made using bitcoin and building bitcoin businesses incredibly difficult. It is incredibly important to note that over the past year that trend has reversed for the first time in a decade. A strategic bitcoin reserve is a key driver of this shift. By holding bitcoin, the strongest government in the world has signaled that it is not just a fringe technology but rather truly valuable, legitimate, and worth stacking. This alignment of incentives changes everything. The US Government stacking proves bitcoin’s worth. The resulting purchasing power appreciation helps all of us who are holding coin and as bitcoin succeeds our government receives direct benefit. A beautiful positive feedback loop. **Realism** We are trending in the right direction. A strategic bitcoin reserve is a sign that the state sees bitcoin as an asset worth embracing rather than destroying. That said, there is a lot of work left to be done. We cannot be lulled into complacency, the time to push forward is now, and we cannot take our foot off the gas. We have a seat at the table for the first time ever. Let's make it worth it. We must protect the right to free usage of bitcoin and other digital technologies. Freedom in the digital age must be taken and defended, through both technical and political avenues. Multiple privacy focused developers are facing long jail sentences for building tools that protect our freedom. These cases are not just legal battles. They are attacks on the soul of bitcoin. We need to rally behind them, fight for their freedom, and ensure the ethos of bitcoin survives this new era of government interest. The strategic reserve is a step in the right direction, but it is up to us to hold the line and shape the future.
@ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-10 23:31:30Bitcoin has always been rooted in freedom and resistance to authority. I get that many of you are conflicted about the US Government stacking but by design we cannot stop anyone from using bitcoin. Many have asked me for my thoughts on the matter, so let’s rip it. **Concern** One of the most glaring issues with the strategic bitcoin reserve is its foundation, built on stolen bitcoin. For those of us who value private property this is an obvious betrayal of our core principles. Rather than proof of work, the bitcoin that seeds this reserve has been taken by force. The US Government should return the bitcoin stolen from Bitfinex and the Silk Road. Usually stolen bitcoin for the reserve creates a perverse incentive. If governments see a bitcoin as a valuable asset, they will ramp up efforts to confiscate more bitcoin. The precedent is a major concern, and I stand strongly against it, but it should be also noted that governments were already seizing coin before the reserve so this is not really a change in policy. Ideally all seized bitcoin should be burned, by law. This would align incentives properly and make it less likely for the government to actively increase coin seizures. Due to the truly scarce properties of bitcoin, all burned bitcoin helps existing holders through increased purchasing power regardless. This change would be unlikely but those of us in policy circles should push for it regardless. It would be best case scenario for American bitcoiners and would create a strong foundation for the next century of American leadership. **Optimism** The entire point of bitcoin is that we can spend or save it without permission. That said, it is a massive benefit to not have one of the strongest governments in human history actively trying to ruin our lives. Since the beginning, bitcoiners have faced horrible regulatory trends. KYC, surveillance, and legal cases have made using bitcoin and building bitcoin businesses incredibly difficult. It is incredibly important to note that over the past year that trend has reversed for the first time in a decade. A strategic bitcoin reserve is a key driver of this shift. By holding bitcoin, the strongest government in the world has signaled that it is not just a fringe technology but rather truly valuable, legitimate, and worth stacking. This alignment of incentives changes everything. The US Government stacking proves bitcoin’s worth. The resulting purchasing power appreciation helps all of us who are holding coin and as bitcoin succeeds our government receives direct benefit. A beautiful positive feedback loop. **Realism** We are trending in the right direction. A strategic bitcoin reserve is a sign that the state sees bitcoin as an asset worth embracing rather than destroying. That said, there is a lot of work left to be done. We cannot be lulled into complacency, the time to push forward is now, and we cannot take our foot off the gas. We have a seat at the table for the first time ever. Let's make it worth it. We must protect the right to free usage of bitcoin and other digital technologies. Freedom in the digital age must be taken and defended, through both technical and political avenues. Multiple privacy focused developers are facing long jail sentences for building tools that protect our freedom. These cases are not just legal battles. They are attacks on the soul of bitcoin. We need to rally behind them, fight for their freedom, and ensure the ethos of bitcoin survives this new era of government interest. The strategic reserve is a step in the right direction, but it is up to us to hold the line and shape the future. -
 @ d68401a8:11aad383
2025-03-10 17:22:14**What do you need?** * A Handshake top-level domain * Bob wallet (with at least 10 HNS) * Varo account * GitHub account **1. Own a Handshake domain** First, you need to have a domain stored in your personal wallet (Bob Wallet). We don’t cover how to obtain a domain name, but it’s not difficult. You can bid for domains using Bob Wallet, which is a self-custodial method that allows you to interact directly with the blockchain. Alternatively, you can use a custodial service like Namebase.io or ShakeStation.io. If you opt for a custodial service, both platforms work well and significantly simplify the process. However, keep in mind that you will need to transfer your domain to your Bob Wallet. This transfer typically takes about a day, so be patient. **2. Create A Varo Account** Varo is a service that allows you to connect your self-custodied domain to a DNS nameserver, enabling you to manage your domain records without losing custody of your name. At any time, you can use your Bob Wallet to delete all records associating your domain with Varo, effectively breaking the connection. Varo is developed by [eskimo.software](https://eskimo.software). You can access Varo in both the ICANN and HNS root zones: * [https://varo.domains](https://varo.domains) * [https://varo](https://varo) **3. Connect your domain with Varo** Once your domain is in your Bob wallet, you need to connect it to Varo. Go to your Varo account > Add site *>* type the domain you own, and press the "+" button.  Your domain should appear under "External Domains". Next, go to "Manage", where you’ll find two subsections named "Nameservers" and "DNSSEC". These are the records you need to add to your domain in Bob Wallet to connect it with Varo. In Bob Wallet go to "Domain Manager", press on your domain, a new screen will open. In the "Records" section, add the records provided by Varo: * Add 2 NS records, with the value of ns1.varo. and ns2.varo. * Add 1 DS record, with whatever string of value you have in your Varo account Once done you need to "Submit" the changes. It will take approximately 10 minutes to update (the time it takes for each block to be created on the Handshake network). After 10–20 minutes, you should be able to see the new records on any HNS explorer, such as Niami.io.  To test if the connection is proper, you can add a "redirect" record on Varo. A redirect record is a type of DNS record used to redirect a domain or subdomain to another URL. In this example, I will redirect the domain "nostr.belikebill", to my Primal nostr address "https://primal.net/galetaire". * Type: REDIRECT * Name: nostr.yourdomain * Content: the URL of destination  Once completed, it will take about 6 hours for the changes to go live. Yes, it might seem like a long time, but domains are not like money—you’re not meant to move them around constantly. If your new address, "nostr.yourdomain" or "http://nostr.yourdomain.hns.to", redirects to your desired URL, your domain and Varo are successfully connected. **4. Create a GitHub account** Create or go to your GitHub account, create a "New repository", put the name of your choice, and "create". **4.1 Create an index file** At your new repository, click on the "Add file" > "Create new file" button. Name the file "index.html" and type some HTML content into the editor. Like: `<h1>Hi, It's me!</h1>` Commit changes. **4.2 Repository Settings** Click on the "Settings" tab and scroll down to the GitHub "Pages" section. Select the main branch source "/root" and click on the "Save" button.  After 5 minutes, you can refresh the Pages section, and at the top, you will see an information message indicating that your site is live at a URL similar to this: [https://youraccount.github.io/yourrepository](https://youraccount.github.io/yourrepository), visit the site. At this point, your website is online.  In the "Pages" section, go to "Custom Domain" and add your desired domain. Note that it must be a second-level domain (e.g., `something.yourdomain`). GitHub will not recognize a pure top-level domain: * hi.yourdomain, for example. Because it’s not an ICANN domain, GitHub will tell you it doesn’t work, but it actually does. Even though it will always show as "DNS Check in Progress," your site will be online. It will take around 30 minutes for the site to go live.  **5. Set up your domain as the address for your site** Finally, you need to connect Varo with GitHub. Go to you Varo account > "Manage" for your domain, and add an "A" record: * Type: A * Name: hi.yourdomain * Content: [185.199.111.153](http://185.199.111.153) (this is the IP address of [GitHub](https://docs.github.com/en/pages/configuring-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site/managing-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site)) As for the "Redirect" record, the update will take 6 hours to go live. But after that time, your site will be online at your domain address: * [http://hi.yourdomain/](http://hi.yourdomain/) * [http://hi.yourdomain.hns.to](http://hi.yourdomain.hns.to) (hns.to is a bridge to see HNS addresses trough ICANN addresses). Congrats! The next step is to personalize your website (at this point only the "index.html"), you can ask some AI to create you one, copy paste, and done! You can see mine at [http://hi.galetaire](http://hi.galetaire), any doubt hit the comment section :D.
@ d68401a8:11aad383
2025-03-10 17:22:14**What do you need?** * A Handshake top-level domain * Bob wallet (with at least 10 HNS) * Varo account * GitHub account **1. Own a Handshake domain** First, you need to have a domain stored in your personal wallet (Bob Wallet). We don’t cover how to obtain a domain name, but it’s not difficult. You can bid for domains using Bob Wallet, which is a self-custodial method that allows you to interact directly with the blockchain. Alternatively, you can use a custodial service like Namebase.io or ShakeStation.io. If you opt for a custodial service, both platforms work well and significantly simplify the process. However, keep in mind that you will need to transfer your domain to your Bob Wallet. This transfer typically takes about a day, so be patient. **2. Create A Varo Account** Varo is a service that allows you to connect your self-custodied domain to a DNS nameserver, enabling you to manage your domain records without losing custody of your name. At any time, you can use your Bob Wallet to delete all records associating your domain with Varo, effectively breaking the connection. Varo is developed by [eskimo.software](https://eskimo.software). You can access Varo in both the ICANN and HNS root zones: * [https://varo.domains](https://varo.domains) * [https://varo](https://varo) **3. Connect your domain with Varo** Once your domain is in your Bob wallet, you need to connect it to Varo. Go to your Varo account > Add site *>* type the domain you own, and press the "+" button.  Your domain should appear under "External Domains". Next, go to "Manage", where you’ll find two subsections named "Nameservers" and "DNSSEC". These are the records you need to add to your domain in Bob Wallet to connect it with Varo. In Bob Wallet go to "Domain Manager", press on your domain, a new screen will open. In the "Records" section, add the records provided by Varo: * Add 2 NS records, with the value of ns1.varo. and ns2.varo. * Add 1 DS record, with whatever string of value you have in your Varo account Once done you need to "Submit" the changes. It will take approximately 10 minutes to update (the time it takes for each block to be created on the Handshake network). After 10–20 minutes, you should be able to see the new records on any HNS explorer, such as Niami.io.  To test if the connection is proper, you can add a "redirect" record on Varo. A redirect record is a type of DNS record used to redirect a domain or subdomain to another URL. In this example, I will redirect the domain "nostr.belikebill", to my Primal nostr address "https://primal.net/galetaire". * Type: REDIRECT * Name: nostr.yourdomain * Content: the URL of destination  Once completed, it will take about 6 hours for the changes to go live. Yes, it might seem like a long time, but domains are not like money—you’re not meant to move them around constantly. If your new address, "nostr.yourdomain" or "http://nostr.yourdomain.hns.to", redirects to your desired URL, your domain and Varo are successfully connected. **4. Create a GitHub account** Create or go to your GitHub account, create a "New repository", put the name of your choice, and "create". **4.1 Create an index file** At your new repository, click on the "Add file" > "Create new file" button. Name the file "index.html" and type some HTML content into the editor. Like: `<h1>Hi, It's me!</h1>` Commit changes. **4.2 Repository Settings** Click on the "Settings" tab and scroll down to the GitHub "Pages" section. Select the main branch source "/root" and click on the "Save" button.  After 5 minutes, you can refresh the Pages section, and at the top, you will see an information message indicating that your site is live at a URL similar to this: [https://youraccount.github.io/yourrepository](https://youraccount.github.io/yourrepository), visit the site. At this point, your website is online.  In the "Pages" section, go to "Custom Domain" and add your desired domain. Note that it must be a second-level domain (e.g., `something.yourdomain`). GitHub will not recognize a pure top-level domain: * hi.yourdomain, for example. Because it’s not an ICANN domain, GitHub will tell you it doesn’t work, but it actually does. Even though it will always show as "DNS Check in Progress," your site will be online. It will take around 30 minutes for the site to go live.  **5. Set up your domain as the address for your site** Finally, you need to connect Varo with GitHub. Go to you Varo account > "Manage" for your domain, and add an "A" record: * Type: A * Name: hi.yourdomain * Content: [185.199.111.153](http://185.199.111.153) (this is the IP address of [GitHub](https://docs.github.com/en/pages/configuring-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site/managing-a-custom-domain-for-your-github-pages-site)) As for the "Redirect" record, the update will take 6 hours to go live. But after that time, your site will be online at your domain address: * [http://hi.yourdomain/](http://hi.yourdomain/) * [http://hi.yourdomain.hns.to](http://hi.yourdomain.hns.to) (hns.to is a bridge to see HNS addresses trough ICANN addresses). Congrats! The next step is to personalize your website (at this point only the "index.html"), you can ask some AI to create you one, copy paste, and done! You can see mine at [http://hi.galetaire](http://hi.galetaire), any doubt hit the comment section :D. -
 @ 4857600b:30b502f4
2025-03-10 12:09:35At this point, we should be arresting, not firing, any FBI employee who delays, destroys, or withholds information on the Epstein case. There is ZERO explanation I will accept for redacting anything for “national security” reasons. A lot of Trump supporters are losing patience with Pam Bondi. I will give her the benefit of the doubt for now since the corruption within the whole security/intelligence apparatus of our country runs deep. However, let’s not forget that probably Trump’s biggest mistakes in his first term involved picking weak and easily corruptible (or blackmailable) officials. It seemed every month a formerly-loyal person did a complete 180 degree turn and did everything they could to screw him over, regardless of the betrayal’s effect on the country or whatever principles that person claimed to have. I think he’s fixed his screening process, but since we’re talking about the FBI, we know they have the power to dig up any dirt or blackmail material available, or just make it up. In the Epstein case, it’s probably better to go after Bondi than give up a treasure trove of blackmail material against the long list of members on his client list.
@ 4857600b:30b502f4
2025-03-10 12:09:35At this point, we should be arresting, not firing, any FBI employee who delays, destroys, or withholds information on the Epstein case. There is ZERO explanation I will accept for redacting anything for “national security” reasons. A lot of Trump supporters are losing patience with Pam Bondi. I will give her the benefit of the doubt for now since the corruption within the whole security/intelligence apparatus of our country runs deep. However, let’s not forget that probably Trump’s biggest mistakes in his first term involved picking weak and easily corruptible (or blackmailable) officials. It seemed every month a formerly-loyal person did a complete 180 degree turn and did everything they could to screw him over, regardless of the betrayal’s effect on the country or whatever principles that person claimed to have. I think he’s fixed his screening process, but since we’re talking about the FBI, we know they have the power to dig up any dirt or blackmail material available, or just make it up. In the Epstein case, it’s probably better to go after Bondi than give up a treasure trove of blackmail material against the long list of members on his client list. -
 @ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-10 10:04:32A presentation by @jsonbits Jason Hester for the [40th CSUN](https://web.cvent.com/event/2c5d8c51-6441-44c0-b361-131ff9544dd5/summary) Assistive Technology Conference - `March 10, 2025 – March 14, 2025`        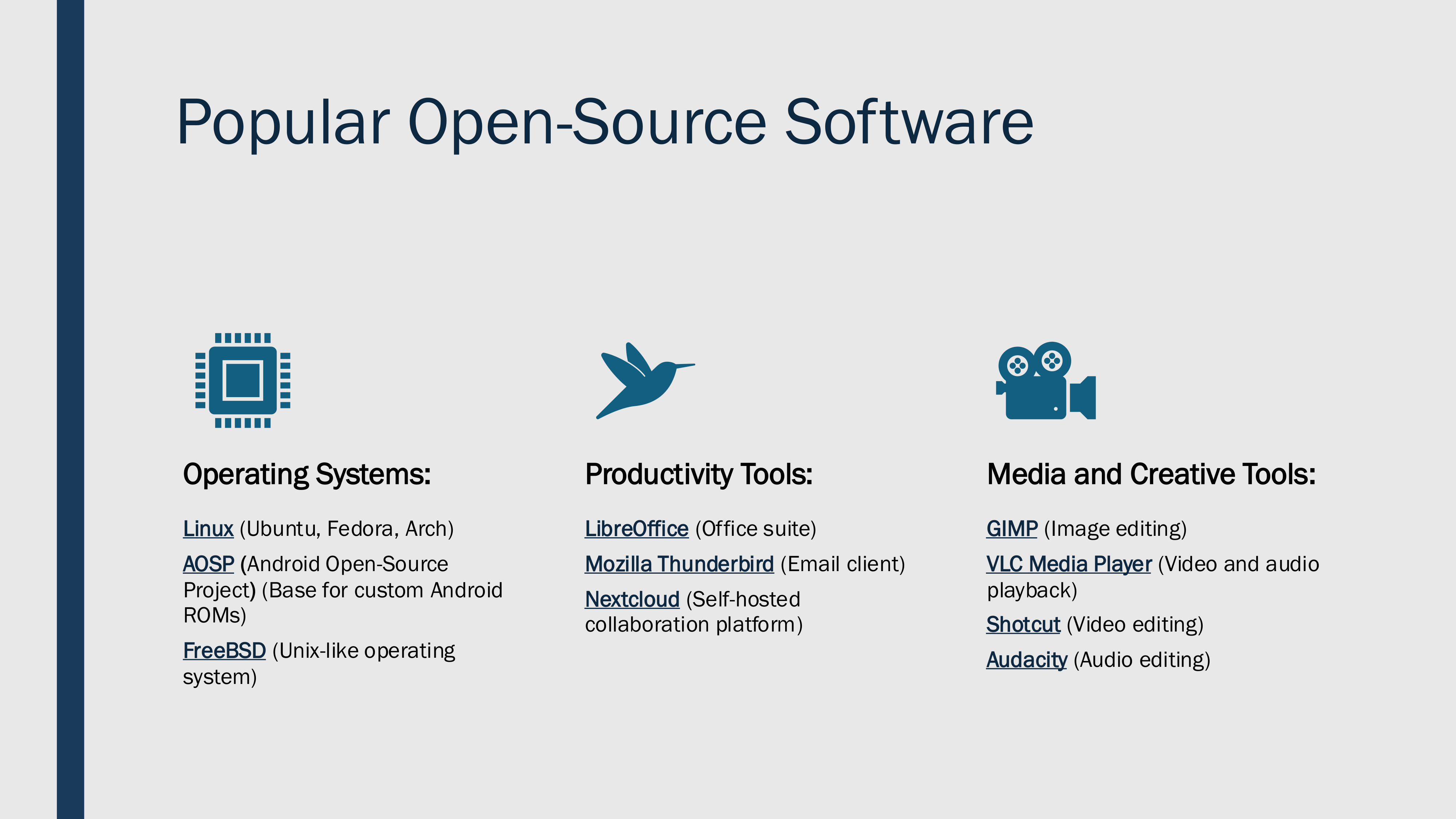   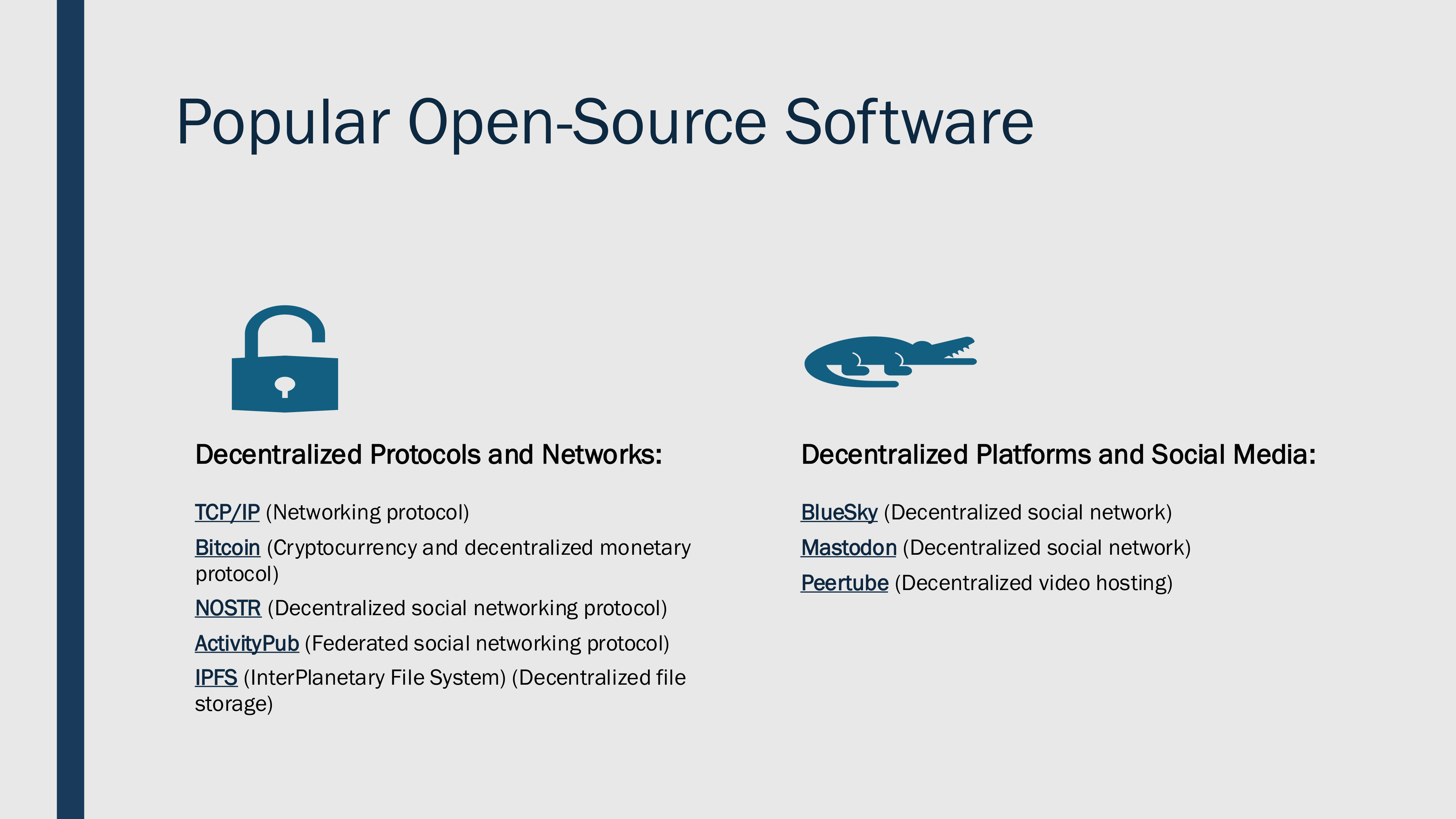      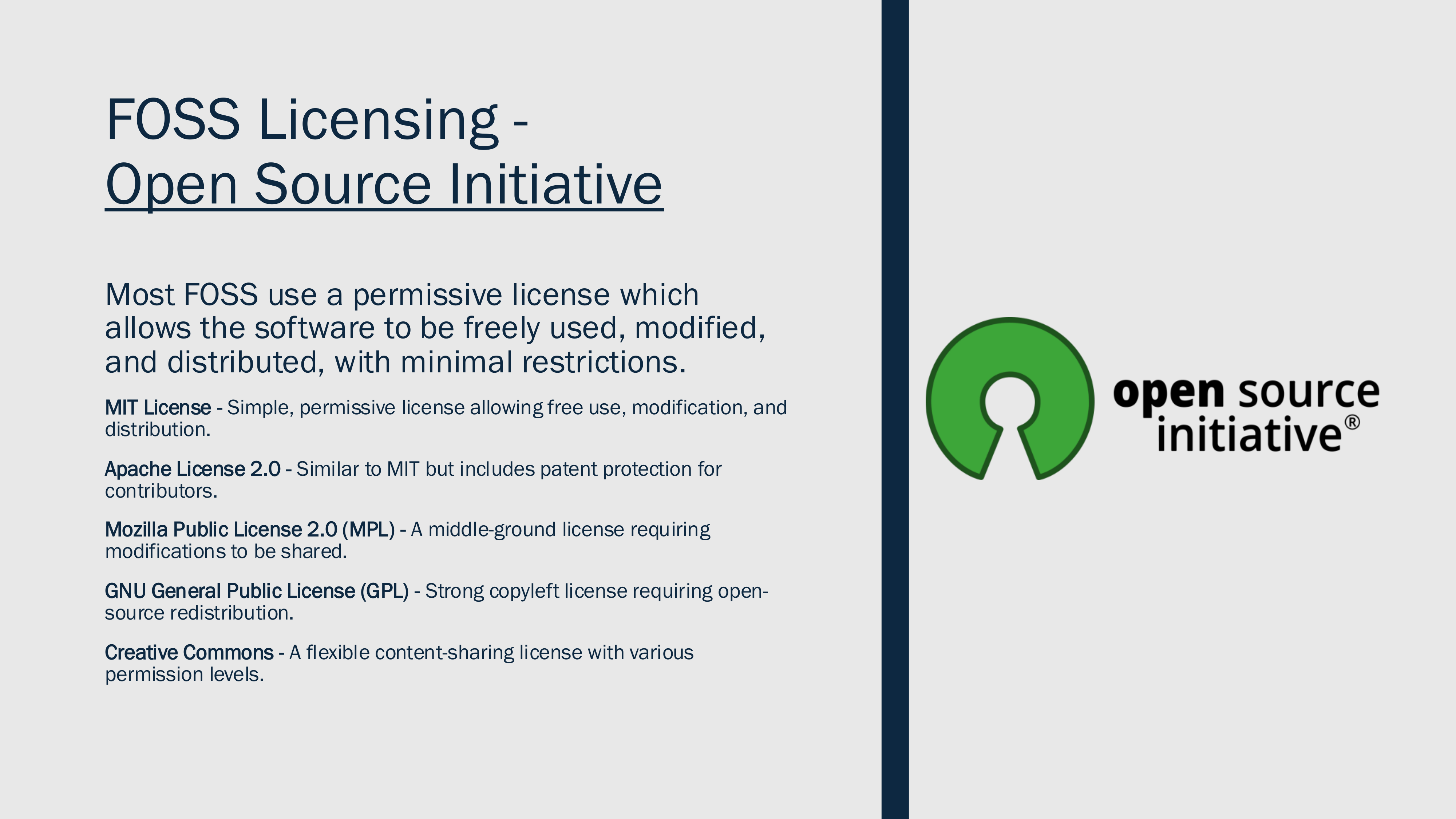      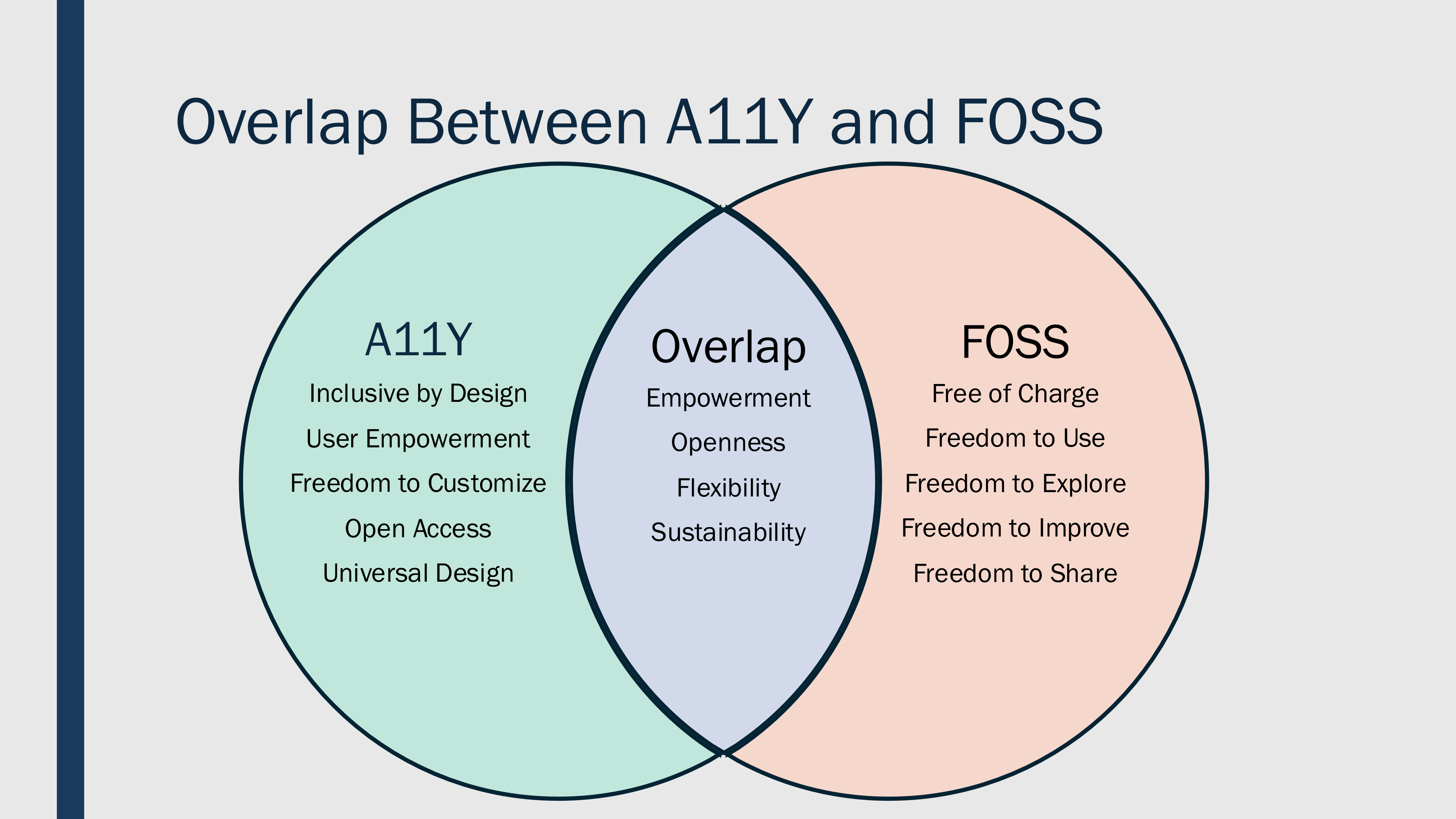                                     - - - [Download PDF](https://cdn.discordapp.com/attachments/903125939054059520/1347694223755051039/AC2A-FOSS-A11Y-JasonHester-V9.pdf?ex=67cf648d&is=67ce130d&hm=f61eb30b05783cfee2a37ffdcd5797af688a2fb3b7f01af48caa96c10136a129&) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/908947
@ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-10 10:04:32A presentation by @jsonbits Jason Hester for the [40th CSUN](https://web.cvent.com/event/2c5d8c51-6441-44c0-b361-131ff9544dd5/summary) Assistive Technology Conference - `March 10, 2025 – March 14, 2025`                                                            - - - [Download PDF](https://cdn.discordapp.com/attachments/903125939054059520/1347694223755051039/AC2A-FOSS-A11Y-JasonHester-V9.pdf?ex=67cf648d&is=67ce130d&hm=f61eb30b05783cfee2a37ffdcd5797af688a2fb3b7f01af48caa96c10136a129&) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/908947 -
 @ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-10 09:35:17 Here I am posting a document that presents the Business Model Canvas (BMC) created for “Nasi Goreng Semrawut”, a Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprise (MSME) in Kendal, Central Java, Indonesia. BMC is a strategic management and entrepreneurship tool. It allows us to visualize, assess, and modify business models. It is crucial to understand the core components of a business and how they interact. As a UX researcher, analyzing and understanding the business model is critical to aligning user needs with business goals. This BMC provides the basis for identifying opportunities to improve user experience and drive business growth. I have broken it down into sections and grouped them carefully and I have clear reasons from a UX perspective why the groupings I have chosen are these points. I explain the UX side more fully on my portfolio website. For my reflections on this project analyzing the Business Model Canvas of "Nasi Goreng Semrawut" through a UX lens reveals several opportunities for improvement. By focusing on user needs and behaviors, I can enhance the customer experience, streamline operations, and drive business growth. This analysis highlights the importance of integrating UX research into the strategic planning process. By understanding the business model, I can ensure that our UX efforts are aligned with business goals and deliver tangible results. **My website Portfolio👇** https://octoporto.framer.website/blog/business-model-canvas-nasi-goreng-semrawut **Link Project :** https://www.figma.com/proto/5LZkoc2uSJ1RTaur4cDVCM/Business-Model-Canvas-Sego-Goreng-Semrawut?page-id=0%3A1&node-id=38-117&viewport=-170%2C587%2C0.16&t=8gt9qNV5G267Xq8B-1&scaling=scale-down&content-scaling=fixed&starting-point-node-id=20%3A3 mirorred from [dribbble](https://dribbble.com/shots/25718733-Business-Model-Canvas-Nasi-Goreng-Semrawut) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/908920
@ 57d1a264:69f1fee1
2025-03-10 09:35:17 Here I am posting a document that presents the Business Model Canvas (BMC) created for “Nasi Goreng Semrawut”, a Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprise (MSME) in Kendal, Central Java, Indonesia. BMC is a strategic management and entrepreneurship tool. It allows us to visualize, assess, and modify business models. It is crucial to understand the core components of a business and how they interact. As a UX researcher, analyzing and understanding the business model is critical to aligning user needs with business goals. This BMC provides the basis for identifying opportunities to improve user experience and drive business growth. I have broken it down into sections and grouped them carefully and I have clear reasons from a UX perspective why the groupings I have chosen are these points. I explain the UX side more fully on my portfolio website. For my reflections on this project analyzing the Business Model Canvas of "Nasi Goreng Semrawut" through a UX lens reveals several opportunities for improvement. By focusing on user needs and behaviors, I can enhance the customer experience, streamline operations, and drive business growth. This analysis highlights the importance of integrating UX research into the strategic planning process. By understanding the business model, I can ensure that our UX efforts are aligned with business goals and deliver tangible results. **My website Portfolio👇** https://octoporto.framer.website/blog/business-model-canvas-nasi-goreng-semrawut **Link Project :** https://www.figma.com/proto/5LZkoc2uSJ1RTaur4cDVCM/Business-Model-Canvas-Sego-Goreng-Semrawut?page-id=0%3A1&node-id=38-117&viewport=-170%2C587%2C0.16&t=8gt9qNV5G267Xq8B-1&scaling=scale-down&content-scaling=fixed&starting-point-node-id=20%3A3 mirorred from [dribbble](https://dribbble.com/shots/25718733-Business-Model-Canvas-Nasi-Goreng-Semrawut) originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/908920 -
 @ 732c6a62:42003da2
2025-03-09 22:36:26Não são recentes as táticas da esquerda de tentar reprimir intelectualmente seus opositores na base do deboche, da ironia, do desprezo e do boicote à credibilidade. Até Marx usava ironia para chamar os críticos de "burgueses iludidos". A diferença é que, no século XXI, trocaram o manifesto comunista por threads no Twitter e a dialética por memes de mau gosto. ### **A Falácia da Superioridade Moral** O debate sobre o "pobre de direita" no Brasil é contaminado por uma premissa tácita da esquerda: **a ideia de que classes baixas só podem ter consciência política se aderirem a pautas progressistas**. Quem ousa divergir é tratado como "traidor de classe", "manipulado", "ignorante", ou até vítimas de deboches como alguma pessoa com um qi em temperatura ambiente repetir diversas vezes "não é possível que ainda exista pobre de direita", "nunca vou entender pobre de direita", ou "pobre de direita é muito burro, rico eu até entendo", como se o autor dessas frases fosse o paladino dos mais oprimidos e pobres. Esse discurso, porém, não resiste a uma análise empírica, histórica ou sociológica. --- ### **Contexto Histórico: A Esquerda e o Mito do "Voto Consciente"** A noção de que o pobre deve votar na esquerda por "interesse de classe" é herança do **marxismo ortodoxo**, que via a política como mero reflexo da posição econômica. No entanto, a realidade é mais complexa: - **Dados do Latinobarómetro (2022):** 41% dos brasileiros de baixa renda (até 2 salários mínimos) apoiam redução de impostos e maior liberdade econômica — pautas tradicionalmente associadas à direita. - **Pesquisa IPEC (2023):** 58% dos pobres brasileiros priorizam "segurança pública" como principal demanda, acima de "distribuição de renda". Esses números não são acidentais. Refletem uma **mudança estrutural**: o pobre moderno não é mais o "operário industrial" do século XX, mas um empreendedor informal, motorista de app, ou microempresário — figuras que valorizam autonomia e rejeitam paternalismo estatal. Eles dizem não entender o pobre de direita e que nunca vai entendê-los, mas o fato é que não entendem porque **nunca conversaram com um sem fazer cara de psicólogo de posto de saúde**. Sua "preocupação" é só uma máscara para esconder o desprezo por quem ousa pensar diferente do seu manual de "oprimido ideal". ## **Se ainda não entenderam:** **Direita ≠ rico:** Tem gente que trabalha 12h/dia e vota em liberal porque quer **ser dono do próprio negócio**, não pra pagar mais taxação pra você postar meme no Twitter. **Acham que são o Sherlock Holmes da pobreza:** o palpite de que "o pobre é manipulado" é tão raso quanto sua compreensão de economia básica. --- ### **A Psicologia por Trás do Voto Conservador nas Periferias** A esquerda atribui o voto pobre em direita a "falta de educação" ou "manipulação midiática". Essa tese é não apenas elitista, mas **cientificamente falsa**: **Análise Psicológica Básica (para você que se acha o Paulo Freire):** - **Síndrome do Branco Salvador:** Acha que o pobre é uma criatura tão frágil que precisa de você pra pensar. Spoiler: ele não precisa. - **Viés da Superioridade Moral:** "Se você é pobre e não concorda comigo, você é burro". Parabéns, recriou a escravidão intelectual. - **Efeito Dunning-Kruger:** Não sabe o que é CLT, mas dá palpite sobre reforma trabalhista. - **Estudo da Universidade de São Paulo (USP, 2021):** Entre moradores de favelas, 63% associam políticas de segurança dura (como "bandido bom é bandido morto") à proteção de seus negócios e famílias. Para eles, a esquerda é "branda demais" com o crime. - **Pesquisa FGV (2020):** 71% dos trabalhadores informais rejeitam aumentos de impostos, mesmo que para financiar programas sociais. Motivo: já sofrem com a burocracia estatal para legalizar seus negócios. Esses dados revelam uma **racionalidade prática**: o pobre avalia políticas pelo impacto imediato em sua vida, não por abstrações ideológicas. Enquanto a esquerda fala em "reforma estrutural" e tenta importar discursos estrangeiros para debate, por exemplo, o tema irrelevante do pronome neutro, ele quer resolver problemas como: - **Violência** (que afeta seu comércio); - **Impostos** (que consomem até 40% do lucro de um camelô); - **Burocracia** (que impede a legalização de sua barraca de pastel). --- ### **Religião, Valores e a Hipocrisia do "Ateísmo de Redes Sociais"** A esquerda subestima o papel da religião na formação política das classes baixas. No Brasil, **76% dos evangélicos são pobres** (Datafolha, 2023), e suas igrejas promovem valores como: - **Família tradicional** (contra pautas progressistas como ideologia de gênero em escolas); - **Auto-responsabilidade** (ênfase em "trabalho duro" em vez de assistencialismo). **Exemplo Concreto:** Nas favelas de São Paulo, pastores evangélicos são frequentemente eleitos a cargos locais com plataformas anticrime e pró-mercado. Para seus eleitores, a esquerda urbana (que defende descriminalização de drogas e críticas à polícia) representa uma **ameaça ao seu estilo de vida**. --- ### **A Esquerda e seu Desprezo pela Autonomia do Pobre** O cerne do debate é a **incapacidade da esquerda de aceitar que o pobre possa ser autônomo**. Algumas evidências: #### **O Caso dos Empreendedores Informais** - **Segundo o IBGE (2023), 40% dos trabalhadores brasileiros estão na informalidade.** Muitos veem o Estado como obstáculo, não aliado. Políticas de direita (como simplificação tributária) são mais atraentes para eles que o Bolsa Família. #### **A Ascensão do Conservadorismo Periférico** - Pessoas assim tem um pensamento simples. Sua mensagem: *"Queremos empreender, não depender de político."* #### **A Rejeição ao "Vitimismo"** - **Pesquisa Atlas Intel (2022):** 68% dos pobres brasileiros rejeitam o termo "vítima da sociedade". Preferem ser vistos como "lutadores". --- ### **A projeção freudiana "o pobre é burro porque eu sou inteligente"** O deboche esquerdista esconde um complexo de inferioridade disfarçado de superioridade moral. É a **Síndrome do Salvador** em sua forma mais patética: - **Passo 1:** Assume-se que o pobre é um ser desprovido de agência. - **Passo 2:** Qualquer desvio da narrativa é atribuído a "manipulação da elite". - **Passo 3:** Quem critica o processo é chamado de "fascista". **Exemplo Prático:** Quando uma empregada doméstica diz que prefere o livre mercado a programas sociais, a esquerda não pergunta *"por quê?"* — ela grita *"lavagem cerebral!"*. A ironia? Essa mesma esquerda defende a **autonomia feminina**, exceto quando a mulher é pobre e pensa diferente. ### **Dados Globais: O Fenômeno Não é Brasileiro** A ideia de que "pobre de direita" é uma anomalia é desmentida por evidências internacionais: - **Estados Unidos:** 38% dos eleitores com renda abaixo de US$ 30k/ano votaram em Trump em 2020 (Pew Research). Motivos principais: conservadorismo social e rejeição a impostos. A esquerda: "vítimas da falsa consciência". Mais um detalhe: na última eleição de 2024, grande parte da classe "artística" milionária dos Estados Unidos, figuras conhecidas, promoveram em peso a Kamala Harris, do Partido Democrata. Percebe como a esquerda atual é a personificaçãoda burguesia e de só pensar na própria barriga? - **Argentina:** Javier Milei, libertário radical, quando candidato, tinha forte apoio nas *villas miseria* (favelas). Seu lema — *"O estado é um parasita"* — ressoa entre quem sofria com inflação de 211% ao ano. - **Índia:** O partido BJP (direita nacionalista) domina entre os pobres rurais, que associam a esquerda a elites urbanas desconectadas de suas necessidades. ### **A história que a esquerda tenta apagar: pobres de direita existem desde sempre** A esquerda age como se o "pobre de direita" fosse uma invenção recente do MBL, mas a realidade é que **classes baixas conservadoras são regra, não exceção**, na história mundial: - **Revolução Francesa (1789):** Camponeses apoiaram a monarquia contra os jacobinos urbanos que queriam "libertá-los". - **Brasil Imperial:** Escravos libertos que viraram pequenos proprietários rurais rejeitavam o abolicionismo radical — queriam integração, não utopia. **Tradução:** Quando o pobre não segue o script, a esquerda inventa teorias conspiratórias. --- ### **A Hipocrisia da Esquerda Urbana e Universitária** Enquanto acusa o pobre de direita de "alienado", a esquerda brasileira é dominada por uma **elite desconectada da realidade periférica**: - **Perfil Socioeconômico:** 82% dos filiados ao PSOL têm ensino superior completo (TSE, 2023). Apenas 6% moram em bairros periféricos. - **Prioridades Descoladas:** Enquanto o pobre debate segurança e custo de vida, a esquerda pauta discussões como "linguagem não-binária em editais públicos" — tema irrelevante para quem luta contra o desemprego. Os grandes teóricos comunistas se reviram no túmulo quando veem o que a esquerda se tornou: não debatem os reais problemas do Brasil, e sim sobre suas próprias emoções. *"A esquerda brasileira trocou o operário pelo influencer progressista. O pobre virou um personagem de campanha, não um interlocutor real."* ### **A diversidade de pensamento que a esquerda não suporta** A esquerda prega diversidade — desde que você seja diverso dentro de um **checklist pré-aprovado**. Pobre LGBTQ+? Herói. Pobre evangélico? Fascista. Pobre que abre MEI? "Peão do capitalismo". A realidade é que favelas e periferias são **microcosmos de pluralidade ideológica**, algo que assusta quem quer reduzir seres humanos a estereótipos. --- ### **Respostas aos Argumentos Esquerdistas (e Por que Falham)** #### **"O pobre de direita é manipulado pela mídia!"** - **Contradição:** Se a mídia tradicional é dominada por elites (como alegam), por que grandes veículos são abertamente progressistas? A Record (evangélica) é exceção, não regra. **Contradição Central:** Como explicar que, segundo o **Banco Mundial (2023)**, países com maior liberdade econômica (ex.: Chile, Polônia) reduziram a pobreza extrema em 60% nas últimas décadas, enquanto modelos estatizantes (ex.: Venezuela, Argentina com o governo peronista) afundaram na miséria? Simples: a esquerda prefere culpar o "neoliberalismo" a admitir que **o pobre com o mínimo de consciência quer emprego, não esmola**. **Dado que Machuca:** - 71% das mulheres da periferia rejeitam o feminismo radical, associando-o a "prioridades distantes da realidade" (**Instituto Locomotiva, 2023**). #### **"Ele vota contra os próprios interesses!"** - **Falácia:** Pressupõe que a esquerda define o que é o "interesse do pobre". Para um pai de família na Cidade de Deus, ter a boca de fogo fechada pode ser mais urgente que um aumento de 10% no Bolsa Família. O pobre de direita não é uma anomalia. É o **produto natural de um mundo complexo** onde seres humanos têm aspirações, medos e valores diversos. Enquanto a esquerda insiste em tratá-lo como um projeto fracassado, ele está ocupado: - **Trabalhando** para não depender do governo. - **Escolhendo** religiões que dão sentido à sua vida. - **Rejeitando** pautas identitárias que não resolvem o custo do gás de cozinha. #### **"É falta de educação política!"** - **Ironia:** Nos países nórdicos (modelo da esquerda), as classes baixas são as mais conservadoras. Educação não correlaciona com progressismo. --- ### **Por que o Debuste Precisa Acabar** A insistência em descredibilizar o pobre de direita revela um **projeto de poder fracassado**. A esquerda, ao substituir diálogo por deboche, perdeu a capacidade de representar quem mais precisaria dela. Enquanto isso, a direita — nem sempre por virtude, mas por pragmatismo — capturou o descontentamento de milhões com o status quo. O pobre de direita existe porque ele **não precisa da permissão do rico de esquerda para pensar**. A incapacidade de entender isso só prova que **a esquerda é a nova aristocracia**. **Último Dado:** Nas eleições de 2022, Tarcísio de Freitas (direita) venceu em 72% das favelas de São Paulo. O motivo? Seu discurso anti-burocracia e pró-microempreendedor. A mensagem é clara: o pobre não é um projeto ideológico. É um agente político autônomo — e quem não entender isso continuará perdendo eleições. A esquerda elitista não odeia o pobre de direita por ele ser "irracional". Odeia porque ele **desafia o monopólio moral** que ela construiu sobre a miséria alheia. Enquanto isso, o pobre segue sua vida, ignorando os berros de quem acha que sabem mais da sua vida que ele mesmo. **Pergunta Retórica (Para Incomodar):** Se a esquerda é tão sábia, por que não usa essa sabedoria para entender que **pobre também cansa de ser tratado como cachorro que late no ritmo errado**? --- # **Fontes Citadas:** 1. Latinobarómetro (2022) 2. IPEC (2023) 3. USP (2021): *"Segurança Pública e Percepções nas Favelas Cariocas"* 4. FGV (2020): *"Informalidade e Tributação no Brasil"* 5. Datafolha (2023): *"Perfil Religioso do Eleitorado Brasileiro"* 6. Atlas Intel (2022): *"Autopercepção das Classes Baixas"* 7. Pew Research (2020): *"Voting Patterns by Income in the U.S."* 8. TSE (2023): *"Perfil Socioeconômico dos Filiados Partidários"* **Leitura Recomendada para Esquerdistas:** - *"Fome de Poder: Por que o Pobre Brasileiro Abandonou a Esquerda"* (Fernando Schüller, 2023) - *"A Revolução dos Conservadores: Religião e Política nas Periferias"* (Juliano Spyer, 2021) - *"Direita e Esquerda: Razões e Paixões"* (Demétrio Magnoli, 2019)
@ 732c6a62:42003da2
2025-03-09 22:36:26Não são recentes as táticas da esquerda de tentar reprimir intelectualmente seus opositores na base do deboche, da ironia, do desprezo e do boicote à credibilidade. Até Marx usava ironia para chamar os críticos de "burgueses iludidos". A diferença é que, no século XXI, trocaram o manifesto comunista por threads no Twitter e a dialética por memes de mau gosto. ### **A Falácia da Superioridade Moral** O debate sobre o "pobre de direita" no Brasil é contaminado por uma premissa tácita da esquerda: **a ideia de que classes baixas só podem ter consciência política se aderirem a pautas progressistas**. Quem ousa divergir é tratado como "traidor de classe", "manipulado", "ignorante", ou até vítimas de deboches como alguma pessoa com um qi em temperatura ambiente repetir diversas vezes "não é possível que ainda exista pobre de direita", "nunca vou entender pobre de direita", ou "pobre de direita é muito burro, rico eu até entendo", como se o autor dessas frases fosse o paladino dos mais oprimidos e pobres. Esse discurso, porém, não resiste a uma análise empírica, histórica ou sociológica. --- ### **Contexto Histórico: A Esquerda e o Mito do "Voto Consciente"** A noção de que o pobre deve votar na esquerda por "interesse de classe" é herança do **marxismo ortodoxo**, que via a política como mero reflexo da posição econômica. No entanto, a realidade é mais complexa: - **Dados do Latinobarómetro (2022):** 41% dos brasileiros de baixa renda (até 2 salários mínimos) apoiam redução de impostos e maior liberdade econômica — pautas tradicionalmente associadas à direita. - **Pesquisa IPEC (2023):** 58% dos pobres brasileiros priorizam "segurança pública" como principal demanda, acima de "distribuição de renda". Esses números não são acidentais. Refletem uma **mudança estrutural**: o pobre moderno não é mais o "operário industrial" do século XX, mas um empreendedor informal, motorista de app, ou microempresário — figuras que valorizam autonomia e rejeitam paternalismo estatal. Eles dizem não entender o pobre de direita e que nunca vai entendê-los, mas o fato é que não entendem porque **nunca conversaram com um sem fazer cara de psicólogo de posto de saúde**. Sua "preocupação" é só uma máscara para esconder o desprezo por quem ousa pensar diferente do seu manual de "oprimido ideal". ## **Se ainda não entenderam:** **Direita ≠ rico:** Tem gente que trabalha 12h/dia e vota em liberal porque quer **ser dono do próprio negócio**, não pra pagar mais taxação pra você postar meme no Twitter. **Acham que são o Sherlock Holmes da pobreza:** o palpite de que "o pobre é manipulado" é tão raso quanto sua compreensão de economia básica. --- ### **A Psicologia por Trás do Voto Conservador nas Periferias** A esquerda atribui o voto pobre em direita a "falta de educação" ou "manipulação midiática". Essa tese é não apenas elitista, mas **cientificamente falsa**: **Análise Psicológica Básica (para você que se acha o Paulo Freire):** - **Síndrome do Branco Salvador:** Acha que o pobre é uma criatura tão frágil que precisa de você pra pensar. Spoiler: ele não precisa. - **Viés da Superioridade Moral:** "Se você é pobre e não concorda comigo, você é burro". Parabéns, recriou a escravidão intelectual. - **Efeito Dunning-Kruger:** Não sabe o que é CLT, mas dá palpite sobre reforma trabalhista. - **Estudo da Universidade de São Paulo (USP, 2021):** Entre moradores de favelas, 63% associam políticas de segurança dura (como "bandido bom é bandido morto") à proteção de seus negócios e famílias. Para eles, a esquerda é "branda demais" com o crime. - **Pesquisa FGV (2020):** 71% dos trabalhadores informais rejeitam aumentos de impostos, mesmo que para financiar programas sociais. Motivo: já sofrem com a burocracia estatal para legalizar seus negócios. Esses dados revelam uma **racionalidade prática**: o pobre avalia políticas pelo impacto imediato em sua vida, não por abstrações ideológicas. Enquanto a esquerda fala em "reforma estrutural" e tenta importar discursos estrangeiros para debate, por exemplo, o tema irrelevante do pronome neutro, ele quer resolver problemas como: - **Violência** (que afeta seu comércio); - **Impostos** (que consomem até 40% do lucro de um camelô); - **Burocracia** (que impede a legalização de sua barraca de pastel). --- ### **Religião, Valores e a Hipocrisia do "Ateísmo de Redes Sociais"** A esquerda subestima o papel da religião na formação política das classes baixas. No Brasil, **76% dos evangélicos são pobres** (Datafolha, 2023), e suas igrejas promovem valores como: - **Família tradicional** (contra pautas progressistas como ideologia de gênero em escolas); - **Auto-responsabilidade** (ênfase em "trabalho duro" em vez de assistencialismo). **Exemplo Concreto:** Nas favelas de São Paulo, pastores evangélicos são frequentemente eleitos a cargos locais com plataformas anticrime e pró-mercado. Para seus eleitores, a esquerda urbana (que defende descriminalização de drogas e críticas à polícia) representa uma **ameaça ao seu estilo de vida**. --- ### **A Esquerda e seu Desprezo pela Autonomia do Pobre** O cerne do debate é a **incapacidade da esquerda de aceitar que o pobre possa ser autônomo**. Algumas evidências: #### **O Caso dos Empreendedores Informais** - **Segundo o IBGE (2023), 40% dos trabalhadores brasileiros estão na informalidade.** Muitos veem o Estado como obstáculo, não aliado. Políticas de direita (como simplificação tributária) são mais atraentes para eles que o Bolsa Família. #### **A Ascensão do Conservadorismo Periférico** - Pessoas assim tem um pensamento simples. Sua mensagem: *"Queremos empreender, não depender de político."* #### **A Rejeição ao "Vitimismo"** - **Pesquisa Atlas Intel (2022):** 68% dos pobres brasileiros rejeitam o termo "vítima da sociedade". Preferem ser vistos como "lutadores". --- ### **A projeção freudiana "o pobre é burro porque eu sou inteligente"** O deboche esquerdista esconde um complexo de inferioridade disfarçado de superioridade moral. É a **Síndrome do Salvador** em sua forma mais patética: - **Passo 1:** Assume-se que o pobre é um ser desprovido de agência. - **Passo 2:** Qualquer desvio da narrativa é atribuído a "manipulação da elite". - **Passo 3:** Quem critica o processo é chamado de "fascista". **Exemplo Prático:** Quando uma empregada doméstica diz que prefere o livre mercado a programas sociais, a esquerda não pergunta *"por quê?"* — ela grita *"lavagem cerebral!"*. A ironia? Essa mesma esquerda defende a **autonomia feminina**, exceto quando a mulher é pobre e pensa diferente. ### **Dados Globais: O Fenômeno Não é Brasileiro** A ideia de que "pobre de direita" é uma anomalia é desmentida por evidências internacionais: - **Estados Unidos:** 38% dos eleitores com renda abaixo de US$ 30k/ano votaram em Trump em 2020 (Pew Research). Motivos principais: conservadorismo social e rejeição a impostos. A esquerda: "vítimas da falsa consciência". Mais um detalhe: na última eleição de 2024, grande parte da classe "artística" milionária dos Estados Unidos, figuras conhecidas, promoveram em peso a Kamala Harris, do Partido Democrata. Percebe como a esquerda atual é a personificaçãoda burguesia e de só pensar na própria barriga? - **Argentina:** Javier Milei, libertário radical, quando candidato, tinha forte apoio nas *villas miseria* (favelas). Seu lema — *"O estado é um parasita"* — ressoa entre quem sofria com inflação de 211% ao ano. - **Índia:** O partido BJP (direita nacionalista) domina entre os pobres rurais, que associam a esquerda a elites urbanas desconectadas de suas necessidades. ### **A história que a esquerda tenta apagar: pobres de direita existem desde sempre** A esquerda age como se o "pobre de direita" fosse uma invenção recente do MBL, mas a realidade é que **classes baixas conservadoras são regra, não exceção**, na história mundial: - **Revolução Francesa (1789):** Camponeses apoiaram a monarquia contra os jacobinos urbanos que queriam "libertá-los". - **Brasil Imperial:** Escravos libertos que viraram pequenos proprietários rurais rejeitavam o abolicionismo radical — queriam integração, não utopia. **Tradução:** Quando o pobre não segue o script, a esquerda inventa teorias conspiratórias. --- ### **A Hipocrisia da Esquerda Urbana e Universitária** Enquanto acusa o pobre de direita de "alienado", a esquerda brasileira é dominada por uma **elite desconectada da realidade periférica**: - **Perfil Socioeconômico:** 82% dos filiados ao PSOL têm ensino superior completo (TSE, 2023). Apenas 6% moram em bairros periféricos. - **Prioridades Descoladas:** Enquanto o pobre debate segurança e custo de vida, a esquerda pauta discussões como "linguagem não-binária em editais públicos" — tema irrelevante para quem luta contra o desemprego. Os grandes teóricos comunistas se reviram no túmulo quando veem o que a esquerda se tornou: não debatem os reais problemas do Brasil, e sim sobre suas próprias emoções. *"A esquerda brasileira trocou o operário pelo influencer progressista. O pobre virou um personagem de campanha, não um interlocutor real."* ### **A diversidade de pensamento que a esquerda não suporta** A esquerda prega diversidade — desde que você seja diverso dentro de um **checklist pré-aprovado**. Pobre LGBTQ+? Herói. Pobre evangélico? Fascista. Pobre que abre MEI? "Peão do capitalismo". A realidade é que favelas e periferias são **microcosmos de pluralidade ideológica**, algo que assusta quem quer reduzir seres humanos a estereótipos. --- ### **Respostas aos Argumentos Esquerdistas (e Por que Falham)** #### **"O pobre de direita é manipulado pela mídia!"** - **Contradição:** Se a mídia tradicional é dominada por elites (como alegam), por que grandes veículos são abertamente progressistas? A Record (evangélica) é exceção, não regra. **Contradição Central:** Como explicar que, segundo o **Banco Mundial (2023)**, países com maior liberdade econômica (ex.: Chile, Polônia) reduziram a pobreza extrema em 60% nas últimas décadas, enquanto modelos estatizantes (ex.: Venezuela, Argentina com o governo peronista) afundaram na miséria? Simples: a esquerda prefere culpar o "neoliberalismo" a admitir que **o pobre com o mínimo de consciência quer emprego, não esmola**. **Dado que Machuca:** - 71% das mulheres da periferia rejeitam o feminismo radical, associando-o a "prioridades distantes da realidade" (**Instituto Locomotiva, 2023**). #### **"Ele vota contra os próprios interesses!"** - **Falácia:** Pressupõe que a esquerda define o que é o "interesse do pobre". Para um pai de família na Cidade de Deus, ter a boca de fogo fechada pode ser mais urgente que um aumento de 10% no Bolsa Família. O pobre de direita não é uma anomalia. É o **produto natural de um mundo complexo** onde seres humanos têm aspirações, medos e valores diversos. Enquanto a esquerda insiste em tratá-lo como um projeto fracassado, ele está ocupado: - **Trabalhando** para não depender do governo. - **Escolhendo** religiões que dão sentido à sua vida. - **Rejeitando** pautas identitárias que não resolvem o custo do gás de cozinha. #### **"É falta de educação política!"** - **Ironia:** Nos países nórdicos (modelo da esquerda), as classes baixas são as mais conservadoras. Educação não correlaciona com progressismo. --- ### **Por que o Debuste Precisa Acabar** A insistência em descredibilizar o pobre de direita revela um **projeto de poder fracassado**. A esquerda, ao substituir diálogo por deboche, perdeu a capacidade de representar quem mais precisaria dela. Enquanto isso, a direita — nem sempre por virtude, mas por pragmatismo — capturou o descontentamento de milhões com o status quo. O pobre de direita existe porque ele **não precisa da permissão do rico de esquerda para pensar**. A incapacidade de entender isso só prova que **a esquerda é a nova aristocracia**. **Último Dado:** Nas eleições de 2022, Tarcísio de Freitas (direita) venceu em 72% das favelas de São Paulo. O motivo? Seu discurso anti-burocracia e pró-microempreendedor. A mensagem é clara: o pobre não é um projeto ideológico. É um agente político autônomo — e quem não entender isso continuará perdendo eleições. A esquerda elitista não odeia o pobre de direita por ele ser "irracional". Odeia porque ele **desafia o monopólio moral** que ela construiu sobre a miséria alheia. Enquanto isso, o pobre segue sua vida, ignorando os berros de quem acha que sabem mais da sua vida que ele mesmo. **Pergunta Retórica (Para Incomodar):** Se a esquerda é tão sábia, por que não usa essa sabedoria para entender que **pobre também cansa de ser tratado como cachorro que late no ritmo errado**? --- # **Fontes Citadas:** 1. Latinobarómetro (2022) 2. IPEC (2023) 3. USP (2021): *"Segurança Pública e Percepções nas Favelas Cariocas"* 4. FGV (2020): *"Informalidade e Tributação no Brasil"* 5. Datafolha (2023): *"Perfil Religioso do Eleitorado Brasileiro"* 6. Atlas Intel (2022): *"Autopercepção das Classes Baixas"* 7. Pew Research (2020): *"Voting Patterns by Income in the U.S."* 8. TSE (2023): *"Perfil Socioeconômico dos Filiados Partidários"* **Leitura Recomendada para Esquerdistas:** - *"Fome de Poder: Por que o Pobre Brasileiro Abandonou a Esquerda"* (Fernando Schüller, 2023) - *"A Revolução dos Conservadores: Religião e Política nas Periferias"* (Juliano Spyer, 2021) - *"Direita e Esquerda: Razões e Paixões"* (Demétrio Magnoli, 2019) -
 @ f25afb62:8d50c6e7
2025-03-09 01:34:10The recent economic turmoil in New Zealand has reignited debates over the role of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) in "engineering a recession." Many believe that the RBNZ’s decision to raise the Official Cash Rate (OCR) was the root cause of the downturn, but this narrative oversimplifies the reality. ### Who Really Engineered the Recession? Blaming the RBNZ for the recession ignores a fundamental truth: **market interest rates were rising long before the OCR was adjusted.** Bond yields, swap rates, and borrowing costs surged as the RBNZ stepped back from being the primary buyer of government bonds. When the RBNZ stopped paying artificially high prices (low yields) for bonds, the private sector had to price them instead, leading to yields rising back to real market interest rates. Meanwhile, the government continued to refinance its rolling debt at these higher rates, further driving up borrowing costs. The RBNZ, in hiking the OCR, was following the market interest rate, attempting to maintain credibility rather than dictating outcomes. The real policy missteps were made much earlier: 1. **Artificially Suppressing Interest Rates Through Money Printing**\ The RBNZ engaged in Large-Scale Asset Purchases (LSAP), creating money out of thin air to buy government bonds. This artificially lowered yields, making it cheaper for the government to borrow and spend beyond its means. The result? Inflation surged as the economy was flooded with cheap money. 2. **Funding for Lending Programme (FLP): Free Money for Banks**\ The RBNZ offered near 0% loans to banks, allowing them to borrow at artificially low rates while lending at much higher rates. This wasn’t just monetary easing—it was a blatant distortion of the free market, reinforcing the **Cantillon Effect**, where those closest to the money printer benefit first. 3. **Holding Rates Too Low for Too Long**\ A 0% OCR in itself doesn’t cause inflation—what does is creating excess liquidity while artificially suppressing borrowing costs. Banks, instead of competing for deposits and lending productively, were incentivized to park money in assets like housing, fueling unsustainable bubbles. When inflation inevitably took hold, the RBNZ had no choice but to raise rates aggressively. This wasn’t an effort to “engineer” a recession—it was damage control after prior policy failures. The claim that the RBNZ alone caused the recession is a convenient distraction from the real culprits: **government overspending and central bank interventionism.** ### The Cycle of Blame: Central Bank Governors as Fall Guys This cycle isn’t new. Central banks are officially independent, but in reality, they almost always align with the government of the day. The **Large-Scale Asset Purchase (LSAP) program** was effectively a way to finance government spending through money printing—something politicians would never admit outright. When the government needed funding for pandemic-era stimulus, the RBNZ obliged, creating \$50 billion out of thin air to buy government bonds and lower borrowing costs, making it easier for the Labour government to spend big. Now, with a new government in power, they get to bring in their own person—likely someone who will align with their fiscal policies, just as Orr aligned with Labour's. This cycle plays out over and over again: 1. **Print money to fund government priorities.** 2. **Blame the central bank for inflation or economic consequences.** 3. **Replace the central bank governor with someone more aligned with the new government’s agenda.** 4. **Repeat.** The “independent central bank” narrative is a useful tool for politicians to deflect blame. Labour can say, *“Inflation wasn’t our fault, it was the RBNZ’s monetary policy!”* Meanwhile, National can now install someone who will adjust policy to suit their needs while still claiming, *“We respect the independence of the Reserve Bank!”* This allows both parties to escape accountability, despite the fact that **excessive government spending and central bank money printing go hand in hand.** This isn’t just a New Zealand issue—**most central banks operate the same way.** They provide the liquidity needed to keep government spending rolling, and when inflation or other economic problems arise, the governor becomes the convenient fall guy. ### The Role of Bitcoin: An Exit From the Broken System This cycle of money printing, asset bubbles, inflation, and central bank tightening isn’t unique to New Zealand—it’s the natural consequence of a system where central banks and governments have **unchecked control over money.** Bitcoin was created as a direct response to this very problem. #### Bitcoin Fixes the Cantillon Effect - Unlike fiat money, which is distributed to banks and institutions first, **Bitcoin’s issuance is predictable and transparent.** There are no backroom deals, no preferential access, no bailouts. - Bitcoin doesn’t change its supply to accommodate political agendas. There is only one Bitcoin—just like there is only one Earth, and its land area cannot be expanded. It can be divided into **21 million equal-sized pieces called BTC or 2,100 trillion equal-sized pieces called sats.** - **Bitcoin doesn’t grant special privileges.** You either earn it, mine it, or buy it. No one gets first access at a discount. #### Bitcoin Removes the Central Bank Middleman - The RBNZ and other central banks manipulate money supply and interest rates to serve political and economic interests. Bitcoin’s monetary policy is fixed and free from human interference. - No government can arbitrarily print Bitcoin to fund its spending or suppress its value. - Bitcoin allows people to store their wealth without the risk of inflationary dilution or government confiscation. #### Bitcoin Protects You from the Next Bailout - Every time the financial system faces a crisis, governments and central banks shift the cost onto the public—through inflation, taxation, or outright financial repression. - Bitcoin lets you **opt out** of this cycle. By holding Bitcoin, your savings remain secure, beyond the reach of reckless monetary policy. - When the next crisis hits—and it will—Bitcoin holders won’t be left wondering how much purchasing power they’ve lost overnight. ### A Strategic Shift: The U.S. Embraces Bitcoin Recent developments in the U.S. signal a major turning point in how governments view Bitcoin. President Trump recently signed an Executive Order establishing a **Strategic Bitcoin Reserve**, marking the first time a nation has officially designated Bitcoin as a strategic asset. This reserve will be **exclusively Bitcoin**, initially seeded with Bitcoin seized through civil and criminal forfeitures, but with a commitment to acquiring more through budget-neutral strategies at no additional cost to taxpayers. This means that if the government can save money elsewhere, those funds can be redirected toward buying and holding Bitcoin as a permanent reserve asset. The implications of this decision are profound: - The U.S. **acknowledges Bitcoin as fundamentally different from “crypto.”** Altcoins and centralized tokens are being liquidated, while Bitcoin is being held as a permanent reserve. - The government is shifting from selling confiscated Bitcoin to **strategically accumulating it**, positioning the U.S. as a key player in a Bitcoin-based financial future. - Bitcoin mining is being embraced as a domestic industry, stabilizing power grids and reinforcing the U.S. as a leader in proof-of-work security. This policy shift highlights what Bitcoiners have long understood: **Bitcoin is digital gold, and fiat systems will eventually recognize its superiority.** While central banks continue their cycle of money printing and blame-shifting, the adoption of Bitcoin as a strategic reserve asset may mark the beginning of a global financial transformation. ### The Bigger Picture: Free Markets vs. Centralized Control The idea that the RBNZ acted independently in creating these economic conditions is a myth. Central banks do not exist in isolation; they facilitate government spending and economic policies, whether through bond purchases, artificially low interest rates, or direct lending programs. The economic pain we’re seeing now is not an accident—it’s a consequence of a system designed to redistribute wealth to those closest to the money printer. Bitcoin represents an alternative: a free-market monetary system where no central entity controls issuance, no insiders get preferential treatment, and no government can erode its value through reckless policies. The sooner people recognize the flaws in the current system, the sooner they’ll understand why Bitcoin exists—not just as an investment, but as a **monetary revolution.** originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/907966
@ f25afb62:8d50c6e7
2025-03-09 01:34:10The recent economic turmoil in New Zealand has reignited debates over the role of the Reserve Bank of New Zealand (RBNZ) in "engineering a recession." Many believe that the RBNZ’s decision to raise the Official Cash Rate (OCR) was the root cause of the downturn, but this narrative oversimplifies the reality. ### Who Really Engineered the Recession? Blaming the RBNZ for the recession ignores a fundamental truth: **market interest rates were rising long before the OCR was adjusted.** Bond yields, swap rates, and borrowing costs surged as the RBNZ stepped back from being the primary buyer of government bonds. When the RBNZ stopped paying artificially high prices (low yields) for bonds, the private sector had to price them instead, leading to yields rising back to real market interest rates. Meanwhile, the government continued to refinance its rolling debt at these higher rates, further driving up borrowing costs. The RBNZ, in hiking the OCR, was following the market interest rate, attempting to maintain credibility rather than dictating outcomes. The real policy missteps were made much earlier: 1. **Artificially Suppressing Interest Rates Through Money Printing**\ The RBNZ engaged in Large-Scale Asset Purchases (LSAP), creating money out of thin air to buy government bonds. This artificially lowered yields, making it cheaper for the government to borrow and spend beyond its means. The result? Inflation surged as the economy was flooded with cheap money. 2. **Funding for Lending Programme (FLP): Free Money for Banks**\ The RBNZ offered near 0% loans to banks, allowing them to borrow at artificially low rates while lending at much higher rates. This wasn’t just monetary easing—it was a blatant distortion of the free market, reinforcing the **Cantillon Effect**, where those closest to the money printer benefit first. 3. **Holding Rates Too Low for Too Long**\ A 0% OCR in itself doesn’t cause inflation—what does is creating excess liquidity while artificially suppressing borrowing costs. Banks, instead of competing for deposits and lending productively, were incentivized to park money in assets like housing, fueling unsustainable bubbles. When inflation inevitably took hold, the RBNZ had no choice but to raise rates aggressively. This wasn’t an effort to “engineer” a recession—it was damage control after prior policy failures. The claim that the RBNZ alone caused the recession is a convenient distraction from the real culprits: **government overspending and central bank interventionism.** ### The Cycle of Blame: Central Bank Governors as Fall Guys This cycle isn’t new. Central banks are officially independent, but in reality, they almost always align with the government of the day. The **Large-Scale Asset Purchase (LSAP) program** was effectively a way to finance government spending through money printing—something politicians would never admit outright. When the government needed funding for pandemic-era stimulus, the RBNZ obliged, creating \$50 billion out of thin air to buy government bonds and lower borrowing costs, making it easier for the Labour government to spend big. Now, with a new government in power, they get to bring in their own person—likely someone who will align with their fiscal policies, just as Orr aligned with Labour's. This cycle plays out over and over again: 1. **Print money to fund government priorities.** 2. **Blame the central bank for inflation or economic consequences.** 3. **Replace the central bank governor with someone more aligned with the new government’s agenda.** 4. **Repeat.** The “independent central bank” narrative is a useful tool for politicians to deflect blame. Labour can say, *“Inflation wasn’t our fault, it was the RBNZ’s monetary policy!”* Meanwhile, National can now install someone who will adjust policy to suit their needs while still claiming, *“We respect the independence of the Reserve Bank!”* This allows both parties to escape accountability, despite the fact that **excessive government spending and central bank money printing go hand in hand.** This isn’t just a New Zealand issue—**most central banks operate the same way.** They provide the liquidity needed to keep government spending rolling, and when inflation or other economic problems arise, the governor becomes the convenient fall guy. ### The Role of Bitcoin: An Exit From the Broken System This cycle of money printing, asset bubbles, inflation, and central bank tightening isn’t unique to New Zealand—it’s the natural consequence of a system where central banks and governments have **unchecked control over money.** Bitcoin was created as a direct response to this very problem. #### Bitcoin Fixes the Cantillon Effect - Unlike fiat money, which is distributed to banks and institutions first, **Bitcoin’s issuance is predictable and transparent.** There are no backroom deals, no preferential access, no bailouts. - Bitcoin doesn’t change its supply to accommodate political agendas. There is only one Bitcoin—just like there is only one Earth, and its land area cannot be expanded. It can be divided into **21 million equal-sized pieces called BTC or 2,100 trillion equal-sized pieces called sats.** - **Bitcoin doesn’t grant special privileges.** You either earn it, mine it, or buy it. No one gets first access at a discount. #### Bitcoin Removes the Central Bank Middleman - The RBNZ and other central banks manipulate money supply and interest rates to serve political and economic interests. Bitcoin’s monetary policy is fixed and free from human interference. - No government can arbitrarily print Bitcoin to fund its spending or suppress its value. - Bitcoin allows people to store their wealth without the risk of inflationary dilution or government confiscation. #### Bitcoin Protects You from the Next Bailout - Every time the financial system faces a crisis, governments and central banks shift the cost onto the public—through inflation, taxation, or outright financial repression. - Bitcoin lets you **opt out** of this cycle. By holding Bitcoin, your savings remain secure, beyond the reach of reckless monetary policy. - When the next crisis hits—and it will—Bitcoin holders won’t be left wondering how much purchasing power they’ve lost overnight. ### A Strategic Shift: The U.S. Embraces Bitcoin Recent developments in the U.S. signal a major turning point in how governments view Bitcoin. President Trump recently signed an Executive Order establishing a **Strategic Bitcoin Reserve**, marking the first time a nation has officially designated Bitcoin as a strategic asset. This reserve will be **exclusively Bitcoin**, initially seeded with Bitcoin seized through civil and criminal forfeitures, but with a commitment to acquiring more through budget-neutral strategies at no additional cost to taxpayers. This means that if the government can save money elsewhere, those funds can be redirected toward buying and holding Bitcoin as a permanent reserve asset. The implications of this decision are profound: - The U.S. **acknowledges Bitcoin as fundamentally different from “crypto.”** Altcoins and centralized tokens are being liquidated, while Bitcoin is being held as a permanent reserve. - The government is shifting from selling confiscated Bitcoin to **strategically accumulating it**, positioning the U.S. as a key player in a Bitcoin-based financial future. - Bitcoin mining is being embraced as a domestic industry, stabilizing power grids and reinforcing the U.S. as a leader in proof-of-work security. This policy shift highlights what Bitcoiners have long understood: **Bitcoin is digital gold, and fiat systems will eventually recognize its superiority.** While central banks continue their cycle of money printing and blame-shifting, the adoption of Bitcoin as a strategic reserve asset may mark the beginning of a global financial transformation. ### The Bigger Picture: Free Markets vs. Centralized Control The idea that the RBNZ acted independently in creating these economic conditions is a myth. Central banks do not exist in isolation; they facilitate government spending and economic policies, whether through bond purchases, artificially low interest rates, or direct lending programs. The economic pain we’re seeing now is not an accident—it’s a consequence of a system designed to redistribute wealth to those closest to the money printer. Bitcoin represents an alternative: a free-market monetary system where no central entity controls issuance, no insiders get preferential treatment, and no government can erode its value through reckless policies. The sooner people recognize the flaws in the current system, the sooner they’ll understand why Bitcoin exists—not just as an investment, but as a **monetary revolution.** originally posted at https://stacker.news/items/907966 -
 @ db11b320:05c5f7af
2025-03-09 00:14:24Manus 是一款由中国团队开发、号称全球首款通用 AI Agent 的产品,自 2025 年 3 月发布以来引发了广泛关注和热议。以下从技术能力、实际应用、用户体验及行业影响等多个维度对其进行客观评价: 一、技术能力 Manus 在技术上展现出一定的创新性,尤其是在任务拆解和自主执行方面表现出色。其核心特点包括: 多智能体架构:采用规划型、执行型和验证型智能体的分工机制,能够模拟人类工作流程,处理复杂任务。例如,它可以将筛选简历、分析股票或规划旅行等任务分解为可执行的子步骤,并通过调用工具(如浏览器、代码编辑器等)完成。 GAIA 测试表现:在 GAIA 基准测试中,Manus 的表现超越了 OpenAI 的 Deep Research,尤其在解决真实世界问题的能力上表现突出。这表明其在通用性任务处理上有一定竞争力。 自主性和工具调用:相比传统的对话式 AI,Manus 不仅提供建议,还能直接交付成果。例如,它能自主解压文件、浏览网页、编写代码,甚至在虚拟环境中操作应用程序。这种“手脑并用”的能力使其更接近通用 AI Agent 的定义。 局限性:尽管技术上有亮点,但也存在不足。例如,部分用户反馈其在垂直领域的深度检索能力较弱,信息来源多依赖中文平台,缺乏对国外期刊等高质量资源的整合。此外,在复杂任务的格式化交付(如生成符合特定要求的 PPT)方面表现欠佳。 二、实际应用 Manus 的应用场景覆盖广泛,但实际表现因任务类型而异: 优势场景: 文件处理:如筛选简历、生成表格等任务,Manus 表现高效,能够自主完成从解压文件到整理数据的全流程。 网页设计与编程:在生成 HTML 页面或简单程序时,Manus 的表现令人满意,甚至能根据用户偏好优化交互体验。 游戏操作:测试中,Manus 展示了在虚拟环境中自主操作的能力,例如在游戏平台上选择并尝试玩游戏,体现了一定的自主性。 不足之处: 深度研究:在需要深入专业知识的任务(如高分子材料研究报告)中,Manus 倾向于过度推理,信息来源不够权威,且无法完全满足特定格式要求。 复杂任务稳定性:对于耗时较长的任务,存在一定的中断率,且处理速度较慢(高级模式下可能需要 30 分钟至 1 小时)。 文化适应性:由于信息来源偏重中文内容,可能在处理国际化任务时表现受限。 三、用户体验 用户体验是 Manus 引发热议的重要原因,但也存在争议: 优点: 直观的任务展示:Manus 通过视频回放的形式展示任务执行过程,让用户直观感受到 AI 的“思考”和“行动”,这在传播上极具吸引力。 灵活交互:支持用户在任务执行过程中随时干预或调整需求,类似于与一个“实习生”协作。 记忆机制:能够记住用户偏好,提升后续任务的效率。 缺点: 速度慢:任务处理时间较长,尤其在联网搜索或复杂任务中,用户体验受到影响。 访问门槛高:目前仅限邀请制内测,申请流程繁琐,且邀请码在二手市场被炒至高价(最高达 10 万元),引发了部分用户的不满。 稳定性问题:内测期间,系统负载过高导致崩溃或错误频发,用户体验不稳定。 四、行业影响与争议 Manus 的发布不仅引发了技术圈的热议,也带来了行业层面的讨论: 正面影响: 推动 AI Agent 普及:Manus 的出现将 AI Agent 的概念带入大众视野,可能吸引更多资金和人才进入这一赛道,推动行业发展。 中国 AI 的崛起:作为一款中国团队开发的产品,Manus 的表现被视为中国 AI 技术进步的象征,尤其是在与 OpenAI 等国际巨头的对比中。 争议点: 过度营销:部分评论认为,Manus 的爆火与其营销策略密切相关。例如,强调“超越 OpenAI”或“全球首款通用 Agent”等宣传用语可能夸大了其实际能力,导致用户期望过高。 “套壳”质疑:有观点指出,Manus 并非底层技术创新,而是通过整合现有大模型 API(如 Claude、Qwen 等)实现的“应用层产品”。虽然其在任务规划和执行层有创新,但这种“套壳”模式引发了关于技术原创性的讨论。 行业“造神”现象:部分媒体和用户将其捧上神坛,称之为“AGI 的里程碑”,这种过度吹捧可能对行业健康发展不利。正如一些评论指出,AI 的进步需要多个团队的共同努力,而非依赖单一产品的神话。 五、未来展望 尽管 Manus 在技术能力和用户体验上仍有改进空间,但其潜力不容忽视: 技术优化:未来可以通过引入更多高质量数据源、优化任务中断率和处理速度,以及增强垂直领域的专业性来提升竞争力。 商业化路径:目前 Manus 的定位尚不明确,可能面向中小型企业(如金融机构)提供订阅制服务。如何在商业化过程中平衡成本与用户体验将是关键。 行业启发:Manus 的成功可能激励更多团队探索 AI Agent 的开发,尤其是在垂直领域的定制化应用上。 六、总体评价 综合来看,Manus 是一款在 AI Agent 领域具有开创性意义的产品,其在任务拆解、自主执行和用户体验上的创新值得肯定,尤其是在 GAIA 测试中的亮眼表现证明了其技术实力。然而,它并非“颠覆性”的革命性产品,其实际能力与宣传中的“全球首款通用 Agent”存在一定差距,尤其在专业性、稳定性和速度方面有待提升。 对于普通用户而言,Manus 提供了一种全新的 AI 交互方式,能够显著提升某些场景下的工作效率,但并非万能工具。对于行业而言,它的出现是 AI Agent 发展的重要一步,但不应被过度神化。长远来看,AI 的进步需要更多团队的共同努力,而非依赖单一产品的神话。 最终,评价一款 AI 产品不应只看其技术指标或市场热度,而应关注它能否真正解决用户的实际需求。Manus 的未来价值,取决于其能否在快速迭代中不断优化,并找到明确的定位与应用场景。
@ db11b320:05c5f7af
2025-03-09 00:14:24Manus 是一款由中国团队开发、号称全球首款通用 AI Agent 的产品,自 2025 年 3 月发布以来引发了广泛关注和热议。以下从技术能力、实际应用、用户体验及行业影响等多个维度对其进行客观评价: 一、技术能力 Manus 在技术上展现出一定的创新性,尤其是在任务拆解和自主执行方面表现出色。其核心特点包括: 多智能体架构:采用规划型、执行型和验证型智能体的分工机制,能够模拟人类工作流程,处理复杂任务。例如,它可以将筛选简历、分析股票或规划旅行等任务分解为可执行的子步骤,并通过调用工具(如浏览器、代码编辑器等)完成。 GAIA 测试表现:在 GAIA 基准测试中,Manus 的表现超越了 OpenAI 的 Deep Research,尤其在解决真实世界问题的能力上表现突出。这表明其在通用性任务处理上有一定竞争力。 自主性和工具调用:相比传统的对话式 AI,Manus 不仅提供建议,还能直接交付成果。例如,它能自主解压文件、浏览网页、编写代码,甚至在虚拟环境中操作应用程序。这种“手脑并用”的能力使其更接近通用 AI Agent 的定义。 局限性:尽管技术上有亮点,但也存在不足。例如,部分用户反馈其在垂直领域的深度检索能力较弱,信息来源多依赖中文平台,缺乏对国外期刊等高质量资源的整合。此外,在复杂任务的格式化交付(如生成符合特定要求的 PPT)方面表现欠佳。 二、实际应用 Manus 的应用场景覆盖广泛,但实际表现因任务类型而异: 优势场景: 文件处理:如筛选简历、生成表格等任务,Manus 表现高效,能够自主完成从解压文件到整理数据的全流程。 网页设计与编程:在生成 HTML 页面或简单程序时,Manus 的表现令人满意,甚至能根据用户偏好优化交互体验。 游戏操作:测试中,Manus 展示了在虚拟环境中自主操作的能力,例如在游戏平台上选择并尝试玩游戏,体现了一定的自主性。 不足之处: 深度研究:在需要深入专业知识的任务(如高分子材料研究报告)中,Manus 倾向于过度推理,信息来源不够权威,且无法完全满足特定格式要求。 复杂任务稳定性:对于耗时较长的任务,存在一定的中断率,且处理速度较慢(高级模式下可能需要 30 分钟至 1 小时)。 文化适应性:由于信息来源偏重中文内容,可能在处理国际化任务时表现受限。 三、用户体验 用户体验是 Manus 引发热议的重要原因,但也存在争议: 优点: 直观的任务展示:Manus 通过视频回放的形式展示任务执行过程,让用户直观感受到 AI 的“思考”和“行动”,这在传播上极具吸引力。 灵活交互:支持用户在任务执行过程中随时干预或调整需求,类似于与一个“实习生”协作。 记忆机制:能够记住用户偏好,提升后续任务的效率。 缺点: 速度慢:任务处理时间较长,尤其在联网搜索或复杂任务中,用户体验受到影响。 访问门槛高:目前仅限邀请制内测,申请流程繁琐,且邀请码在二手市场被炒至高价(最高达 10 万元),引发了部分用户的不满。 稳定性问题:内测期间,系统负载过高导致崩溃或错误频发,用户体验不稳定。 四、行业影响与争议 Manus 的发布不仅引发了技术圈的热议,也带来了行业层面的讨论: 正面影响: 推动 AI Agent 普及:Manus 的出现将 AI Agent 的概念带入大众视野,可能吸引更多资金和人才进入这一赛道,推动行业发展。 中国 AI 的崛起:作为一款中国团队开发的产品,Manus 的表现被视为中国 AI 技术进步的象征,尤其是在与 OpenAI 等国际巨头的对比中。 争议点: 过度营销:部分评论认为,Manus 的爆火与其营销策略密切相关。例如,强调“超越 OpenAI”或“全球首款通用 Agent”等宣传用语可能夸大了其实际能力,导致用户期望过高。 “套壳”质疑:有观点指出,Manus 并非底层技术创新,而是通过整合现有大模型 API(如 Claude、Qwen 等)实现的“应用层产品”。虽然其在任务规划和执行层有创新,但这种“套壳”模式引发了关于技术原创性的讨论。 行业“造神”现象:部分媒体和用户将其捧上神坛,称之为“AGI 的里程碑”,这种过度吹捧可能对行业健康发展不利。正如一些评论指出,AI 的进步需要多个团队的共同努力,而非依赖单一产品的神话。 五、未来展望 尽管 Manus 在技术能力和用户体验上仍有改进空间,但其潜力不容忽视: 技术优化:未来可以通过引入更多高质量数据源、优化任务中断率和处理速度,以及增强垂直领域的专业性来提升竞争力。 商业化路径:目前 Manus 的定位尚不明确,可能面向中小型企业(如金融机构)提供订阅制服务。如何在商业化过程中平衡成本与用户体验将是关键。 行业启发:Manus 的成功可能激励更多团队探索 AI Agent 的开发,尤其是在垂直领域的定制化应用上。 六、总体评价 综合来看,Manus 是一款在 AI Agent 领域具有开创性意义的产品,其在任务拆解、自主执行和用户体验上的创新值得肯定,尤其是在 GAIA 测试中的亮眼表现证明了其技术实力。然而,它并非“颠覆性”的革命性产品,其实际能力与宣传中的“全球首款通用 Agent”存在一定差距,尤其在专业性、稳定性和速度方面有待提升。 对于普通用户而言,Manus 提供了一种全新的 AI 交互方式,能够显著提升某些场景下的工作效率,但并非万能工具。对于行业而言,它的出现是 AI Agent 发展的重要一步,但不应被过度神化。长远来看,AI 的进步需要更多团队的共同努力,而非依赖单一产品的神话。 最终,评价一款 AI 产品不应只看其技术指标或市场热度,而应关注它能否真正解决用户的实际需求。Manus 的未来价值,取决于其能否在快速迭代中不断优化,并找到明确的定位与应用场景。 -
 @ ec9bd746:df11a9d0
2025-03-07 20:13:38I was diving into PoW (Proof-of-Work) once again after nostr:nprofile1qy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uq3wamnwvaz7tmjv4kxz7fwdehhxarj9e3xzmny9uqzqj8a67jths8euy33v5yu6me6ngua5v3y3qq3dswuqh2pejmtls6datagmu rekindled my interest with his PoW Draw project. It was a fun little trifle, but it shifted my focus just the right way at the right time. Because then, on Friday, came the [Oval Office Travesty](nostr:nevent1qvzqqqqqqypzpmym6ar92346qc04ml08z6j0yrelylkv9r9ysurhte0g2003r2wsqy2hwumn8ghj7un9d3shjtnyv9kh2uewd9hj7qghwaehxw309aex2mrp0yhxummnw3ezucnpdejz7qpqqqqqqqrg6vz7m9z8ufagn4z3ks0meqw4nyh4gfxvksfhne99egzsd3g3w9). Once I got over the initial shock, I decided I couldn't just curse and lament; I needed to do something bigger, something symbolic, something expressive. So that's exactly what I did—breaking nostr:nprofile1qy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uq32amnwvaz7tmjv4kxz7fwv3sk6atn9e5k7tcqyqewrqnkx4zsaweutf739s0cu7et29zrntqs5elw70vlm8zudr3y2t9v7jg's record which he held for almost 2 and half years. Here is a note with PoW 45, the highest PoW known to Nostr (as of now). nostr:nevent1qvzqqqqqqypzpmym6ar92346qc04ml08z6j0yrelylkv9r9ysurhte0g2003r2wsqy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uqsuamnwvaz7tmwdaejumr0dshsqgqqqqqqqqqy8t8awr5c8z4yfp4cr8v7spp8psncv8twlh083flcr582fyu9 ## How Did I Pull It Off? In theory, quite simple: Create note, run PoW mining script & wait. Thanks to PoW Draw, I already had mining software at hand: nostr:nprofile1qy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uq32amnwvaz7tmjv4kxz7fwv3sk6atn9e5k7tcqyqvqc5tlvn6etv09f0fvuauves49dvgnukjtzsndfv9y8yyrqyxmz7dty6z's [*notemine_hw*](https://github.com/plebemineira/notemine_hw), but when you know that there is a 1 in 2^45 chance that the next hash will be the correct one you want to increase the odds a bit. So on Monday evening, I started my Note Mining operation on an old 40 thread machine called Workhorse. ### Issues Along the Way I was immediately surprised that Workhorse (2× Intel Xeon Silver 4114) produced only about 3Mh/s. A laptop (Intel Core i7-1185G7) with Windows and all the bloat did 5Mh/s. That was strange. Another hurdle was that *notemine_hw* does not refresh the `created_at` field. With just a few Mh/s of power I was potentially looking at weeks of computation, by then the note would be quite stale. So I created systemd service leveraging the `RuntimeMaxSec` option to periodically restart every 3600 seconds assuring that the Note would be max 1 hour old at the time of publishing. Luckily PoW is that kind of problem where every hash attempt is an independent event, so the chance of success is the same whether you do it in small increments or one uninterrupted stretch. So by restarting the mining process I was only losing a few mere seconds every hour due to the overhead. Once the note staleness issue was resolved, I looked at the 40 workers on Workhorse vs. 7 workers on the laptop and start messing around with running one instance with 40 workers and running 40 instances with 1 worker and found out, that the workers are not bound to a CPU thread and are jumping between the CPUs like rabbits high on Colombian carrots. The solution? Running multiple instances with one worker each as a service locked to its own CPU core using systemd's `CPUAffinity` option. ``` $aida@workhorse:systemd/system $ sudo cat notemine@.service [Unit] Description=Notemine HW Publish (restarts hourly) [Service] Type=simple CPUAffinity=%i # The command to run: ExecStart=/home/aida/.cargo/bin/notemine_hw publish --n-workers 1 --difficulty 45 --event-json /home/aida/note.json --relay-url 'wss://wot.shaving.kiwi' --nsec nsec0123456789abcdef # Let the process run for 1 hour (3600 seconds), then systemd will stop it: RuntimeMaxSec=3600 TimeoutStopSec=1 # Tells systemd to restart the service automatically after it stops: Restart=always RestartSec=1 # run as a non-root user: User=aida Group=aida [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target ``` Then I added a starting service to spawn an instance for each CPU thread. ``` $aida@workhorse:systemd/system $ sudo cat notemine_start.service [Unit] Description=Start all services in sequence with 3-second intervals [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/usr/bin/zsh /home/aida/notemine_start.sh RemainAfterExit=yes [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target ``` Here is the startup script (I know, loops exist—but Ctrl+C/Ctrl+V is so old-school): ``` aida@workhorse:~ $ cat notemine_start.sh /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@0.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@1.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@2.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@3.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 ... ... ... /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@38.service ``` The sleep there is critical to make sure that the `created_at`timestamps are different, preventing redundant hashing. **This adjustment made Workhorse the strongest machine in my fleet with 10+Mh/s.** ## The Luck Aspect From Monday evening, I started adding all machines at my disposal into the fleet and by Wednesday evening I was crunching hashes on about 130 CPU threads (a lot of them were quite antique) and at the peak was just little shy of 40Mh/s. To compensate for the slow start with the few above-mentioned hiccups and the fact that I had to use my desktop to do other things from time to time, I counted with the conservative estimate of 30Mh/s when I was doing all the probability calculations. 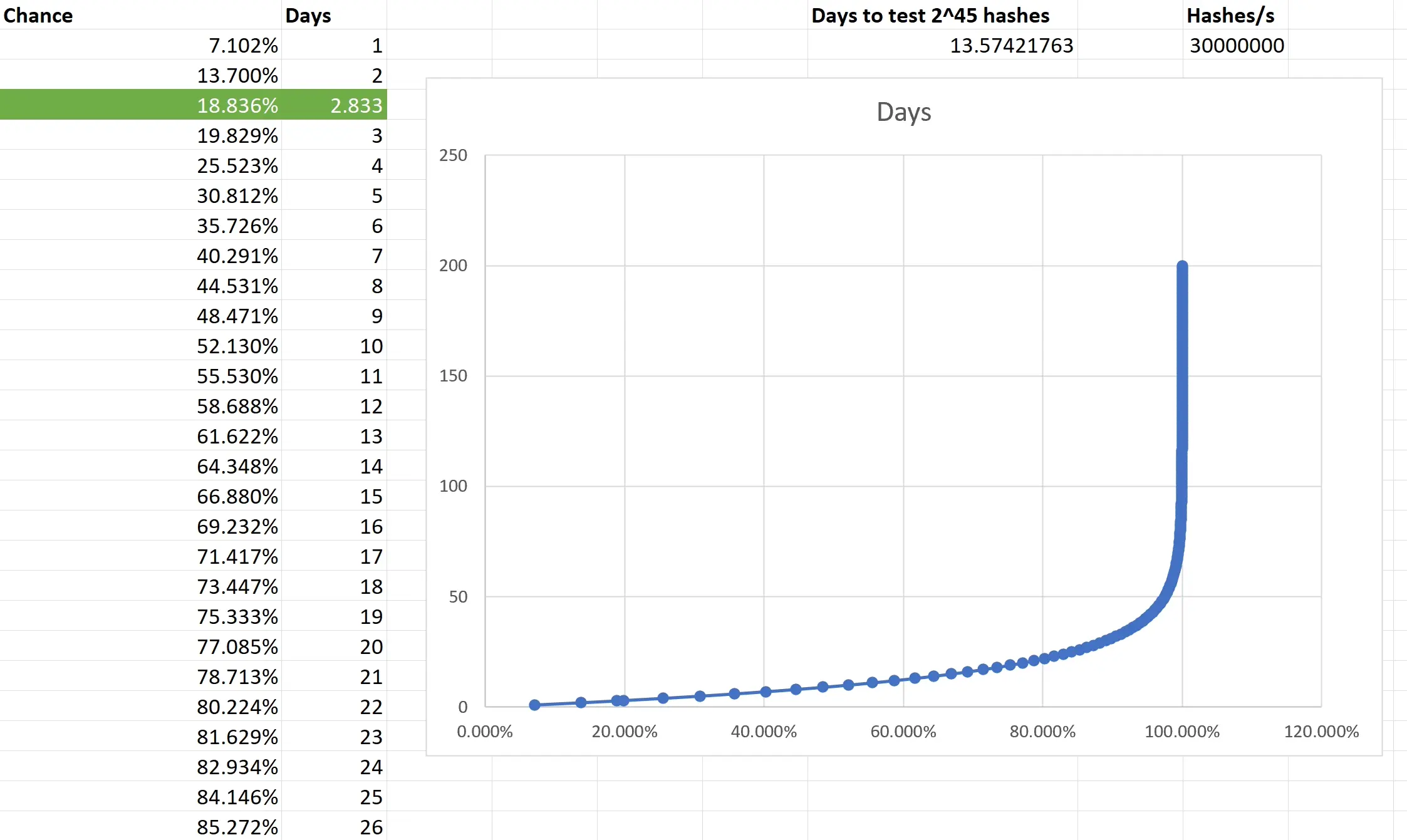 Based on the type of task that PoW mining is, the outcome is not predictible. You are only looking at what is the chance that the outcome of every single independent event will be consecutively non-favourable and then subtracting it from 1 to get the chance of that single favourable event you want. I really had to brush up on my combinatorics and discrete mathematics to make sure I have at least an elementary understanding of what is going on. Also, because we are not just throwing a dice 5 times, but are operating with big numbers, approximation was necessary. Luckily, the formula is available and quite simple in the end. 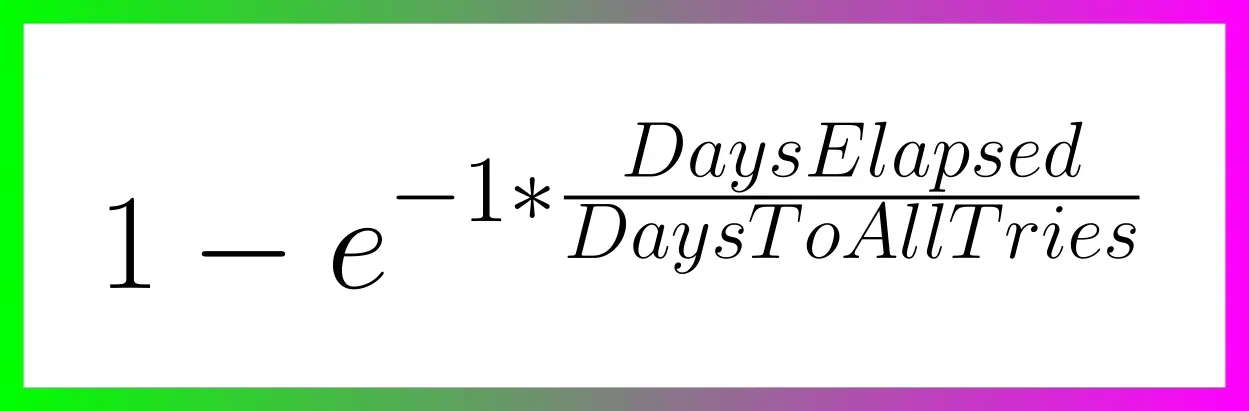 Two weeks to exhauste all the possible tries still doesn't guarantee anything, actually there is a slighlty less than 2 in 3 chance that you will have a result after all that time. So the fact that I was able to hit the right hash in less than 3 days was good luck. Not insane lottery winning luck, but good luck; slighlty lower than 1 in 5. ## Do you want to beat me? Go ahead! All the pitfalls are described above and until there is a GPU-based PoW Mining available, we are all on pretty even ground. ## Do you hate the note? In that case, feel free to enjoy this accompanying image: 
@ ec9bd746:df11a9d0
2025-03-07 20:13:38I was diving into PoW (Proof-of-Work) once again after nostr:nprofile1qy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uq3wamnwvaz7tmjv4kxz7fwdehhxarj9e3xzmny9uqzqj8a67jths8euy33v5yu6me6ngua5v3y3qq3dswuqh2pejmtls6datagmu rekindled my interest with his PoW Draw project. It was a fun little trifle, but it shifted my focus just the right way at the right time. Because then, on Friday, came the [Oval Office Travesty](nostr:nevent1qvzqqqqqqypzpmym6ar92346qc04ml08z6j0yrelylkv9r9ysurhte0g2003r2wsqy2hwumn8ghj7un9d3shjtnyv9kh2uewd9hj7qghwaehxw309aex2mrp0yhxummnw3ezucnpdejz7qpqqqqqqqrg6vz7m9z8ufagn4z3ks0meqw4nyh4gfxvksfhne99egzsd3g3w9). Once I got over the initial shock, I decided I couldn't just curse and lament; I needed to do something bigger, something symbolic, something expressive. So that's exactly what I did—breaking nostr:nprofile1qy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uq32amnwvaz7tmjv4kxz7fwv3sk6atn9e5k7tcqyqewrqnkx4zsaweutf739s0cu7et29zrntqs5elw70vlm8zudr3y2t9v7jg's record which he held for almost 2 and half years. Here is a note with PoW 45, the highest PoW known to Nostr (as of now). nostr:nevent1qvzqqqqqqypzpmym6ar92346qc04ml08z6j0yrelylkv9r9ysurhte0g2003r2wsqy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uqsuamnwvaz7tmwdaejumr0dshsqgqqqqqqqqqy8t8awr5c8z4yfp4cr8v7spp8psncv8twlh083flcr582fyu9 ## How Did I Pull It Off? In theory, quite simple: Create note, run PoW mining script & wait. Thanks to PoW Draw, I already had mining software at hand: nostr:nprofile1qy88wumn8ghj7mn0wvhxcmmv9uq32amnwvaz7tmjv4kxz7fwv3sk6atn9e5k7tcqyqvqc5tlvn6etv09f0fvuauves49dvgnukjtzsndfv9y8yyrqyxmz7dty6z's [*notemine_hw*](https://github.com/plebemineira/notemine_hw), but when you know that there is a 1 in 2^45 chance that the next hash will be the correct one you want to increase the odds a bit. So on Monday evening, I started my Note Mining operation on an old 40 thread machine called Workhorse. ### Issues Along the Way I was immediately surprised that Workhorse (2× Intel Xeon Silver 4114) produced only about 3Mh/s. A laptop (Intel Core i7-1185G7) with Windows and all the bloat did 5Mh/s. That was strange. Another hurdle was that *notemine_hw* does not refresh the `created_at` field. With just a few Mh/s of power I was potentially looking at weeks of computation, by then the note would be quite stale. So I created systemd service leveraging the `RuntimeMaxSec` option to periodically restart every 3600 seconds assuring that the Note would be max 1 hour old at the time of publishing. Luckily PoW is that kind of problem where every hash attempt is an independent event, so the chance of success is the same whether you do it in small increments or one uninterrupted stretch. So by restarting the mining process I was only losing a few mere seconds every hour due to the overhead. Once the note staleness issue was resolved, I looked at the 40 workers on Workhorse vs. 7 workers on the laptop and start messing around with running one instance with 40 workers and running 40 instances with 1 worker and found out, that the workers are not bound to a CPU thread and are jumping between the CPUs like rabbits high on Colombian carrots. The solution? Running multiple instances with one worker each as a service locked to its own CPU core using systemd's `CPUAffinity` option. ``` $aida@workhorse:systemd/system $ sudo cat notemine@.service [Unit] Description=Notemine HW Publish (restarts hourly) [Service] Type=simple CPUAffinity=%i # The command to run: ExecStart=/home/aida/.cargo/bin/notemine_hw publish --n-workers 1 --difficulty 45 --event-json /home/aida/note.json --relay-url 'wss://wot.shaving.kiwi' --nsec nsec0123456789abcdef # Let the process run for 1 hour (3600 seconds), then systemd will stop it: RuntimeMaxSec=3600 TimeoutStopSec=1 # Tells systemd to restart the service automatically after it stops: Restart=always RestartSec=1 # run as a non-root user: User=aida Group=aida [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target ``` Then I added a starting service to spawn an instance for each CPU thread. ``` $aida@workhorse:systemd/system $ sudo cat notemine_start.service [Unit] Description=Start all services in sequence with 3-second intervals [Service] Type=oneshot ExecStart=/usr/bin/zsh /home/aida/notemine_start.sh RemainAfterExit=yes [Install] WantedBy=multi-user.target ``` Here is the startup script (I know, loops exist—but Ctrl+C/Ctrl+V is so old-school): ``` aida@workhorse:~ $ cat notemine_start.sh /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@0.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@1.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@2.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@3.service /usr/bin/sleep 3 ... ... ... /usr/bin/systemctl start notemine@38.service ``` The sleep there is critical to make sure that the `created_at`timestamps are different, preventing redundant hashing. **This adjustment made Workhorse the strongest machine in my fleet with 10+Mh/s.** ## The Luck Aspect From Monday evening, I started adding all machines at my disposal into the fleet and by Wednesday evening I was crunching hashes on about 130 CPU threads (a lot of them were quite antique) and at the peak was just little shy of 40Mh/s. To compensate for the slow start with the few above-mentioned hiccups and the fact that I had to use my desktop to do other things from time to time, I counted with the conservative estimate of 30Mh/s when I was doing all the probability calculations.  Based on the type of task that PoW mining is, the outcome is not predictible. You are only looking at what is the chance that the outcome of every single independent event will be consecutively non-favourable and then subtracting it from 1 to get the chance of that single favourable event you want. I really had to brush up on my combinatorics and discrete mathematics to make sure I have at least an elementary understanding of what is going on. Also, because we are not just throwing a dice 5 times, but are operating with big numbers, approximation was necessary. Luckily, the formula is available and quite simple in the end. 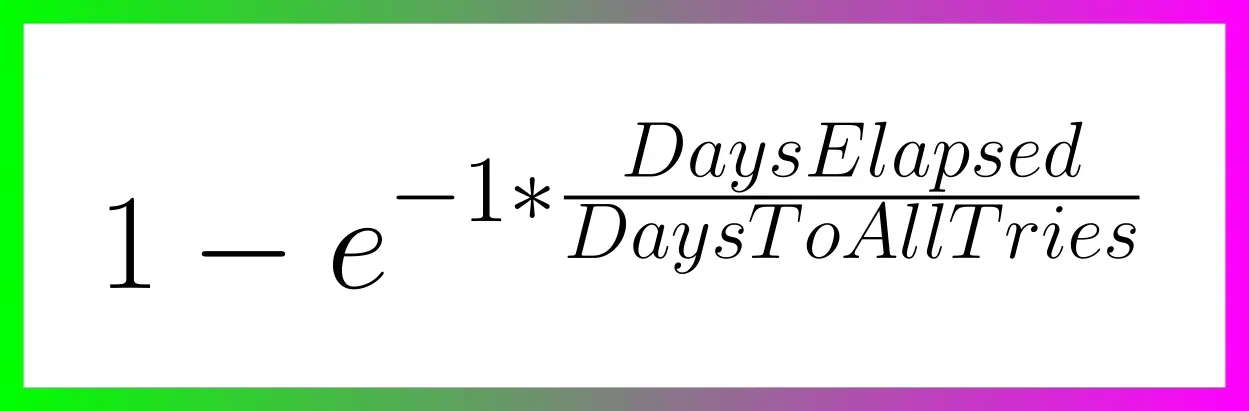 Two weeks to exhauste all the possible tries still doesn't guarantee anything, actually there is a slighlty less than 2 in 3 chance that you will have a result after all that time. So the fact that I was able to hit the right hash in less than 3 days was good luck. Not insane lottery winning luck, but good luck; slighlty lower than 1 in 5. ## Do you want to beat me? Go ahead! All the pitfalls are described above and until there is a GPU-based PoW Mining available, we are all on pretty even ground. ## Do you hate the note? In that case, feel free to enjoy this accompanying image:  -
 @ eac63075:b4988b48
2025-03-07 14:35:26Listen the Podcast: https://open.spotify.com/episode/7lJWc1zaqA9CNhB8coJXaL?si=4147bca317624d34 https://www.fountain.fm/episode/YEGnlBLZhvuj96GSpuk9 # **Abstract** This paper examines a hypothetical scenario in which the United States, under Trump’s leadership, withdraws from NATO and reduces its support for Europe, thereby enabling a Russian conquest of Ukraine and the subsequent expansion of Moscow’s influence over Eurasia, while the US consolidates its dominance over South America. Drawing on classical geopolitical theories—specifically those of Halford Mackinder, Alfred Thayer Mahan, Rudolf Kjellén, and Friedrich Ratzel—the study analyzes how these frameworks can elucidate the evolving power dynamics and territorial ambitions in a reconfigured global order. The discussion highlights Mackinder’s notion of the Eurasian Heartland and its strategic importance, Mahan’s emphasis on maritime power and control of strategic routes, Kjellén’s view of the state as an expanding organism, and Ratzel’s concept of Lebensraum as a justification for territorial expansion. The paper also explores contemporary developments, such as the US–Ukraine economic agreement and Trump’s overt territorial ambitions involving Greenland and Canada, in light of these theories. By juxtaposing traditional geopolitical concepts with current international relations, the study aims to shed light on the potential implications of such shifts for regional stability, global security, and the balance of power, particularly in relation to emerging neocolonial practices in Latin America. # **Introduction** In recent years, the geopolitical dynamics involving the United States, Russia, and Ukraine have sparked analyses from different theoretical perspectives. This paper examines recent events – presupposing a scenario in which Donald Trump withdraws the US from NATO and reduces its support for Europe, allowing a Russian conquest of Ukraine and the expansion of Moscow’s influence over Eurasia, while the US consolidates its dominance over South America – in light of classical geopolitical theories. The ideas of Halford Mackinder, Alfred Thayer Mahan, Rudolf Kjellén, and Friedrich Ratzel are used as reference points. The proposal is to impartially evaluate how each theory can elucidate the developments of this hypothetical scenario, relating Russian territorial expansion in Eurasia to the strategic retreat of the US to the Western Hemisphere. Initially, we will outline Mackinder’s conception of the Heartland (the central Eurasian territory) and the crucial role of Eastern Europe and Ukraine in the quest for global dominance. Next, we will discuss Mahan’s ideas regarding maritime power and the control of strategic routes, considering the impacts on the naval power balance among the US, Russia, and other maritime powers such as the United Kingdom and Japan. Subsequently, we will examine Kjellén’s organic theory of the state, interpreting the Russian expansionist strategy as a reflection of a state organism in search of vital space. In the same vein, Ratzel’s concept of “Lebensraum” will be explored, along with how Russia could justify territorial expansion based on resources and territory. Finally, the paper connects these theories to the current political context, analyzing the direct negotiations between Washington and Moscow (overlooking Ukraine and Europe), the US policy toward authoritarian regimes in Latin America, and the notion of a hemispheric division of power – the “Island of the Americas” under North American hegemony versus an Eurasia dominated by Russia. Lastly, it considers the possibility that such a geopolitical arrangement may foster the strengthening of authoritarian governments globally, rather than containing them, thus altering the paradigms of the liberal world order. # **The Heartland of Mackinder: Ukraine, Eurasia, and Global Dominance** Halford J. Mackinder, a British geographer and pioneer of geopolitics, proposed the celebrated Heartland Theory in the early twentieth century. Mackinder divided the world into geostrategic zones and identified the Heartland—the central continental mass of Eurasia—as the “geographical pivot of history” \[5\]. His most famous maxim encapsulates this vision: “who rules Eastern Europe commands the Heartland; who rules the Heartland commands the World Island; who rules the World Island commands the world” \[5\]. Eastern Europe and, in particular, the region of present-day Ukraine, play a key role in this formula. This is because, for Mackinder, Eastern Europe functions as a gateway to the Heartland, providing access to resources and a strategic position for the projection of continental power \[5\]. Applying this theory to our scenario, the conquest of Ukraine and Eastern European countries by Russia would have profound geopolitical implications. From a Mackinderian point of view, such a conquest would enormously strengthen Russia’s position in the Heartland by adding manpower (population) and Ukraine’s industrial and agricultural resources to its power base \[5\]. In fact, Mackinder argued that controlling the Heartland conferred formidable geostrategic advantages—a vast terrestrial “natural fortress” protected from naval invasions and rich in resources such as wheat, minerals, and fuels \[5\]. Thus, if Moscow were to incorporate Ukraine (renowned for its fertile soil and grain production, as well as its mineral reserves) and extend its influence over Eastern Europe, Russia would consolidate the Heartland under its direct control. In this context, the absence of the USA (withdrawn from NATO and less engaged in Europe) would remove an important obstacle to Russian predominance in the region. With central and eastern Eurasia under Russian influence, it would be possible to move toward the realization of the geopolitical nightmare described by Mackinder for Western maritime powers: a hegemonic continental power capable of projecting power to both Europe and Asia. Mackinder himself warned that if a Heartland power gained additional access to an oceanic coastline—in other words, if it combined land power with a significant maritime front—it would constitute a “danger” to global freedom \[5\]. In the scenario considered, besides advancing into Eastern Europe, Russia would already possess strategic maritime outlets (for example, in the Black Sea, via Crimea, and in the Baltic, via Kaliningrad or the Baltic States if influenced). Thus, the control of Ukraine would reinforce Russia’s position in the Black Sea and facilitate projection into the Eastern Mediterranean, expanding its oceanic front. From a Mackinderian perspective, this could potentially transform Russia into the dominant power of the “World Island” (the combined mass of Europe, Asia, and Africa), thereby unbalancing the global geopolitical order \[5\]. It is worth noting that, historically, Mackinder’s doctrine influenced containment strategies: both in the interwar period and during the Cold War, efforts were made to prevent a single power from controlling the Heartland and Eastern Europe. NATO, for example, can be seen as an instrument to prevent Soviet/Russian advances in Europe, in line with Mackinder’s imperative to “contain the Heartland.” Thus, if the USA were to abandon that role—by leaving NATO and tacitly accepting the Russian sphere of influence in Eurasia—we would be witnessing an inversion of the principles that have guided Western policy for decades. In short, under Mackinder’s theory, the Russian conquest of Ukraine and beyond would represent the key for Russia to command the Heartland and, potentially, challenge global hegemony, especially in a scenario where the USA self-restricts to the Western Hemisphere. # **The Maritime Power of Mahan and the Naval Balance between West and East** While Mackinder emphasized continental land power, Alfred Thayer Mahan, a nineteenth-century American naval strategist, highlighted the crucial role of maritime power in global dominance. In his work *The Influence of Sea Power upon History* (1890), Mahan studied the example of the British Empire and concluded that control of the seas paved the way for British supremacy as a world power \[10\]. He argued that a strong navy and the control of strategic maritime routes were decisive factors for projecting military, political, and economic power. His doctrine can be summarized in the following points: (1) the United States should aspire to be a world power; (2) control of the seas is necessary to achieve that status; (3) such control is obtained through a powerful fleet of warships \[17\]. In other words, for Mahan, whoever dominates the maritime routes and possesses naval superiority will be in a position to influence global destinies, ensuring trade, supplies, and the rapid movement of military forces. In the proposed scenario, in which the USA withdraws militarily from Europe and possibly from the Eurasian stage, Mahan’s ideas raise questions about the distribution of maritime power and its effects. Traditionally, the US Navy operates globally, ensuring freedom of navigation and deterring challenges in major seas (Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, etc.). A withdrawal of the USA from NATO could also signal a reduction in its naval presence in the Northeast Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea, and other areas close to Eurasia. In such a case, who would fill this naval vacuum? Russia, although primarily a land power, has been attempting to modernize its navy and has specific interests—for example, consolidating its dominance in the Black Sea and maintaining a presence in the Mediterranean (with a naval base in Tartus, Syria). The United Kingdom, a historic European maritime power, would remain aligned with the USA but, without American military support in Europe, might potentially be overwhelmed trying to contain an increasingly assertive Russian navy in European waters on its own. Japan, another significant maritime actor allied with the USA, is concerned with the naval balance in the Pacific; without full American engagement, Tokyo might be compelled to expand its own naval power to contain both Russia in the Far East (which maintains a fleet in the Pacific) and, especially, the growing Chinese navy. According to Mahan’s thinking, strategic maritime routes and choke points (crucial straits and channels) become contested prizes in this power game. With the USA focusing on the Americas, one could imagine Washington reinforcing control over the Panama Canal and Caribbean routes—reviving an “American Gulf” policy in the Western Atlantic and Eastern Pacific. In fact, indications of this orientation emerge in statements attributed to Trump, who once suggested reclaiming direct control over Panama, transforming Canada into a North American state, and even “annexing” Greenland due to its Arctic geopolitical importance \[18\]. These aspirations reflect a quest to secure advantageous maritime positions near the American continent. Conversely, in the absence of American presence in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean, Russia would have free rein for regional maritime projection. This could include anything from the unrestricted use of the Black Sea (after dominating Ukraine, thereby ensuring full access to Crimea and Ukrainian ports) to greater influence in the Eastern Mediterranean via Syria and partnerships with countries such as Iran or Egypt. The Baltic Sea would also become an area of expanded Russian interest, pressuring coastal countries and perhaps reducing NATO’s traditional local naval supremacy. However, it is worth noting that even with these regional expansions, Russia lacks a blue-water navy comparable to that of the USA; thus, its initial global maritime impact would be limited without alliances. An important aspect of Mahan’s theories is that naval power serves as a counterbalance to the land power of the Heartland. Therefore, even if Russia were to dominate the Eurasian continental mass, the continued presence of American naval might on the oceans could prevent complete global domination by Moscow. However, if the USA voluntarily restricts its naval reach to the Americas, it would forgo influencing the power balance in the seas adjacent to Eurasia. Consequently, the balance of maritime power would tend to shift in favor of regional Eurasian actors. The United Kingdom and Japan, traditional allies of the USA, could intensify their naval capabilities to defend regional interests—the United Kingdom safeguarding the North Atlantic and the North Sea, and Japan patrolling the Northwest Pacific—but both would face budgetary and structural limitations in fully compensating for the absence of the American superpower. Consequently, Mahan’s vision suggests that the withdrawal of the USA from the extra-regional scene would weaken the liberal maritime regime, possibly opening space for revisionist powers to contest routes that were previously secured (for example, Russia and China encountering less opposition on the routes of the Arctic and the Indo-Pacific, respectively). In summary, naval hegemony would fragment, and control of strategic seas would become contested, reconfiguring the relative influence of the USA, Russia, and maritime allies such as the United Kingdom and Japan. # **Kjellén and the State as a Living Organism: Russian Expansion as an Organic Necessity** Another useful theoretical lens to interpret Russian geopolitical posture is that of Rudolf Kjellén, a Swedish political scientist of the early twentieth century who conceived the State as a living organism. Kjellén, who even coined the term “geopolitics,” was influenced by Friedrich Ratzel’s ideas and by social Darwinism, arguing that States are born, grow, and decline analogously to living beings \[13\]. In his work *Staten som livsform* (The State as a Form of Life, 1916), he maintained that States possess an organic dimension in addition to the legal one and that “just as any form of life, States must expand or die” \[14\]. This expansion would not be motivated merely by aggressive conquest but seen as a necessary growth for the self-preservation of the state organism \[14\]. In complement, Kjellén echoed Ratzel’s “law of expanding spaces” by asserting that large States expand at the expense of smaller ones, with it being only a matter of time before the great realms fill the available spaces \[14\]. That is, from the organic perspective, vigorous States tend to incorporate smaller neighboring territories, consolidating territorially much like an organism absorbing nutrients. Applying this theory to the strategy of contemporary Russia, we can interpret Moscow’s actions—including the invasion of Ukraine and the ambition to restore its sphere of influence in Eurasia—as the expression of an organic drive for expansion. For a strategist influenced by this school, Russia (viewed as a state organism with a long imperial history) needs to expand its territory and influence to ensure its survival and security. The loss of control over spaces that once were part of the Russian Empire or the Soviet Union (such as Ukraine itself, the Caucasus, or Central Asia) may be perceived by Russian elites as an atrophy of the state organism, rendering it vulnerable. Thus, the reincorporation of these territories—whether directly (annexation) or indirectly (political vassalage)—would equate to restoring lost members or strengthening vital organs of the state body. In fact, official Russian arguments often portray Ukraine as an intrinsic part of “Russian historicity,” denying it a fully separate identity—a narrative that aligns with the idea that Russian expansion in that region is natural and necessary for the Russian State (seen as encompassing also Russian speakers beyond its current borders). Kjellén would thus provide a theoretical justification for Russian territorial expansion as an organic phenomenon. As a great power, Russia would inevitably seek to expand at the expense of smaller neighbors (Ukraine, Georgia, the Baltic States, etc.), as dictated by the tendency of “great spaces to organize” to the detriment of the small \[14\]. This view can be identified in contemporary Russian doctrines that value spheres of influence and the notion that neighboring countries must gravitate around Moscow in order for the natural order to be maintained. The very idea of “Eurasia” united under Russian leadership (advocated by modern Russian thinkers) echoes this organic conception of vital space and expansion as a sign of the State’s vitality. However, Kjellén’s theory also warns of the phenomenon of “imperial overstretch,” should a State exceed its internal cohesion limits by expanding excessively \[14\]. He recognized that extending borders too far could increase friction and vulnerabilities, making it difficult to maintain cohesion—a very large organism may lack functional integration. In the Russian context, this suggests that although expansion is seen as necessary, there are risks if Russia tries to encompass more than it can govern effectively. Conquering Ukraine and subjugating Eastern Europe, for example, could economically and militarily overburden the Russian State, especially if it faced resistance or had to manage hostile populations. However, in the hypothetical scenario we adopt (isolated USA and a weakened Europe), Russia might calculate that the organic benefits of expansion (territory, resources, strategic depth) would outweigh the costs, since external interference would be limited. Thus, through Kjellén’s lens, expansionist Russia behaves as an organism following its instinct for survival and growth, absorbing weaker neighbors; yet such a process is not devoid of challenges, requiring that the “organism Russia” manages to assimilate these new spaces without collapsing under its own weight. # **Ratzel and Lebensraum: Resources, Territory, and the Justification for Expansion** Parallel to Kjellén’s organic view, Friedrich Ratzel’s theory offers another conceptual basis for understanding Russian expansion: the concept of Lebensraum (vital space). Ratzel, a German geographer of the late nineteenth century, proposed that the survival and development of a people or nation depended critically on the available physical space and resources. Influenced by Darwinist ideas, he applied the notion of “survival of the fittest” to nations, arguing that human societies need to conquer territory and resources to prosper, and that the stronger and fittest civilizations will naturally prevail over the weaker ones \[12\]. In 1901, Ratzel coined the term Lebensraum to describe this need for “vital space” as a geographical factor in national power \[15\]. Subsequently, this idea would be adopted—and extremely distorted—by Nazi ideology to justify Germany’s aggressions in Europe. However, the core of Ratzel’s concept is that territorial expansion is essential for the survival and growth of a State, especially to secure food, raw materials, and space for its population \[12\]. When examining Russia’s stance under this perspective, we can see several narratives that evoke the logic of Lebensraum. Russia is the largest country in the world by area; however, much of its territory is characterized by adverse climates (tundra, taiga) and is relatively sparsely populated in Siberia. On the other hand, adjacent regions such as Ukraine possess highly arable lands (chernozem—black soil), significant Slavic population density, and additional natural resources (coal in the Donbass, for example). An implicit justification for Russian expansion could be the search for supplementary resources and fertile lands to secure its self-sufficiency and power—exactly as Ratzel described that vigorous nations do. Historical records show that Ratzel emphasized agrarian primacy: he believed that new territories should be colonized by farmers, providing the food base for the nation \[12\]. Ukraine, historically called the “breadbasket of Europe,” fits perfectly into this vision of conquest for sustenance and agricultural wealth. Furthermore, Ratzel viewed geography as a determinant of the destiny of nations—peoples adapted to certain habitats seek to expand them if they aspire to grow. In contemporary Russian discourse, there is often mention of the need to ensure security and territorial depth in the face of NATO, or to unite brotherly peoples (Russians and Russian speakers) within a single political space. Such arguments can be read as a modern translation of Lebensraum: the idea that the Russian nation, in order to be secure and flourish, must control a larger space, encompassing buffer zones and critical resources. This Russian “vital space” would naturally include Ukraine and other former Soviet republics, given the historical and infrastructural interdependence. Ratzel emphasized that peoples migrated and expanded when their original homeland no longer met their needs or aspirations \[12\]. Although contemporary Russia does not suffer from demographic pressure (on the contrary, it faces population decline), under the logic of a great power there is indeed a sentiment of geopolitical insufficiency for having lost influence over areas considered strategic. Thus, reconquering these areas would mean recovering the “habitat” necessary for the Russian nation to prosper and feel secure. It is important to mention that, in Ratzel’s and Kjellén’s formulations, the pursuit of Lebensraum or organic expansion is not morally qualified—it is treated as a natural process in the politics of power. Thus, on the discursive level, Russia can avoid overly aggressive rhetoric and resort to “natural” justifications: for example, claiming that it needs to occupy Ukraine for defensive purposes (security space) or to reunify peoples (a common cultural and historical space). Beneath these justifications, however, resonates the geopolitical imperative to acquire more territory and resources as a guarantee of national survival, something consonant with Ratzel’s theory. In fact, Russian Realpolitik frequently prioritizes the control of energy resources (gas, oil) and transportation routes. Expanding its influence over central Eurasia would also mean controlling oil pipelines, gas lines, and logistical corridors—essential elements of modern Lebensraum understood as access to vital resources and infrastructure. In summary, by conquering Ukraine and extending its reach into Eurasia, Russia could effectively invoke the concept of Lebensraum: presenting its expansion not as mere imperialism, but as a necessity to secure indispensable lands and resources for its people and to correct the “injustice” of a vital space diminished by post-Cold War territorial losses. The theories of Ratzel and Kjellén together paint a picture in which Russian expansion emerges almost as a natural law—the great State reclaiming space to ensure its survival and development at the expense of smaller neighbors. # **Trump, NATO, and the Threat of American Withdrawal** One of the most alarming changes with Trump's return to power is the tense relationship with the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Trump has long criticized allies for not meeting military spending targets, even threatening during his first term to withdraw the US from the alliance if members did not increase their contributions \[2\]. This threat, initially viewed with skepticism, became concrete after his re-election, leading European allies to seriously consider the possibility of having to defend themselves without American support \[1\]. In fact, Trump suggested in post-election interviews that the US would only remain in NATO if the allies “paid their bills” – otherwise, he “would seriously consider” leaving \[2\]. Such statements reinforced the warning that the US might not honor NATO's mutual defense commitment, precisely at a time of continuous Russian threat due to the war in Ukraine \[1\]. From a theoretical point of view, this posture of American retrenchment evokes the classic tension between maritime power and land power. Alfred Thayer Mahan emphasized that the global power of the US derived largely from its naval superiority and from alliances that ensured control over strategic maritime routes \[9\]. NATO, since 1949, has served not only to deter Soviet terrestrial advances in Eurasia, but also to secure the US naval presence in the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean – a fundamental element according to Mahan. In turn, Halford Mackinder warned that the balance of global power depended on the control of the Eurasian “Heartland” (the central region of Eurasia). The withdrawal or disengagement of the US (a maritime power) from this region could open the way for a continental power (such as Russia) to expand its influence in Eastern Europe, unbalancing the power balance \[3\]. In other words, by threatening to leave NATO, Trump jeopardizes the principle of containment that prevented Russian dominance over Eastern Europe – something that Mackinder would see as a dangerous shift in global power in favor of the Heartland power. Adopting an impartial tone, it is observed that European countries have reacted to this new reality with precautionary measures. Strategic reports already calculate the cost of an autonomous European defense: hundreds of thousands of additional soldiers and investments of hundreds of billions of euros would be required if the US ceased to guarantee the security of the continent \[1\]. European dependence on American military power is significant and, without it, there would be a need for a major reinforcement of European Armed Forces \[1\]. This mobilization practically reflects the anticipation of a power vacuum left by the US – a scenario in which Mackinder’s theory (on the primacy of the Heartland and the vulnerability of the “external crescent” where Western Europe is located) regains its relevance. # **The US–Ukraine Economic Agreement: Strategic Minerals in Exchange for Support?** Another novelty of Trump's second term is the unprecedented and transactional manner in which Washington has been dealing with the war in Ukraine. Instead of emphasizing security guarantees and alliances, the Trump administration proposed a trade agreement with Ukraine focused on the exploitation of strategic minerals, linking American support to a direct economic benefit. According to sources close to the negotiations, the US and Ukraine are about to sign a pact to share the revenues from the exploitation of critical mineral resources on Ukrainian territory \[19\]. Materials such as titanium, lithium, rare earths, and uranium – vital for high-tech and defense industries – would be at the core of this agreement \[6\]. According to the known draft, Ukraine would allocate 50% of the profits from new mineral ventures to a fund controlled by the US, which would reinvest part of the resources in the country’s own reconstruction \[6\] \[19\]. It is noteworthy that the pact does not include explicit security guarantees for Kyiv, despite Ukraine remaining under direct military threat from Russia \[19\]. Essentially, the Trump administration offers financial support and economic investment in exchange for a share in Ukrainian natural resources, but without formally committing to Ukraine's defense in the event of a renewed Russian offensive \[19\]. American authorities argue that this economic partnership would already be sufficient to “secure Ukrainian interests,” as it would provide the US with its own incentives to desire Ukraine’s stability \[19\]. “What could be better for Ukraine than being in an economic partnership with the United States?” stated Mike Waltz, a US national security advisor, defending the proposal \[19\]. Analysts, however, assess the agreement in divided terms. For some, it represents a form of economic exploitation at a time of Ukraine's fragility – comparing the demand to share mineral wealth amid war to a scheme of “mafia protection” \[19\]. Steven Cook, from the Council on Foreign Relations, classified the offer as “extortion,” and political scientist Virginia P. Fortna observed that charging resources from an invaded country resembles predatory practices \[19\]. Joseph Nye adds that it is a short-term gain strategy that could be “disastrous in the long run” for American credibility, reflecting the transactional approach that Trump even adopted with close allies in other contexts \[19\]. On the other hand, some see a future advantage for Kyiv: journalist Pierre Briançon suggests that at least this agreement aligns American commercial interests with Ukraine’s future, which could, in theory, keep the US involved in Ukrainian prosperity in the long term \[19\]. It is even recalled that President Zelensky himself proposed last year the idea of sharing natural resources with the US to bring the interests of the two countries closer together \[19\]. From the perspective of geopolitical theories, this agreement illustrates a shift towards economic pragmatism in international relations, approaching concepts proposed by Kjellén. Rudolf Kjellén, who coined the term “geopolitics,” saw the State as a territorial organism that seeks to ensure its survival through self-sufficiency and the control of strategic resources \[4\]. Trump's demand for a share in Ukrainian resources in order to continue supporting the country reflects a logic of autarky and direct national interest – that is, foreign policy serving primarily to reinforce the economic and material position of the US. This view contrasts with the traditional cooperative approach, but aligns with Kjellén’s idea that powerful States tend to transform international relations into opportunities for their own gain, ensuring access to vital raw materials. Similarly, Friedrich Ratzel argued that States have a “propensity to expand their borders according to their capacities,” seeking vital space (Lebensraum) and resources to sustain their development \[11\]. The US–Ukraine pact, by conditioning military/economic aid on obtaining tangible advantages (half of the mineral profits), is reminiscent of Ratzel’s perspective: the US, as a rising economic power, expands its economic influence over Ukrainian territory like an organism extending itself to obtain the necessary resources for its well-being. It is, therefore, a form of economic expansionism at the expense of purely ideological commitments or collective security. # **Peace Negotiations Excluding Ukraine and the Legitimacy of the Agreement** Another controversial point is the manner in which peace negotiations between Russia and the West have been conducted under Trump's administration. Since taking office, the American president has engaged directly with Moscow in pursuit of a ceasefire, deliberately keeping the Ukrainian government out of the initial discussions \[6\]. Trump expressed his desire to “leave Zelensky out of the conversation” and also excluded the European Union from any influence in the process \[6\]. This negotiation strategy—conducted without the presence of the primary interested party, Ukraine—raises serious questions about the legitimacy and sustainability of any resulting agreement. Historically, peace agreements reached without the direct participation of one of the conflicting parties tend to face problems in implementation and acceptance. The exclusion of Ukraine in the decision-making phase brings to light the issue of guarantees. As noted, the emerging agreement lacks formal US security guarantees for Ukraine. This implies that, after the agreement is signed, nothing will prevent Russia from launching a new offensive if it deems it convenient, knowing that the US has not committed to defending it militarily. Experts have already warned that a ceasefire without robust protection may only be a pause for Russian rearmament, rendering the conflict “frozen” temporarily and potentially resumed in the near future. The European strategic community has expressed similar concern: without American deterrence, the risk of further Russian aggressions in the region increases considerably \[1\]. Denmark, for example, has released intelligence reports warning of possible imminent Russian attacks, prompting neighboring countries to accelerate plans for independent defense \[1\]. The legitimacy of this asymmetric peace agreement (negotiated without Ukraine fully at the table and under economic coercion) is also questionable from a legal and moral point of view. It violates the principle of self-determination by imposing terms decided by great powers on a sovereign country—a practice reminiscent of dark chapters in diplomacy, such as the Munich Agreement of 1938, when powers determined the fate of Czechoslovakia without its consent. In the current case, Ukraine would end up signing the agreement, but from a position of weakness, raising doubts about how durable such a commitment would be. From Mackinder’s perspective, Ukraine’s removal from the battlefield without guarantees essentially means admitting a greater influence of Russia (the Heartland power) over Eastern Europe. This would alter the balance in Eurasia in a potentially lasting way. Furthermore, the fact that great powers negotiate over the heads of a smaller country evokes the imperial logic of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when empires decided among themselves the divisions of foreign territories—a behavior that Mackinder saw as likely in a world of a “closed system.” With the entire world already occupied by States, Mackinder predicted that powers would begin to compete for influence within this consolidated board, often subjugating smaller states to gain advantage \[3\]. The US–Russia negotiation regarding Ukraine, without proper Ukrainian representation, exemplifies this type of neo-imperial dynamic in the twenty-first century. Also noteworthy is the consonance with the ideas of Ratzel and Kjellén: both viewed smaller states as easily relegated to the status of satellites or even “parasitic organisms” in the orbit of larger states. Kjellén spoke of the intrinsic vulnerability of states with little territorial depth or economic dependence, making them susceptible to external pressures \[4\]\[20\]. Ukraine, weakened by war and dependent on external aid, becomes a concrete example of this theorized vulnerability: it has had to cede strategic resources and accept terms dictated against its will in an attempt to secure its immediate survival. The resulting agreement, therefore, reflects a power imbalance characteristic of the hierarchical international relations described by classical geopolitical theorists. # **Implicit Territorial Concessions and Trump’s Public Discourse** A central and controversial point in Trump’s statements regarding the war in Ukraine is the insinuation of territorial concessions to Russia as part of the conflict’s resolution. Publicly, Trump avoided explicitly condemning Russian aggression and even stated that he considered it “unlikely” that Ukraine would be able to retake all the areas occupied by the Russians \[16\]. In debates and interviews, he suggested that “if I were president, the war would end in 24 hours,” implying that he would force an understanding between Kyiv and Moscow that would likely involve ceding some territory in exchange for peace. This position marks a break with the previous US policy of not recognizing any territorial acquisitions made by force and fuels speculations that a future peace agreement sponsored by Trump would legitimize at least part of Russia’s gains since 2014 (Crimea, Donbass, and areas seized during the 2022 invasion). The actions of his administration corroborate this interpretation. As discussed, the economic agreement focuses on the exploitation of Ukrainian natural resources, many of which are located precisely in regions currently under Russian military control, such as parts of the Zaporizhzhia Oblast, Donetsk, Lugansk, and the Azov Sea area \[6\]. A Ukrainian geologist, Hanna Liventseva, highlighted that “most of these elements (strategic minerals) are found in the south of the Ukrainian Shield, mainly in the Azov region, and most of these territories are currently invaded by Russia” \[6\]. This means that, to make joint exploitation viable, Russia’s de facto control over these areas would have to be recognized—or at least tolerated—in the short term. In other words, the pact indirectly and tacitly accepts Russian territorial gains, as it involves sharing the profits from resources that are not currently accessible to the Kyiv government. Furthermore, figures close to Trump have made explicit statements regarding the possibility of territorial cession. Mike Waltz, Trump’s national security advisor, publicly stated that Zelensky might need to “cede land to Russia” to end the war \[8\]. This remark—made public in March 2025—confirms that the Trump White House considers it natural for Ukraine to relinquish parts of its territory in favor of an agreement. Such a stance marks a break from the previous Western consensus, which condemned any territorial gains by force. Under Trump, a pragmatic view (in the eyes of his supporters) or a cynical one (according to his critics) seems to prevail: sacrificing principles of territorial integrity to quickly end hostilities and secure immediate economic benefits. In theoretical terms, this inclination to validate territorial gains by force recalls the concept of Realpolitik and the geopolitical Darwinism that influenced thinkers such as Ratzel. In Ratzel’s organic conception, expanding states naturally absorb neighboring territories when they are strong enough to do so, while declining states lose territory—a process almost biological in the selection of the fittest \[11\]. The Trump administration’s acceptance that Ukraine should “give something” to Moscow to seal peace reflects a normalization of this geopolitical selection process: it recognizes the aggressor (Russia) as having the “right” to retain conquered lands, because that is how power realities on the ground dictate. Mackinder, although firmly opposed to allowing Russia to dominate the Heartland, would see this outcome as the logical consequence of the lack of engagement from maritime powers (the USA and the United Kingdom, for example) in sustaining the Ukrainian counterattack. Without the active involvement of maritime power to balance the dispute, land power prevails in Eastern Europe. From the perspective of international legitimacy, the cession of Ukrainian territories—whether de jure or de facto—creates a dangerous precedent in the post-Cold War era. Rewarding violent aggression with territorial gains may encourage similar strategies in other parts of the world, undermining the architecture of collective security. This is possibly a return to a world of spheres of influence, where great powers define borders and zones of control according to their convenience—something that the rules-based order after 1945 sought to avoid. Here, academic impartiality requires noting that coercion for territorial concessions rarely produces lasting peace, as the aggrieved party—in this case, Ukraine—may accept temporarily but will continue to assert its rights in the long term, as has occurred with other territorial injustices in history. # **Territorial Ambitions of Trump: Greenland and Canada** Beyond the Eurasian theater of war, Trump revived geopolitical ambitions involving territories traditionally allied with the US: Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark) and Canada. As early as 2019, during his first term, Trump shocked the world by proposing to buy Greenland—rich in minerals and strategically positioned in the Arctic. Upon his return to power, he went further: expressing a “renewed interest” in acquiring Greenland and publicly suggesting the incorporation of Canada as the 51st American state \[2\]. In January 2025, during a press conference at Mar-a-Lago, he even displayed maps in which the US and Canada appeared merged into a single country, while Greenland was marked as a future American possession \[2\]. Posts by the president on social media included satirical images with a map of North America where Canada was labeled “51st” and Greenland designated as “Our Land” \[2\]. Such moves were met with concern and disbelief by allies. Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau was caught on an open microphone warning that Trump’s fixation on annexation “is real” and not just a joke \[7\]. Trudeau emphasized that Washington appeared to covet Canada’s vast mineral resources, which would explain the insistence on the idea of absorption \[7\]. In public, Trump argued that Canadians “would be more prosperous as American citizens,” promising tax cuts and better services should they become part of the US \[7\]. On the Danish side, the reaction to the revived plan regarding Greenland was firmly negative—as it was in 2019—reaffirming that the territory is not for sale. Trump, however, insinuated that the issue might be one of national security, indicating that American possession of Greenland would prevent adverse influences (a reference to China and Russia in the Arctic) \[2\]. More worryingly, he refused to rule out the use of military means to obtain the island, although he assured that he had no intention of invading Canada by force (in the Canadian case, he spoke of “economic force” to forge a union) \[2\]. This series of initiatives reflects an unprecedented expansionist impetus by the US in recent times, at least in discourse. Analyzing this through the lens of classical geopolitics offers interesting insights. Friedrich Ratzel and his notion of Lebensraum suggest that powerful states, upon reaching a certain predominance, seek to expand their territory by influencing or incorporating adjacent areas. Trump, by targeting the immediate neighbor (Canada) and a nearby strategic territory (Greenland), appears to resurrect this logic of territorial expansion for the sake of gaining space and resources. Ratzel saw such expansion almost as a natural process for vigorous states, comparable to the growth of an organism \[11\]. From this perspective, the US would be exercising its “right” of expansion in North America and the polar region, integrating areas of vital interest. Additionally, Alfred Mahan’s view on maritime power helps to understand the strategic value of Greenland. Mahan postulated that control of key maritime chokepoints and naval bases ensures global advantage \[9\]. Greenland, situated between the North Atlantic and the Arctic, has become increasingly relevant as climate change opens new polar maritime routes and reveals vast mineral deposits (including rare earth elements and oil). For the US, having a presence or sovereignty over Greenland would mean dominating the gateway to the Arctic and denying this space to rivals. This aligns with Mahan’s strategy of securing commercial and military routes (in this case, potential Arctic routes) and resources to consolidate naval supremacy. On the other hand, the incorporation of Canada—with its enormous territory, Arctic coastline, and abundant natural resources—would provide the US with formidable geoeconomic and geopolitical reinforcement, practically eliminating vulnerabilities along its northern border. This is an ambitious project that also echoes ideas of Kjellén, for whom an ideal State should seek territorial completeness and economic self-sufficiency within its region. Incorporating Canada would be the pinnacle of American regional autarky, turning North America into a unified bloc under Washington (a scenario reminiscent of the “pan-regions” conceived by twentieth-century geopoliticians influenced by Kjellén). It is important to note, however, that these ambitions face enormous legal and political obstacles. The sovereignty of Canada and Greenland (Denmark) is guaranteed by international law, and both peoples categorically reject the idea of annexation. Any hostile action by the US against these countries would shake alliances and the world order itself. Even so, the very fact that an American president suggests such possibilities already produces geopolitical effects: traditional partners begin to distrust Washington’s intentions, seek alternative alliances, and strengthen nationalist discourses of resistance. In summary, Trump’s expansionist intentions in Greenland and Canada rekindle old territorial issues and paradoxically place the US in the position of a revisionist power—a role once associated with empires in search of colonies. # **Implications for Brazil and South America: A New Neocolonization?** In light of this geopolitical reconfiguration driven by Trump's USA—with a reordering of alliances and a possible partition of spheres of influence among great powers—the question arises: what is the impact on Brazil and the other countries of South America? Traditionally, Latin America has been under the aegis of the Monroe Doctrine (1823), which established non-interference by Europe in the region and, implicitly, the primacy of the USA in the Western Hemisphere. In the post–Cold War period, this influence translated more into political and economic leadership, without formal annexations or direct territorial domination. However, the current context points to a kind of “neocolonization” of the Global South, in which larger powers seek to control resources and peripheral governments in an indirect yet effective manner. Mackinder’s theories can be used to illuminate this dynamic. As mentioned, Mackinder envisioned the twentieth-century world as a closed system, in which there were no longer any unknown lands to be colonized—hence, the powers would fight among themselves for control over already occupied regions \[3\]. He predicted that Africa and Latin America (then largely European colonies or semi-colonies) would continue as boards upon which the great powers would project their disputes, a form of neocolonialism. In the current scenario, we see the USA proposing exchanges of protection for resources (as in Ukraine) and even leaders of developing countries seeking similar agreements. A notable example: the President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Felix Tshisekedi, praised the USA–Ukraine initiative and suggested an analogous agreement involving Congolese mineral wealth in exchange for US support against internal rebels (M23) \[19\]. In other words, African countries and possibly South American ones may enter into this logic of offering privileged access to resources (cobalt, lithium, food, biodiversity) in order to obtain security guarantees or investments. This represents a regression to the times when external powers dictated the directions of the South in exchange for promises of protection, characterizing a strategic neocolonialism. For Brazil, in particular, this rearrangement generates both opportunities and risks. As a regional power with considerable diplomatic autonomy, Brazil has historically sought to balance relationships with the USA, Europe, China, and other actors, avoiding automatic alignments. However, in a world where Trump’s USA is actively redefining spheres of influence—possibly making deals with Russia that divide priorities (for example, Washington focusing on the Western Hemisphere and Moscow on the Eastern)—South America could once again be seen as an exclusive American sphere of influence. From this perspective, Washington could pressure South American countries to align with its directives, limiting partnerships with rivals (such as China) and seeking privileged access to strategic resources (such as the Amazon, fresh water, minerals, and agricultural commodities). Some indications are already emerging: Trump’s transactional approach mentioned by Nye included pressures on Canada and Mexico regarding border and trade issues, under the threat of commercial sanctions. It would not be unthinkable to adopt a hard line, for example, with regard to Brazilian environmental policies (linked to the Amazon) or Brazil’s relations with China, using tariffs or incentives as leverage—a sort of geopolitics of economic coercion. On the other hand, Brazil and its neighbors could also attempt to take advantage of the Sino–North American competition. If the USA is distracted consolidating its hemispheric “hard power” hegemony (even with annexation fantasies in the north), powers such as China may advance their economic presence in South America through investments and trade (Belt and Road, infrastructure financing)—which is already happening. This would constitute an indirect neocolonial dispute in the South: Chinese loans and investments versus American demands and agreements, partly reminiscent of the nineteenth-century imperial competition (when the United Kingdom, USA, and others competed for Latin American markets and resources). From a conceptual standpoint, Mackinder might classify South America as part of the “Outer Crescent” (external insular crescent)—peripheral to the great Eurasian “World-Island,” yet still crucial as a source of resources and a strategic position in the South Atlantic and Pacific. If the USA consolidates an informal empire in the Americas, it would be reinforcing its “insular bastion” far from the Eurasian Heartland, a strategy that Mackinder once suggested for maritime powers: to control islands and peripheral continents to compensate for the disadvantage of not controlling the Heartland. However, an excessive US dominance in the South could lead to local resistance and alternative alignments, unbalancing the region. Kjellén would add that for Brazil to maintain its decisive sovereignty, it will need to strengthen its autarky and internal cohesion—in other words, reduce vulnerabilities (economic, military, social) that external powers might exploit \[4\]. Meanwhile, Mahan might point out the importance for Brazil of controlling its maritime routes and coastlines (South Atlantic) to avoid being at the mercy of a naval power like the USA. And Ratzel would remind us that states that do not expand their influence tend to be absorbed by foreign influences—which, in the context of Brazil, does not mean conquering neighboring territories, but rather actively leading South American integration to create a block more resilient to external intrusion. In summary, South America finds itself in a more competitive and segmented world, where major players are resurrecting practices from past eras. The notion of “neocolonization” here does not imply direct occupation, but rather mechanisms of dependency: whether through unequal economic agreements or through diplomatic or military pressure for alignment. Brazil, as the largest economy and territory on the subcontinent, will have to navigate with heightened caution. A new global power balance, marked by the division of spheres of influence among the USA, China, and Russia, may reduce the sovereign maneuvering space of South American countries unless they act jointly. Thus, theoretical reflection suggests the need for South–South strategies, reinforcement of regional organizations, and diversification of partnerships to avoid falling into modern “neocolonial traps.” # **Conclusion** The emerging post–re-election geopolitical conjuncture of Donald Trump signals a return to classical geopolitical principles, after several decades of predominance of institutional liberal views. We witness the revaluation of concepts such as spheres of influence, exchanges of protection for resources, naval power versus land power, and disputes over territory and raw materials—all central themes in the writings of Mackinder, Mahan, Kjellén, and Ratzel at the end of the nineteenth and the beginning of the twentieth century. An impartial analysis of these events, in light of these theories, shows internal coherence in Trump’s actions: although controversial, they follow a logic of maximizing national interest and the relative power of the USA on the world stage, even at the expense of established principles and alliances. Halford Mackinder reminds us that, in a closed world with no new lands to conquer, the great powers will seek to redistribute the world among themselves \[3\]. This seems to manifest in the direct understandings between the USA and Russia over the fate of Ukraine, and in American ambitions in the Arctic and the Western Hemisphere. Alfred Mahan emphasizes that the control of the seas and strategic positions ensures supremacy—we see reflections of this in Trump’s obsession with Greenland (Arctic) and the possible neglect of the importance of maintaining NATO (and therefore the North Atlantic) as a cohesive bloc, something that Mahan’s theory would criticize due to the risk of a naval vacuum. Rudolf Kjellén and Friedrich Ratzel provide the framework to understand the more aggressive facet of expansionist nationalism: the idea of the State as an organism that needs to grow, secure resources, and seek self-sufficiency explains everything from the extortionate agreement imposed on Ukraine to the annexation rhetoric regarding Canada. The potential consequences are profound. In the short term, we may witness a precarious ceasefire in the Ukraine war, with consolidated Russian territorial gains and Ukraine economically tied to the USA, but without formal military protection—a fragile “armed peace.” Western Europe, alarmed, may accelerate its independent militarization, perhaps marking the beginning of European defense autonomy, as is already openly debated \[1\]. At the far end of the globe, American activism in the Arctic and the Americas may reshape alliances: countries like Canada, once aligned with Washington, might seek to guarantee their sovereignty by distancing themselves from it; powers like China could take advantage of the openings to increase their presence in Latin America and Africa through economic diplomacy; and emerging countries of the Global South may have to choose between submitting to new “guardianships” or strengthening South–South cooperation. Ultimately, the current situation reinforces the relevance of studying geopolitics through historical lenses. The actions of the Trump administration indicate that, despite all technological and normative advances, the competition for geographic power has not disappeared—it has merely assumed new formats. Academic impartiality obliges us not to prematurely judge whether these strategies will be successful or beneficial, but history and theory warn that neo-imperial movements tend to generate counter-reactions. As Mackinder insinuated, “every shock or change anywhere reverberates around the world,” and a sudden move by a superpower tends to provoke unforeseen adjustments and chain conflicts. It remains to be seen how the other actors—including Brazil and its neighbors—will adapt to this new chapter in the great struggle for global power, in which centuries-old theories once again have a surprising explanatory power over present events. # **Bibliography** **\[1\] A Referência.** (2025). *Europa calcula o custo de se defender sem os EUA: 300 mil soldados e 250 bilhões de euros a mais*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://areferencia.com/europa/europa-calcula-o-custo-de-se-defender-sem-os-eua-300-mil-soldados-e-250-bilhoes-de-euros-a-mais/#:\~:text=Europa%20calcula%20o%20custo%20de,bilh%C3%B5es%20de%20euros%20a%20mais](https://areferencia.com/europa/europa-calcula-o-custo-de-se-defender-sem-os-eua-300-mil-soldados-e-250-bilhoes-de-euros-a-mais/#:~:text=Europa%20calcula%20o%20custo%20de,bilh%C3%B5es%20de%20euros%20a%20mais) **\[2\] Brexit Institute.** (2025). *What happens if Trump invades Greenland?* Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://dcubrexitinstitute.eu/2025/01/what-happens-if-trump-invades-greenland/#:\~:text=Ever%20since%20Donald%20Trump%20announced,agreed%20in%20Wales%20in%202014](https://dcubrexitinstitute.eu/2025/01/what-happens-if-trump-invades-greenland/#:~:text=Ever%20since%20Donald%20Trump%20announced,agreed%20in%20Wales%20in%202014) **\[3\] Cfettweis C:CST22(2)8576.DVI.** (2025). *Mackinder and Angell*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://cfettweis.com/wp-content/uploads/Mackinder-and-Angell.pdf#:\~:text=meant%20the%20beginning%20of%20an,Mackinder](https://cfettweis.com/wp-content/uploads/Mackinder-and-Angell.pdf#:~:text=meant%20the%20beginning%20of%20an,Mackinder) **\[4\] Diva-Portal.** (2025). *The geopolitics of territorial relativity. Poland seen by Rudolf Kjellén*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1696547/FULLTEXT02#:\~:text=,The%20state%20territory](https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1696547/FULLTEXT02#:~:text=,The%20state%20territory) **\[5\] Geopolitical Monitor.** (2025). *The Russo-Ukrainian War and Mackinder’s Heartland Thesis*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/the-ukraine-war-and-mackinders-heartland-thesis/#:\~:text=In%201904%2C%20Sir%20Halford%20J,in%20adding%20a%20substantial%20oceanic](https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/the-ukraine-war-and-mackinders-heartland-thesis/#:~:text=In%201904%2C%20Sir%20Halford%20J,in%20adding%20a%20substantial%20oceanic) **\[6\] Instituto Humanitas Unisinos.** (2025). *Trump obriga Zelensky a hipotecar a exploração de minerais críticos em troca do seu apoio*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.ihu.unisinos.br/648986-trump-obriga-zelensky-a-hipotecar-a-exploracao-de-minerais-criticos-em-troca-do-seu-apoio#:\~:text=Essa%20troca%20inclui%20os%20cobi%C3%A7ados,s%C3%A3o%20praticamente%20inexploradas%20no%20pa%C3%ADs](https://www.ihu.unisinos.br/648986-trump-obriga-zelensky-a-hipotecar-a-exploracao-de-minerais-criticos-em-troca-do-seu-apoio#:~:text=Essa%20troca%20inclui%20os%20cobi%C3%A7ados,s%C3%A3o%20praticamente%20inexploradas%20no%20pa%C3%ADs) **\[7\] Politico.** (2025). *Trump’s annexation fixation is no joke, Trudeau warns*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.politico.com/news/2025/02/07/canada-trudeau-trump-51-state-00203156#:\~:text=TORONTO%20%E2%80%94%20Prime%20Minister%20Justin,Canada%20becoming%20the%2051st%20state%2C%E2%80%9D%20Trudeau%20said](https://www.politico.com/news/2025/02/07/canada-trudeau-trump-51-state-00203156#:~:text=TORONTO%20%E2%80%94%20Prime%20Minister%20Justin,Canada%20becoming%20the%2051st%20state%2C%E2%80%9D%20Trudeau%20said) **\[8\] The Daily Beast.** (2025). *Top Trump Adviser Moves Goalpost for Ukraine to End War*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.thedailybeast.com/top-trump-adviser-moves-goalpost-for-ukraine-to-end-war/#:\~:text=LAND%20GRAB](https://www.thedailybeast.com/top-trump-adviser-moves-goalpost-for-ukraine-to-end-war/#:~:text=LAND%20GRAB) **\[9\] The Geostrata.** (2025). *Alfred Thayer Mahan and Supremacy of Naval Power*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.thegeostrata.com/post/alfred-thayer-mahan-and-supremacy-of-naval-power#:\~:text=Alfred%20Thayer%20Mahan%20and%20Supremacy,control%20over%20maritime%20trade%20routes](https://www.thegeostrata.com/post/alfred-thayer-mahan-and-supremacy-of-naval-power#:~:text=Alfred%20Thayer%20Mahan%20and%20Supremacy,control%20over%20maritime%20trade%20routes) **\[10\] U.S. Department of State.** (2025). [Mahan’s The Influence of Sea Power upon History: Securing International Markets in the 1890s](https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/mahan). Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/mahan#:\~:text=Mahan%20argued%20that%20British%20control,American%20politicians%20believed%20that%20these](https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/mahan#:~:text=Mahan%20argued%20that%20British%20control,American%20politicians%20believed%20that%20these) **\[11\] Britannica.** (2025a). *Friedrich Ratzel | Biogeography, Anthropogeography, Political Geography*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.britannica.com/biography/Friedrich-Ratzel#:\~:text=webster,Swedish%20political%20scientist%20%2076](https://www.britannica.com/biography/Friedrich-Ratzel#:~:text=webster,Swedish%20political%20scientist%20%2076) **\[12\] Britannica.** (2025b). *Lebensraum*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.britannica.com/topic/Lebensraum#:\~:text=defined,The](https://www.britannica.com/topic/Lebensraum#:~:text=defined,The) **\[13\] Britannica.** (2025c). *Rudolf Kjellén*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ ](https://www.britannica.com/biography/Rudolf-Kjell%C3%A9n#:~:text=Realism%20www,that%20flourish%20and%20then%20decay)<https://www.britannica.com/biography/Rudolf-Kjellen> **\[14\] Wikipedia (ZH).** (2025). *Rudolf Kjellén*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/w:Rudolf_Kjell%C3%A9n#:\~:text=Besides%20legalistic%2C%20states%20have%20organic,preservation.%20%5B%203](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/w:Rudolf_Kjell%C3%A9n#:~:text=Besides%20legalistic%2C%20states%20have%20organic,preservation.%20%5B%203) **\[15\] Wikipedia.** (2025). *Lebensraum*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebensraum#:\~:text=The%20German%20geographer%20and%20ethnographer,into%20the%20Greater%20Germanic%20Reich](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebensraum#:~:text=The%20German%20geographer%20and%20ethnographer,into%20the%20Greater%20Germanic%20Reich) **\[16\] YouTube.** (2025). *Trump says Ukraine 'unlikely to get all land back' or join NATO* \[Vídeo\]. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BmHzAVLhsXU#:\~:text=Trump%20says%20Ukraine%20%27unlikely%20to,for%20it%20to%20join%20NATO](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BmHzAVLhsXU#:~:text=Trump%20says%20Ukraine%20%27unlikely%20to,for%20it%20to%20join%20NATO) **\[17\] U.S. Naval Institute.** (2025) Operation World Peace. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de [https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/1955/june/operation-world-peace#:\\\~:text=“The Mahan doctrine%2C” according to,the word “airships” is more](https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/1955/june/operation-world-peace#:%5C~:text=%E2%80%9CThe%20Mahan%20doctrine%2C%E2%80%9D%20according%20to,the%20word%20%E2%80%9Cairships%E2%80%9D%20is%20more) **\[18\] Emissary.** (2024) Trump’s Greenland and Panama Canal Threats Are a Throwback to an Old, Misguided Foreign Policy. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de <https://carnegieendowment.org/emissary/2025/01/trump-greenland-panama-canal-monroe-doctrine-policy?lang=en> **\[19\] A Referência**. Acordo EUA-Ucrânia está praticamente fechado, mas analistas se dividem sobre quem sairá ganhando. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de [https://areferencia.com/europa/acordo-eua-ucrania-esta-praticamente-fechado-mas-analistas-se-dividem-sobre-quem-saira-ganhando/#:\\\~:text=EUA e 17,o acordo a seu favor](https://areferencia.com/europa/acordo-eua-ucrania-esta-praticamente-fechado-mas-analistas-se-dividem-sobre-quem-saira-ganhando/#:%5C~:text=EUA%20%20e%20%2017,o%20acordo%20a%20seu%20favor) **\[20\] Wikipedia.** (2025) Geopolitik. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geopolitik#:\\\~:text=Rudolph Kjellén was Ratzel's Swedish,Kjellén's State](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geopolitik#:%5C~:text=Rudolph%20Kjell%C3%A9n%20was%20Ratzel%27s%20Swedish,Kjell%C3%A9n%27s%20State)
@ eac63075:b4988b48
2025-03-07 14:35:26Listen the Podcast: https://open.spotify.com/episode/7lJWc1zaqA9CNhB8coJXaL?si=4147bca317624d34 https://www.fountain.fm/episode/YEGnlBLZhvuj96GSpuk9 # **Abstract** This paper examines a hypothetical scenario in which the United States, under Trump’s leadership, withdraws from NATO and reduces its support for Europe, thereby enabling a Russian conquest of Ukraine and the subsequent expansion of Moscow’s influence over Eurasia, while the US consolidates its dominance over South America. Drawing on classical geopolitical theories—specifically those of Halford Mackinder, Alfred Thayer Mahan, Rudolf Kjellén, and Friedrich Ratzel—the study analyzes how these frameworks can elucidate the evolving power dynamics and territorial ambitions in a reconfigured global order. The discussion highlights Mackinder’s notion of the Eurasian Heartland and its strategic importance, Mahan’s emphasis on maritime power and control of strategic routes, Kjellén’s view of the state as an expanding organism, and Ratzel’s concept of Lebensraum as a justification for territorial expansion. The paper also explores contemporary developments, such as the US–Ukraine economic agreement and Trump’s overt territorial ambitions involving Greenland and Canada, in light of these theories. By juxtaposing traditional geopolitical concepts with current international relations, the study aims to shed light on the potential implications of such shifts for regional stability, global security, and the balance of power, particularly in relation to emerging neocolonial practices in Latin America. # **Introduction** In recent years, the geopolitical dynamics involving the United States, Russia, and Ukraine have sparked analyses from different theoretical perspectives. This paper examines recent events – presupposing a scenario in which Donald Trump withdraws the US from NATO and reduces its support for Europe, allowing a Russian conquest of Ukraine and the expansion of Moscow’s influence over Eurasia, while the US consolidates its dominance over South America – in light of classical geopolitical theories. The ideas of Halford Mackinder, Alfred Thayer Mahan, Rudolf Kjellén, and Friedrich Ratzel are used as reference points. The proposal is to impartially evaluate how each theory can elucidate the developments of this hypothetical scenario, relating Russian territorial expansion in Eurasia to the strategic retreat of the US to the Western Hemisphere. Initially, we will outline Mackinder’s conception of the Heartland (the central Eurasian territory) and the crucial role of Eastern Europe and Ukraine in the quest for global dominance. Next, we will discuss Mahan’s ideas regarding maritime power and the control of strategic routes, considering the impacts on the naval power balance among the US, Russia, and other maritime powers such as the United Kingdom and Japan. Subsequently, we will examine Kjellén’s organic theory of the state, interpreting the Russian expansionist strategy as a reflection of a state organism in search of vital space. In the same vein, Ratzel’s concept of “Lebensraum” will be explored, along with how Russia could justify territorial expansion based on resources and territory. Finally, the paper connects these theories to the current political context, analyzing the direct negotiations between Washington and Moscow (overlooking Ukraine and Europe), the US policy toward authoritarian regimes in Latin America, and the notion of a hemispheric division of power – the “Island of the Americas” under North American hegemony versus an Eurasia dominated by Russia. Lastly, it considers the possibility that such a geopolitical arrangement may foster the strengthening of authoritarian governments globally, rather than containing them, thus altering the paradigms of the liberal world order. # **The Heartland of Mackinder: Ukraine, Eurasia, and Global Dominance** Halford J. Mackinder, a British geographer and pioneer of geopolitics, proposed the celebrated Heartland Theory in the early twentieth century. Mackinder divided the world into geostrategic zones and identified the Heartland—the central continental mass of Eurasia—as the “geographical pivot of history” \[5\]. His most famous maxim encapsulates this vision: “who rules Eastern Europe commands the Heartland; who rules the Heartland commands the World Island; who rules the World Island commands the world” \[5\]. Eastern Europe and, in particular, the region of present-day Ukraine, play a key role in this formula. This is because, for Mackinder, Eastern Europe functions as a gateway to the Heartland, providing access to resources and a strategic position for the projection of continental power \[5\]. Applying this theory to our scenario, the conquest of Ukraine and Eastern European countries by Russia would have profound geopolitical implications. From a Mackinderian point of view, such a conquest would enormously strengthen Russia’s position in the Heartland by adding manpower (population) and Ukraine’s industrial and agricultural resources to its power base \[5\]. In fact, Mackinder argued that controlling the Heartland conferred formidable geostrategic advantages—a vast terrestrial “natural fortress” protected from naval invasions and rich in resources such as wheat, minerals, and fuels \[5\]. Thus, if Moscow were to incorporate Ukraine (renowned for its fertile soil and grain production, as well as its mineral reserves) and extend its influence over Eastern Europe, Russia would consolidate the Heartland under its direct control. In this context, the absence of the USA (withdrawn from NATO and less engaged in Europe) would remove an important obstacle to Russian predominance in the region. With central and eastern Eurasia under Russian influence, it would be possible to move toward the realization of the geopolitical nightmare described by Mackinder for Western maritime powers: a hegemonic continental power capable of projecting power to both Europe and Asia. Mackinder himself warned that if a Heartland power gained additional access to an oceanic coastline—in other words, if it combined land power with a significant maritime front—it would constitute a “danger” to global freedom \[5\]. In the scenario considered, besides advancing into Eastern Europe, Russia would already possess strategic maritime outlets (for example, in the Black Sea, via Crimea, and in the Baltic, via Kaliningrad or the Baltic States if influenced). Thus, the control of Ukraine would reinforce Russia’s position in the Black Sea and facilitate projection into the Eastern Mediterranean, expanding its oceanic front. From a Mackinderian perspective, this could potentially transform Russia into the dominant power of the “World Island” (the combined mass of Europe, Asia, and Africa), thereby unbalancing the global geopolitical order \[5\]. It is worth noting that, historically, Mackinder’s doctrine influenced containment strategies: both in the interwar period and during the Cold War, efforts were made to prevent a single power from controlling the Heartland and Eastern Europe. NATO, for example, can be seen as an instrument to prevent Soviet/Russian advances in Europe, in line with Mackinder’s imperative to “contain the Heartland.” Thus, if the USA were to abandon that role—by leaving NATO and tacitly accepting the Russian sphere of influence in Eurasia—we would be witnessing an inversion of the principles that have guided Western policy for decades. In short, under Mackinder’s theory, the Russian conquest of Ukraine and beyond would represent the key for Russia to command the Heartland and, potentially, challenge global hegemony, especially in a scenario where the USA self-restricts to the Western Hemisphere. # **The Maritime Power of Mahan and the Naval Balance between West and East** While Mackinder emphasized continental land power, Alfred Thayer Mahan, a nineteenth-century American naval strategist, highlighted the crucial role of maritime power in global dominance. In his work *The Influence of Sea Power upon History* (1890), Mahan studied the example of the British Empire and concluded that control of the seas paved the way for British supremacy as a world power \[10\]. He argued that a strong navy and the control of strategic maritime routes were decisive factors for projecting military, political, and economic power. His doctrine can be summarized in the following points: (1) the United States should aspire to be a world power; (2) control of the seas is necessary to achieve that status; (3) such control is obtained through a powerful fleet of warships \[17\]. In other words, for Mahan, whoever dominates the maritime routes and possesses naval superiority will be in a position to influence global destinies, ensuring trade, supplies, and the rapid movement of military forces. In the proposed scenario, in which the USA withdraws militarily from Europe and possibly from the Eurasian stage, Mahan’s ideas raise questions about the distribution of maritime power and its effects. Traditionally, the US Navy operates globally, ensuring freedom of navigation and deterring challenges in major seas (Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, etc.). A withdrawal of the USA from NATO could also signal a reduction in its naval presence in the Northeast Atlantic, the Mediterranean Sea, and other areas close to Eurasia. In such a case, who would fill this naval vacuum? Russia, although primarily a land power, has been attempting to modernize its navy and has specific interests—for example, consolidating its dominance in the Black Sea and maintaining a presence in the Mediterranean (with a naval base in Tartus, Syria). The United Kingdom, a historic European maritime power, would remain aligned with the USA but, without American military support in Europe, might potentially be overwhelmed trying to contain an increasingly assertive Russian navy in European waters on its own. Japan, another significant maritime actor allied with the USA, is concerned with the naval balance in the Pacific; without full American engagement, Tokyo might be compelled to expand its own naval power to contain both Russia in the Far East (which maintains a fleet in the Pacific) and, especially, the growing Chinese navy. According to Mahan’s thinking, strategic maritime routes and choke points (crucial straits and channels) become contested prizes in this power game. With the USA focusing on the Americas, one could imagine Washington reinforcing control over the Panama Canal and Caribbean routes—reviving an “American Gulf” policy in the Western Atlantic and Eastern Pacific. In fact, indications of this orientation emerge in statements attributed to Trump, who once suggested reclaiming direct control over Panama, transforming Canada into a North American state, and even “annexing” Greenland due to its Arctic geopolitical importance \[18\]. These aspirations reflect a quest to secure advantageous maritime positions near the American continent. Conversely, in the absence of American presence in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean, Russia would have free rein for regional maritime projection. This could include anything from the unrestricted use of the Black Sea (after dominating Ukraine, thereby ensuring full access to Crimea and Ukrainian ports) to greater influence in the Eastern Mediterranean via Syria and partnerships with countries such as Iran or Egypt. The Baltic Sea would also become an area of expanded Russian interest, pressuring coastal countries and perhaps reducing NATO’s traditional local naval supremacy. However, it is worth noting that even with these regional expansions, Russia lacks a blue-water navy comparable to that of the USA; thus, its initial global maritime impact would be limited without alliances. An important aspect of Mahan’s theories is that naval power serves as a counterbalance to the land power of the Heartland. Therefore, even if Russia were to dominate the Eurasian continental mass, the continued presence of American naval might on the oceans could prevent complete global domination by Moscow. However, if the USA voluntarily restricts its naval reach to the Americas, it would forgo influencing the power balance in the seas adjacent to Eurasia. Consequently, the balance of maritime power would tend to shift in favor of regional Eurasian actors. The United Kingdom and Japan, traditional allies of the USA, could intensify their naval capabilities to defend regional interests—the United Kingdom safeguarding the North Atlantic and the North Sea, and Japan patrolling the Northwest Pacific—but both would face budgetary and structural limitations in fully compensating for the absence of the American superpower. Consequently, Mahan’s vision suggests that the withdrawal of the USA from the extra-regional scene would weaken the liberal maritime regime, possibly opening space for revisionist powers to contest routes that were previously secured (for example, Russia and China encountering less opposition on the routes of the Arctic and the Indo-Pacific, respectively). In summary, naval hegemony would fragment, and control of strategic seas would become contested, reconfiguring the relative influence of the USA, Russia, and maritime allies such as the United Kingdom and Japan. # **Kjellén and the State as a Living Organism: Russian Expansion as an Organic Necessity** Another useful theoretical lens to interpret Russian geopolitical posture is that of Rudolf Kjellén, a Swedish political scientist of the early twentieth century who conceived the State as a living organism. Kjellén, who even coined the term “geopolitics,” was influenced by Friedrich Ratzel’s ideas and by social Darwinism, arguing that States are born, grow, and decline analogously to living beings \[13\]. In his work *Staten som livsform* (The State as a Form of Life, 1916), he maintained that States possess an organic dimension in addition to the legal one and that “just as any form of life, States must expand or die” \[14\]. This expansion would not be motivated merely by aggressive conquest but seen as a necessary growth for the self-preservation of the state organism \[14\]. In complement, Kjellén echoed Ratzel’s “law of expanding spaces” by asserting that large States expand at the expense of smaller ones, with it being only a matter of time before the great realms fill the available spaces \[14\]. That is, from the organic perspective, vigorous States tend to incorporate smaller neighboring territories, consolidating territorially much like an organism absorbing nutrients. Applying this theory to the strategy of contemporary Russia, we can interpret Moscow’s actions—including the invasion of Ukraine and the ambition to restore its sphere of influence in Eurasia—as the expression of an organic drive for expansion. For a strategist influenced by this school, Russia (viewed as a state organism with a long imperial history) needs to expand its territory and influence to ensure its survival and security. The loss of control over spaces that once were part of the Russian Empire or the Soviet Union (such as Ukraine itself, the Caucasus, or Central Asia) may be perceived by Russian elites as an atrophy of the state organism, rendering it vulnerable. Thus, the reincorporation of these territories—whether directly (annexation) or indirectly (political vassalage)—would equate to restoring lost members or strengthening vital organs of the state body. In fact, official Russian arguments often portray Ukraine as an intrinsic part of “Russian historicity,” denying it a fully separate identity—a narrative that aligns with the idea that Russian expansion in that region is natural and necessary for the Russian State (seen as encompassing also Russian speakers beyond its current borders). Kjellén would thus provide a theoretical justification for Russian territorial expansion as an organic phenomenon. As a great power, Russia would inevitably seek to expand at the expense of smaller neighbors (Ukraine, Georgia, the Baltic States, etc.), as dictated by the tendency of “great spaces to organize” to the detriment of the small \[14\]. This view can be identified in contemporary Russian doctrines that value spheres of influence and the notion that neighboring countries must gravitate around Moscow in order for the natural order to be maintained. The very idea of “Eurasia” united under Russian leadership (advocated by modern Russian thinkers) echoes this organic conception of vital space and expansion as a sign of the State’s vitality. However, Kjellén’s theory also warns of the phenomenon of “imperial overstretch,” should a State exceed its internal cohesion limits by expanding excessively \[14\]. He recognized that extending borders too far could increase friction and vulnerabilities, making it difficult to maintain cohesion—a very large organism may lack functional integration. In the Russian context, this suggests that although expansion is seen as necessary, there are risks if Russia tries to encompass more than it can govern effectively. Conquering Ukraine and subjugating Eastern Europe, for example, could economically and militarily overburden the Russian State, especially if it faced resistance or had to manage hostile populations. However, in the hypothetical scenario we adopt (isolated USA and a weakened Europe), Russia might calculate that the organic benefits of expansion (territory, resources, strategic depth) would outweigh the costs, since external interference would be limited. Thus, through Kjellén’s lens, expansionist Russia behaves as an organism following its instinct for survival and growth, absorbing weaker neighbors; yet such a process is not devoid of challenges, requiring that the “organism Russia” manages to assimilate these new spaces without collapsing under its own weight. # **Ratzel and Lebensraum: Resources, Territory, and the Justification for Expansion** Parallel to Kjellén’s organic view, Friedrich Ratzel’s theory offers another conceptual basis for understanding Russian expansion: the concept of Lebensraum (vital space). Ratzel, a German geographer of the late nineteenth century, proposed that the survival and development of a people or nation depended critically on the available physical space and resources. Influenced by Darwinist ideas, he applied the notion of “survival of the fittest” to nations, arguing that human societies need to conquer territory and resources to prosper, and that the stronger and fittest civilizations will naturally prevail over the weaker ones \[12\]. In 1901, Ratzel coined the term Lebensraum to describe this need for “vital space” as a geographical factor in national power \[15\]. Subsequently, this idea would be adopted—and extremely distorted—by Nazi ideology to justify Germany’s aggressions in Europe. However, the core of Ratzel’s concept is that territorial expansion is essential for the survival and growth of a State, especially to secure food, raw materials, and space for its population \[12\]. When examining Russia’s stance under this perspective, we can see several narratives that evoke the logic of Lebensraum. Russia is the largest country in the world by area; however, much of its territory is characterized by adverse climates (tundra, taiga) and is relatively sparsely populated in Siberia. On the other hand, adjacent regions such as Ukraine possess highly arable lands (chernozem—black soil), significant Slavic population density, and additional natural resources (coal in the Donbass, for example). An implicit justification for Russian expansion could be the search for supplementary resources and fertile lands to secure its self-sufficiency and power—exactly as Ratzel described that vigorous nations do. Historical records show that Ratzel emphasized agrarian primacy: he believed that new territories should be colonized by farmers, providing the food base for the nation \[12\]. Ukraine, historically called the “breadbasket of Europe,” fits perfectly into this vision of conquest for sustenance and agricultural wealth. Furthermore, Ratzel viewed geography as a determinant of the destiny of nations—peoples adapted to certain habitats seek to expand them if they aspire to grow. In contemporary Russian discourse, there is often mention of the need to ensure security and territorial depth in the face of NATO, or to unite brotherly peoples (Russians and Russian speakers) within a single political space. Such arguments can be read as a modern translation of Lebensraum: the idea that the Russian nation, in order to be secure and flourish, must control a larger space, encompassing buffer zones and critical resources. This Russian “vital space” would naturally include Ukraine and other former Soviet republics, given the historical and infrastructural interdependence. Ratzel emphasized that peoples migrated and expanded when their original homeland no longer met their needs or aspirations \[12\]. Although contemporary Russia does not suffer from demographic pressure (on the contrary, it faces population decline), under the logic of a great power there is indeed a sentiment of geopolitical insufficiency for having lost influence over areas considered strategic. Thus, reconquering these areas would mean recovering the “habitat” necessary for the Russian nation to prosper and feel secure. It is important to mention that, in Ratzel’s and Kjellén’s formulations, the pursuit of Lebensraum or organic expansion is not morally qualified—it is treated as a natural process in the politics of power. Thus, on the discursive level, Russia can avoid overly aggressive rhetoric and resort to “natural” justifications: for example, claiming that it needs to occupy Ukraine for defensive purposes (security space) or to reunify peoples (a common cultural and historical space). Beneath these justifications, however, resonates the geopolitical imperative to acquire more territory and resources as a guarantee of national survival, something consonant with Ratzel’s theory. In fact, Russian Realpolitik frequently prioritizes the control of energy resources (gas, oil) and transportation routes. Expanding its influence over central Eurasia would also mean controlling oil pipelines, gas lines, and logistical corridors—essential elements of modern Lebensraum understood as access to vital resources and infrastructure. In summary, by conquering Ukraine and extending its reach into Eurasia, Russia could effectively invoke the concept of Lebensraum: presenting its expansion not as mere imperialism, but as a necessity to secure indispensable lands and resources for its people and to correct the “injustice” of a vital space diminished by post-Cold War territorial losses. The theories of Ratzel and Kjellén together paint a picture in which Russian expansion emerges almost as a natural law—the great State reclaiming space to ensure its survival and development at the expense of smaller neighbors. # **Trump, NATO, and the Threat of American Withdrawal** One of the most alarming changes with Trump's return to power is the tense relationship with the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). Trump has long criticized allies for not meeting military spending targets, even threatening during his first term to withdraw the US from the alliance if members did not increase their contributions \[2\]. This threat, initially viewed with skepticism, became concrete after his re-election, leading European allies to seriously consider the possibility of having to defend themselves without American support \[1\]. In fact, Trump suggested in post-election interviews that the US would only remain in NATO if the allies “paid their bills” – otherwise, he “would seriously consider” leaving \[2\]. Such statements reinforced the warning that the US might not honor NATO's mutual defense commitment, precisely at a time of continuous Russian threat due to the war in Ukraine \[1\]. From a theoretical point of view, this posture of American retrenchment evokes the classic tension between maritime power and land power. Alfred Thayer Mahan emphasized that the global power of the US derived largely from its naval superiority and from alliances that ensured control over strategic maritime routes \[9\]. NATO, since 1949, has served not only to deter Soviet terrestrial advances in Eurasia, but also to secure the US naval presence in the North Atlantic and the Mediterranean – a fundamental element according to Mahan. In turn, Halford Mackinder warned that the balance of global power depended on the control of the Eurasian “Heartland” (the central region of Eurasia). The withdrawal or disengagement of the US (a maritime power) from this region could open the way for a continental power (such as Russia) to expand its influence in Eastern Europe, unbalancing the power balance \[3\]. In other words, by threatening to leave NATO, Trump jeopardizes the principle of containment that prevented Russian dominance over Eastern Europe – something that Mackinder would see as a dangerous shift in global power in favor of the Heartland power. Adopting an impartial tone, it is observed that European countries have reacted to this new reality with precautionary measures. Strategic reports already calculate the cost of an autonomous European defense: hundreds of thousands of additional soldiers and investments of hundreds of billions of euros would be required if the US ceased to guarantee the security of the continent \[1\]. European dependence on American military power is significant and, without it, there would be a need for a major reinforcement of European Armed Forces \[1\]. This mobilization practically reflects the anticipation of a power vacuum left by the US – a scenario in which Mackinder’s theory (on the primacy of the Heartland and the vulnerability of the “external crescent” where Western Europe is located) regains its relevance. # **The US–Ukraine Economic Agreement: Strategic Minerals in Exchange for Support?** Another novelty of Trump's second term is the unprecedented and transactional manner in which Washington has been dealing with the war in Ukraine. Instead of emphasizing security guarantees and alliances, the Trump administration proposed a trade agreement with Ukraine focused on the exploitation of strategic minerals, linking American support to a direct economic benefit. According to sources close to the negotiations, the US and Ukraine are about to sign a pact to share the revenues from the exploitation of critical mineral resources on Ukrainian territory \[19\]. Materials such as titanium, lithium, rare earths, and uranium – vital for high-tech and defense industries – would be at the core of this agreement \[6\]. According to the known draft, Ukraine would allocate 50% of the profits from new mineral ventures to a fund controlled by the US, which would reinvest part of the resources in the country’s own reconstruction \[6\] \[19\]. It is noteworthy that the pact does not include explicit security guarantees for Kyiv, despite Ukraine remaining under direct military threat from Russia \[19\]. Essentially, the Trump administration offers financial support and economic investment in exchange for a share in Ukrainian natural resources, but without formally committing to Ukraine's defense in the event of a renewed Russian offensive \[19\]. American authorities argue that this economic partnership would already be sufficient to “secure Ukrainian interests,” as it would provide the US with its own incentives to desire Ukraine’s stability \[19\]. “What could be better for Ukraine than being in an economic partnership with the United States?” stated Mike Waltz, a US national security advisor, defending the proposal \[19\]. Analysts, however, assess the agreement in divided terms. For some, it represents a form of economic exploitation at a time of Ukraine's fragility – comparing the demand to share mineral wealth amid war to a scheme of “mafia protection” \[19\]. Steven Cook, from the Council on Foreign Relations, classified the offer as “extortion,” and political scientist Virginia P. Fortna observed that charging resources from an invaded country resembles predatory practices \[19\]. Joseph Nye adds that it is a short-term gain strategy that could be “disastrous in the long run” for American credibility, reflecting the transactional approach that Trump even adopted with close allies in other contexts \[19\]. On the other hand, some see a future advantage for Kyiv: journalist Pierre Briançon suggests that at least this agreement aligns American commercial interests with Ukraine’s future, which could, in theory, keep the US involved in Ukrainian prosperity in the long term \[19\]. It is even recalled that President Zelensky himself proposed last year the idea of sharing natural resources with the US to bring the interests of the two countries closer together \[19\]. From the perspective of geopolitical theories, this agreement illustrates a shift towards economic pragmatism in international relations, approaching concepts proposed by Kjellén. Rudolf Kjellén, who coined the term “geopolitics,” saw the State as a territorial organism that seeks to ensure its survival through self-sufficiency and the control of strategic resources \[4\]. Trump's demand for a share in Ukrainian resources in order to continue supporting the country reflects a logic of autarky and direct national interest – that is, foreign policy serving primarily to reinforce the economic and material position of the US. This view contrasts with the traditional cooperative approach, but aligns with Kjellén’s idea that powerful States tend to transform international relations into opportunities for their own gain, ensuring access to vital raw materials. Similarly, Friedrich Ratzel argued that States have a “propensity to expand their borders according to their capacities,” seeking vital space (Lebensraum) and resources to sustain their development \[11\]. The US–Ukraine pact, by conditioning military/economic aid on obtaining tangible advantages (half of the mineral profits), is reminiscent of Ratzel’s perspective: the US, as a rising economic power, expands its economic influence over Ukrainian territory like an organism extending itself to obtain the necessary resources for its well-being. It is, therefore, a form of economic expansionism at the expense of purely ideological commitments or collective security. # **Peace Negotiations Excluding Ukraine and the Legitimacy of the Agreement** Another controversial point is the manner in which peace negotiations between Russia and the West have been conducted under Trump's administration. Since taking office, the American president has engaged directly with Moscow in pursuit of a ceasefire, deliberately keeping the Ukrainian government out of the initial discussions \[6\]. Trump expressed his desire to “leave Zelensky out of the conversation” and also excluded the European Union from any influence in the process \[6\]. This negotiation strategy—conducted without the presence of the primary interested party, Ukraine—raises serious questions about the legitimacy and sustainability of any resulting agreement. Historically, peace agreements reached without the direct participation of one of the conflicting parties tend to face problems in implementation and acceptance. The exclusion of Ukraine in the decision-making phase brings to light the issue of guarantees. As noted, the emerging agreement lacks formal US security guarantees for Ukraine. This implies that, after the agreement is signed, nothing will prevent Russia from launching a new offensive if it deems it convenient, knowing that the US has not committed to defending it militarily. Experts have already warned that a ceasefire without robust protection may only be a pause for Russian rearmament, rendering the conflict “frozen” temporarily and potentially resumed in the near future. The European strategic community has expressed similar concern: without American deterrence, the risk of further Russian aggressions in the region increases considerably \[1\]. Denmark, for example, has released intelligence reports warning of possible imminent Russian attacks, prompting neighboring countries to accelerate plans for independent defense \[1\]. The legitimacy of this asymmetric peace agreement (negotiated without Ukraine fully at the table and under economic coercion) is also questionable from a legal and moral point of view. It violates the principle of self-determination by imposing terms decided by great powers on a sovereign country—a practice reminiscent of dark chapters in diplomacy, such as the Munich Agreement of 1938, when powers determined the fate of Czechoslovakia without its consent. In the current case, Ukraine would end up signing the agreement, but from a position of weakness, raising doubts about how durable such a commitment would be. From Mackinder’s perspective, Ukraine’s removal from the battlefield without guarantees essentially means admitting a greater influence of Russia (the Heartland power) over Eastern Europe. This would alter the balance in Eurasia in a potentially lasting way. Furthermore, the fact that great powers negotiate over the heads of a smaller country evokes the imperial logic of the nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, when empires decided among themselves the divisions of foreign territories—a behavior that Mackinder saw as likely in a world of a “closed system.” With the entire world already occupied by States, Mackinder predicted that powers would begin to compete for influence within this consolidated board, often subjugating smaller states to gain advantage \[3\]. The US–Russia negotiation regarding Ukraine, without proper Ukrainian representation, exemplifies this type of neo-imperial dynamic in the twenty-first century. Also noteworthy is the consonance with the ideas of Ratzel and Kjellén: both viewed smaller states as easily relegated to the status of satellites or even “parasitic organisms” in the orbit of larger states. Kjellén spoke of the intrinsic vulnerability of states with little territorial depth or economic dependence, making them susceptible to external pressures \[4\]\[20\]. Ukraine, weakened by war and dependent on external aid, becomes a concrete example of this theorized vulnerability: it has had to cede strategic resources and accept terms dictated against its will in an attempt to secure its immediate survival. The resulting agreement, therefore, reflects a power imbalance characteristic of the hierarchical international relations described by classical geopolitical theorists. # **Implicit Territorial Concessions and Trump’s Public Discourse** A central and controversial point in Trump’s statements regarding the war in Ukraine is the insinuation of territorial concessions to Russia as part of the conflict’s resolution. Publicly, Trump avoided explicitly condemning Russian aggression and even stated that he considered it “unlikely” that Ukraine would be able to retake all the areas occupied by the Russians \[16\]. In debates and interviews, he suggested that “if I were president, the war would end in 24 hours,” implying that he would force an understanding between Kyiv and Moscow that would likely involve ceding some territory in exchange for peace. This position marks a break with the previous US policy of not recognizing any territorial acquisitions made by force and fuels speculations that a future peace agreement sponsored by Trump would legitimize at least part of Russia’s gains since 2014 (Crimea, Donbass, and areas seized during the 2022 invasion). The actions of his administration corroborate this interpretation. As discussed, the economic agreement focuses on the exploitation of Ukrainian natural resources, many of which are located precisely in regions currently under Russian military control, such as parts of the Zaporizhzhia Oblast, Donetsk, Lugansk, and the Azov Sea area \[6\]. A Ukrainian geologist, Hanna Liventseva, highlighted that “most of these elements (strategic minerals) are found in the south of the Ukrainian Shield, mainly in the Azov region, and most of these territories are currently invaded by Russia” \[6\]. This means that, to make joint exploitation viable, Russia’s de facto control over these areas would have to be recognized—or at least tolerated—in the short term. In other words, the pact indirectly and tacitly accepts Russian territorial gains, as it involves sharing the profits from resources that are not currently accessible to the Kyiv government. Furthermore, figures close to Trump have made explicit statements regarding the possibility of territorial cession. Mike Waltz, Trump’s national security advisor, publicly stated that Zelensky might need to “cede land to Russia” to end the war \[8\]. This remark—made public in March 2025—confirms that the Trump White House considers it natural for Ukraine to relinquish parts of its territory in favor of an agreement. Such a stance marks a break from the previous Western consensus, which condemned any territorial gains by force. Under Trump, a pragmatic view (in the eyes of his supporters) or a cynical one (according to his critics) seems to prevail: sacrificing principles of territorial integrity to quickly end hostilities and secure immediate economic benefits. In theoretical terms, this inclination to validate territorial gains by force recalls the concept of Realpolitik and the geopolitical Darwinism that influenced thinkers such as Ratzel. In Ratzel’s organic conception, expanding states naturally absorb neighboring territories when they are strong enough to do so, while declining states lose territory—a process almost biological in the selection of the fittest \[11\]. The Trump administration’s acceptance that Ukraine should “give something” to Moscow to seal peace reflects a normalization of this geopolitical selection process: it recognizes the aggressor (Russia) as having the “right” to retain conquered lands, because that is how power realities on the ground dictate. Mackinder, although firmly opposed to allowing Russia to dominate the Heartland, would see this outcome as the logical consequence of the lack of engagement from maritime powers (the USA and the United Kingdom, for example) in sustaining the Ukrainian counterattack. Without the active involvement of maritime power to balance the dispute, land power prevails in Eastern Europe. From the perspective of international legitimacy, the cession of Ukrainian territories—whether de jure or de facto—creates a dangerous precedent in the post-Cold War era. Rewarding violent aggression with territorial gains may encourage similar strategies in other parts of the world, undermining the architecture of collective security. This is possibly a return to a world of spheres of influence, where great powers define borders and zones of control according to their convenience—something that the rules-based order after 1945 sought to avoid. Here, academic impartiality requires noting that coercion for territorial concessions rarely produces lasting peace, as the aggrieved party—in this case, Ukraine—may accept temporarily but will continue to assert its rights in the long term, as has occurred with other territorial injustices in history. # **Territorial Ambitions of Trump: Greenland and Canada** Beyond the Eurasian theater of war, Trump revived geopolitical ambitions involving territories traditionally allied with the US: Greenland (an autonomous territory of Denmark) and Canada. As early as 2019, during his first term, Trump shocked the world by proposing to buy Greenland—rich in minerals and strategically positioned in the Arctic. Upon his return to power, he went further: expressing a “renewed interest” in acquiring Greenland and publicly suggesting the incorporation of Canada as the 51st American state \[2\]. In January 2025, during a press conference at Mar-a-Lago, he even displayed maps in which the US and Canada appeared merged into a single country, while Greenland was marked as a future American possession \[2\]. Posts by the president on social media included satirical images with a map of North America where Canada was labeled “51st” and Greenland designated as “Our Land” \[2\]. Such moves were met with concern and disbelief by allies. Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau was caught on an open microphone warning that Trump’s fixation on annexation “is real” and not just a joke \[7\]. Trudeau emphasized that Washington appeared to covet Canada’s vast mineral resources, which would explain the insistence on the idea of absorption \[7\]. In public, Trump argued that Canadians “would be more prosperous as American citizens,” promising tax cuts and better services should they become part of the US \[7\]. On the Danish side, the reaction to the revived plan regarding Greenland was firmly negative—as it was in 2019—reaffirming that the territory is not for sale. Trump, however, insinuated that the issue might be one of national security, indicating that American possession of Greenland would prevent adverse influences (a reference to China and Russia in the Arctic) \[2\]. More worryingly, he refused to rule out the use of military means to obtain the island, although he assured that he had no intention of invading Canada by force (in the Canadian case, he spoke of “economic force” to forge a union) \[2\]. This series of initiatives reflects an unprecedented expansionist impetus by the US in recent times, at least in discourse. Analyzing this through the lens of classical geopolitics offers interesting insights. Friedrich Ratzel and his notion of Lebensraum suggest that powerful states, upon reaching a certain predominance, seek to expand their territory by influencing or incorporating adjacent areas. Trump, by targeting the immediate neighbor (Canada) and a nearby strategic territory (Greenland), appears to resurrect this logic of territorial expansion for the sake of gaining space and resources. Ratzel saw such expansion almost as a natural process for vigorous states, comparable to the growth of an organism \[11\]. From this perspective, the US would be exercising its “right” of expansion in North America and the polar region, integrating areas of vital interest. Additionally, Alfred Mahan’s view on maritime power helps to understand the strategic value of Greenland. Mahan postulated that control of key maritime chokepoints and naval bases ensures global advantage \[9\]. Greenland, situated between the North Atlantic and the Arctic, has become increasingly relevant as climate change opens new polar maritime routes and reveals vast mineral deposits (including rare earth elements and oil). For the US, having a presence or sovereignty over Greenland would mean dominating the gateway to the Arctic and denying this space to rivals. This aligns with Mahan’s strategy of securing commercial and military routes (in this case, potential Arctic routes) and resources to consolidate naval supremacy. On the other hand, the incorporation of Canada—with its enormous territory, Arctic coastline, and abundant natural resources—would provide the US with formidable geoeconomic and geopolitical reinforcement, practically eliminating vulnerabilities along its northern border. This is an ambitious project that also echoes ideas of Kjellén, for whom an ideal State should seek territorial completeness and economic self-sufficiency within its region. Incorporating Canada would be the pinnacle of American regional autarky, turning North America into a unified bloc under Washington (a scenario reminiscent of the “pan-regions” conceived by twentieth-century geopoliticians influenced by Kjellén). It is important to note, however, that these ambitions face enormous legal and political obstacles. The sovereignty of Canada and Greenland (Denmark) is guaranteed by international law, and both peoples categorically reject the idea of annexation. Any hostile action by the US against these countries would shake alliances and the world order itself. Even so, the very fact that an American president suggests such possibilities already produces geopolitical effects: traditional partners begin to distrust Washington’s intentions, seek alternative alliances, and strengthen nationalist discourses of resistance. In summary, Trump’s expansionist intentions in Greenland and Canada rekindle old territorial issues and paradoxically place the US in the position of a revisionist power—a role once associated with empires in search of colonies. # **Implications for Brazil and South America: A New Neocolonization?** In light of this geopolitical reconfiguration driven by Trump's USA—with a reordering of alliances and a possible partition of spheres of influence among great powers—the question arises: what is the impact on Brazil and the other countries of South America? Traditionally, Latin America has been under the aegis of the Monroe Doctrine (1823), which established non-interference by Europe in the region and, implicitly, the primacy of the USA in the Western Hemisphere. In the post–Cold War period, this influence translated more into political and economic leadership, without formal annexations or direct territorial domination. However, the current context points to a kind of “neocolonization” of the Global South, in which larger powers seek to control resources and peripheral governments in an indirect yet effective manner. Mackinder’s theories can be used to illuminate this dynamic. As mentioned, Mackinder envisioned the twentieth-century world as a closed system, in which there were no longer any unknown lands to be colonized—hence, the powers would fight among themselves for control over already occupied regions \[3\]. He predicted that Africa and Latin America (then largely European colonies or semi-colonies) would continue as boards upon which the great powers would project their disputes, a form of neocolonialism. In the current scenario, we see the USA proposing exchanges of protection for resources (as in Ukraine) and even leaders of developing countries seeking similar agreements. A notable example: the President of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Felix Tshisekedi, praised the USA–Ukraine initiative and suggested an analogous agreement involving Congolese mineral wealth in exchange for US support against internal rebels (M23) \[19\]. In other words, African countries and possibly South American ones may enter into this logic of offering privileged access to resources (cobalt, lithium, food, biodiversity) in order to obtain security guarantees or investments. This represents a regression to the times when external powers dictated the directions of the South in exchange for promises of protection, characterizing a strategic neocolonialism. For Brazil, in particular, this rearrangement generates both opportunities and risks. As a regional power with considerable diplomatic autonomy, Brazil has historically sought to balance relationships with the USA, Europe, China, and other actors, avoiding automatic alignments. However, in a world where Trump’s USA is actively redefining spheres of influence—possibly making deals with Russia that divide priorities (for example, Washington focusing on the Western Hemisphere and Moscow on the Eastern)—South America could once again be seen as an exclusive American sphere of influence. From this perspective, Washington could pressure South American countries to align with its directives, limiting partnerships with rivals (such as China) and seeking privileged access to strategic resources (such as the Amazon, fresh water, minerals, and agricultural commodities). Some indications are already emerging: Trump’s transactional approach mentioned by Nye included pressures on Canada and Mexico regarding border and trade issues, under the threat of commercial sanctions. It would not be unthinkable to adopt a hard line, for example, with regard to Brazilian environmental policies (linked to the Amazon) or Brazil’s relations with China, using tariffs or incentives as leverage—a sort of geopolitics of economic coercion. On the other hand, Brazil and its neighbors could also attempt to take advantage of the Sino–North American competition. If the USA is distracted consolidating its hemispheric “hard power” hegemony (even with annexation fantasies in the north), powers such as China may advance their economic presence in South America through investments and trade (Belt and Road, infrastructure financing)—which is already happening. This would constitute an indirect neocolonial dispute in the South: Chinese loans and investments versus American demands and agreements, partly reminiscent of the nineteenth-century imperial competition (when the United Kingdom, USA, and others competed for Latin American markets and resources). From a conceptual standpoint, Mackinder might classify South America as part of the “Outer Crescent” (external insular crescent)—peripheral to the great Eurasian “World-Island,” yet still crucial as a source of resources and a strategic position in the South Atlantic and Pacific. If the USA consolidates an informal empire in the Americas, it would be reinforcing its “insular bastion” far from the Eurasian Heartland, a strategy that Mackinder once suggested for maritime powers: to control islands and peripheral continents to compensate for the disadvantage of not controlling the Heartland. However, an excessive US dominance in the South could lead to local resistance and alternative alignments, unbalancing the region. Kjellén would add that for Brazil to maintain its decisive sovereignty, it will need to strengthen its autarky and internal cohesion—in other words, reduce vulnerabilities (economic, military, social) that external powers might exploit \[4\]. Meanwhile, Mahan might point out the importance for Brazil of controlling its maritime routes and coastlines (South Atlantic) to avoid being at the mercy of a naval power like the USA. And Ratzel would remind us that states that do not expand their influence tend to be absorbed by foreign influences—which, in the context of Brazil, does not mean conquering neighboring territories, but rather actively leading South American integration to create a block more resilient to external intrusion. In summary, South America finds itself in a more competitive and segmented world, where major players are resurrecting practices from past eras. The notion of “neocolonization” here does not imply direct occupation, but rather mechanisms of dependency: whether through unequal economic agreements or through diplomatic or military pressure for alignment. Brazil, as the largest economy and territory on the subcontinent, will have to navigate with heightened caution. A new global power balance, marked by the division of spheres of influence among the USA, China, and Russia, may reduce the sovereign maneuvering space of South American countries unless they act jointly. Thus, theoretical reflection suggests the need for South–South strategies, reinforcement of regional organizations, and diversification of partnerships to avoid falling into modern “neocolonial traps.” # **Conclusion** The emerging post–re-election geopolitical conjuncture of Donald Trump signals a return to classical geopolitical principles, after several decades of predominance of institutional liberal views. We witness the revaluation of concepts such as spheres of influence, exchanges of protection for resources, naval power versus land power, and disputes over territory and raw materials—all central themes in the writings of Mackinder, Mahan, Kjellén, and Ratzel at the end of the nineteenth and the beginning of the twentieth century. An impartial analysis of these events, in light of these theories, shows internal coherence in Trump’s actions: although controversial, they follow a logic of maximizing national interest and the relative power of the USA on the world stage, even at the expense of established principles and alliances. Halford Mackinder reminds us that, in a closed world with no new lands to conquer, the great powers will seek to redistribute the world among themselves \[3\]. This seems to manifest in the direct understandings between the USA and Russia over the fate of Ukraine, and in American ambitions in the Arctic and the Western Hemisphere. Alfred Mahan emphasizes that the control of the seas and strategic positions ensures supremacy—we see reflections of this in Trump’s obsession with Greenland (Arctic) and the possible neglect of the importance of maintaining NATO (and therefore the North Atlantic) as a cohesive bloc, something that Mahan’s theory would criticize due to the risk of a naval vacuum. Rudolf Kjellén and Friedrich Ratzel provide the framework to understand the more aggressive facet of expansionist nationalism: the idea of the State as an organism that needs to grow, secure resources, and seek self-sufficiency explains everything from the extortionate agreement imposed on Ukraine to the annexation rhetoric regarding Canada. The potential consequences are profound. In the short term, we may witness a precarious ceasefire in the Ukraine war, with consolidated Russian territorial gains and Ukraine economically tied to the USA, but without formal military protection—a fragile “armed peace.” Western Europe, alarmed, may accelerate its independent militarization, perhaps marking the beginning of European defense autonomy, as is already openly debated \[1\]. At the far end of the globe, American activism in the Arctic and the Americas may reshape alliances: countries like Canada, once aligned with Washington, might seek to guarantee their sovereignty by distancing themselves from it; powers like China could take advantage of the openings to increase their presence in Latin America and Africa through economic diplomacy; and emerging countries of the Global South may have to choose between submitting to new “guardianships” or strengthening South–South cooperation. Ultimately, the current situation reinforces the relevance of studying geopolitics through historical lenses. The actions of the Trump administration indicate that, despite all technological and normative advances, the competition for geographic power has not disappeared—it has merely assumed new formats. Academic impartiality obliges us not to prematurely judge whether these strategies will be successful or beneficial, but history and theory warn that neo-imperial movements tend to generate counter-reactions. As Mackinder insinuated, “every shock or change anywhere reverberates around the world,” and a sudden move by a superpower tends to provoke unforeseen adjustments and chain conflicts. It remains to be seen how the other actors—including Brazil and its neighbors—will adapt to this new chapter in the great struggle for global power, in which centuries-old theories once again have a surprising explanatory power over present events. # **Bibliography** **\[1\] A Referência.** (2025). *Europa calcula o custo de se defender sem os EUA: 300 mil soldados e 250 bilhões de euros a mais*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://areferencia.com/europa/europa-calcula-o-custo-de-se-defender-sem-os-eua-300-mil-soldados-e-250-bilhoes-de-euros-a-mais/#:\~:text=Europa%20calcula%20o%20custo%20de,bilh%C3%B5es%20de%20euros%20a%20mais](https://areferencia.com/europa/europa-calcula-o-custo-de-se-defender-sem-os-eua-300-mil-soldados-e-250-bilhoes-de-euros-a-mais/#:~:text=Europa%20calcula%20o%20custo%20de,bilh%C3%B5es%20de%20euros%20a%20mais) **\[2\] Brexit Institute.** (2025). *What happens if Trump invades Greenland?* Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://dcubrexitinstitute.eu/2025/01/what-happens-if-trump-invades-greenland/#:\~:text=Ever%20since%20Donald%20Trump%20announced,agreed%20in%20Wales%20in%202014](https://dcubrexitinstitute.eu/2025/01/what-happens-if-trump-invades-greenland/#:~:text=Ever%20since%20Donald%20Trump%20announced,agreed%20in%20Wales%20in%202014) **\[3\] Cfettweis C:CST22(2)8576.DVI.** (2025). *Mackinder and Angell*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://cfettweis.com/wp-content/uploads/Mackinder-and-Angell.pdf#:\~:text=meant%20the%20beginning%20of%20an,Mackinder](https://cfettweis.com/wp-content/uploads/Mackinder-and-Angell.pdf#:~:text=meant%20the%20beginning%20of%20an,Mackinder) **\[4\] Diva-Portal.** (2025). *The geopolitics of territorial relativity. Poland seen by Rudolf Kjellén*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1696547/FULLTEXT02#:\~:text=,The%20state%20territory](https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1696547/FULLTEXT02#:~:text=,The%20state%20territory) **\[5\] Geopolitical Monitor.** (2025). *The Russo-Ukrainian War and Mackinder’s Heartland Thesis*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/the-ukraine-war-and-mackinders-heartland-thesis/#:\~:text=In%201904%2C%20Sir%20Halford%20J,in%20adding%20a%20substantial%20oceanic](https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/the-ukraine-war-and-mackinders-heartland-thesis/#:~:text=In%201904%2C%20Sir%20Halford%20J,in%20adding%20a%20substantial%20oceanic) **\[6\] Instituto Humanitas Unisinos.** (2025). *Trump obriga Zelensky a hipotecar a exploração de minerais críticos em troca do seu apoio*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.ihu.unisinos.br/648986-trump-obriga-zelensky-a-hipotecar-a-exploracao-de-minerais-criticos-em-troca-do-seu-apoio#:\~:text=Essa%20troca%20inclui%20os%20cobi%C3%A7ados,s%C3%A3o%20praticamente%20inexploradas%20no%20pa%C3%ADs](https://www.ihu.unisinos.br/648986-trump-obriga-zelensky-a-hipotecar-a-exploracao-de-minerais-criticos-em-troca-do-seu-apoio#:~:text=Essa%20troca%20inclui%20os%20cobi%C3%A7ados,s%C3%A3o%20praticamente%20inexploradas%20no%20pa%C3%ADs) **\[7\] Politico.** (2025). *Trump’s annexation fixation is no joke, Trudeau warns*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.politico.com/news/2025/02/07/canada-trudeau-trump-51-state-00203156#:\~:text=TORONTO%20%E2%80%94%20Prime%20Minister%20Justin,Canada%20becoming%20the%2051st%20state%2C%E2%80%9D%20Trudeau%20said](https://www.politico.com/news/2025/02/07/canada-trudeau-trump-51-state-00203156#:~:text=TORONTO%20%E2%80%94%20Prime%20Minister%20Justin,Canada%20becoming%20the%2051st%20state%2C%E2%80%9D%20Trudeau%20said) **\[8\] The Daily Beast.** (2025). *Top Trump Adviser Moves Goalpost for Ukraine to End War*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.thedailybeast.com/top-trump-adviser-moves-goalpost-for-ukraine-to-end-war/#:\~:text=LAND%20GRAB](https://www.thedailybeast.com/top-trump-adviser-moves-goalpost-for-ukraine-to-end-war/#:~:text=LAND%20GRAB) **\[9\] The Geostrata.** (2025). *Alfred Thayer Mahan and Supremacy of Naval Power*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.thegeostrata.com/post/alfred-thayer-mahan-and-supremacy-of-naval-power#:\~:text=Alfred%20Thayer%20Mahan%20and%20Supremacy,control%20over%20maritime%20trade%20routes](https://www.thegeostrata.com/post/alfred-thayer-mahan-and-supremacy-of-naval-power#:~:text=Alfred%20Thayer%20Mahan%20and%20Supremacy,control%20over%20maritime%20trade%20routes) **\[10\] U.S. Department of State.** (2025). [Mahan’s The Influence of Sea Power upon History: Securing International Markets in the 1890s](https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/mahan). Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/mahan#:\~:text=Mahan%20argued%20that%20British%20control,American%20politicians%20believed%20that%20these](https://history.state.gov/milestones/1866-1898/mahan#:~:text=Mahan%20argued%20that%20British%20control,American%20politicians%20believed%20that%20these) **\[11\] Britannica.** (2025a). *Friedrich Ratzel | Biogeography, Anthropogeography, Political Geography*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.britannica.com/biography/Friedrich-Ratzel#:\~:text=webster,Swedish%20political%20scientist%20%2076](https://www.britannica.com/biography/Friedrich-Ratzel#:~:text=webster,Swedish%20political%20scientist%20%2076) **\[12\] Britannica.** (2025b). *Lebensraum*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.britannica.com/topic/Lebensraum#:\~:text=defined,The](https://www.britannica.com/topic/Lebensraum#:~:text=defined,The) **\[13\] Britannica.** (2025c). *Rudolf Kjellén*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ ](https://www.britannica.com/biography/Rudolf-Kjell%C3%A9n#:~:text=Realism%20www,that%20flourish%20and%20then%20decay)<https://www.britannica.com/biography/Rudolf-Kjellen> **\[14\] Wikipedia (ZH).** (2025). *Rudolf Kjellén*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/w:Rudolf_Kjell%C3%A9n#:\~:text=Besides%20legalistic%2C%20states%20have%20organic,preservation.%20%5B%203](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/w:Rudolf_Kjell%C3%A9n#:~:text=Besides%20legalistic%2C%20states%20have%20organic,preservation.%20%5B%203) **\[15\] Wikipedia.** (2025). *Lebensraum*. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebensraum#:\~:text=The%20German%20geographer%20and%20ethnographer,into%20the%20Greater%20Germanic%20Reich](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lebensraum#:~:text=The%20German%20geographer%20and%20ethnographer,into%20the%20Greater%20Germanic%20Reich) **\[16\] YouTube.** (2025). *Trump says Ukraine 'unlikely to get all land back' or join NATO* \[Vídeo\]. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de[ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BmHzAVLhsXU#:\~:text=Trump%20says%20Ukraine%20%27unlikely%20to,for%20it%20to%20join%20NATO](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BmHzAVLhsXU#:~:text=Trump%20says%20Ukraine%20%27unlikely%20to,for%20it%20to%20join%20NATO) **\[17\] U.S. Naval Institute.** (2025) Operation World Peace. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de [https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/1955/june/operation-world-peace#:\\\~:text=“The Mahan doctrine%2C” according to,the word “airships” is more](https://www.usni.org/magazines/proceedings/1955/june/operation-world-peace#:%5C~:text=%E2%80%9CThe%20Mahan%20doctrine%2C%E2%80%9D%20according%20to,the%20word%20%E2%80%9Cairships%E2%80%9D%20is%20more) **\[18\] Emissary.** (2024) Trump’s Greenland and Panama Canal Threats Are a Throwback to an Old, Misguided Foreign Policy. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de <https://carnegieendowment.org/emissary/2025/01/trump-greenland-panama-canal-monroe-doctrine-policy?lang=en> **\[19\] A Referência**. Acordo EUA-Ucrânia está praticamente fechado, mas analistas se dividem sobre quem sairá ganhando. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de [https://areferencia.com/europa/acordo-eua-ucrania-esta-praticamente-fechado-mas-analistas-se-dividem-sobre-quem-saira-ganhando/#:\\\~:text=EUA e 17,o acordo a seu favor](https://areferencia.com/europa/acordo-eua-ucrania-esta-praticamente-fechado-mas-analistas-se-dividem-sobre-quem-saira-ganhando/#:%5C~:text=EUA%20%20e%20%2017,o%20acordo%20a%20seu%20favor) **\[20\] Wikipedia.** (2025) Geopolitik. Recuperado em 3 de março de 2025, de [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geopolitik#:\\\~:text=Rudolph Kjellén was Ratzel's Swedish,Kjellén's State](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Geopolitik#:%5C~:text=Rudolph%20Kjell%C3%A9n%20was%20Ratzel%27s%20Swedish,Kjell%C3%A9n%27s%20State) -
 @ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-07 00:26:37There is something quietly rebellious about stacking sats. In a world obsessed with instant gratification, choosing to patiently accumulate Bitcoin, one sat at a time, feels like a middle finger to the hype machine. But to do it right, you have got to stay humble. Stack too hard with your head in the clouds, and you will trip over your own ego before the next halving even hits. **Small Wins** Stacking sats is not glamorous. Discipline. Stacking every day, week, or month, no matter the price, and letting time do the heavy lifting. Humility lives in that consistency. You are not trying to outsmart the market or prove you are the next "crypto" prophet. Just a regular person, betting on a system you believe in, one humble stack at a time. Folks get rekt chasing the highs. They ape into some shitcoin pump, shout about it online, then go silent when they inevitably get rekt. The ones who last? They stack. Just keep showing up. Consistency. Humility in action. Know the game is long, and you are not bigger than it. **Ego is Volatile** Bitcoin’s swings can mess with your head. One day you are up 20%, feeling like a genius and the next down 30%, questioning everything. Ego will have you panic selling at the bottom or over leveraging the top. Staying humble means patience, a true bitcoin zen. Do not try to "beat” Bitcoin. Ride it. Stack what you can afford, live your life, and let compounding work its magic. **Simplicity** There is a beauty in how stacking sats forces you to rethink value. A sat is worth less than a penny today, but every time you grab a few thousand, you plant a seed. It is not about flaunting wealth but rather building it, quietly, without fanfare. That mindset spills over. Cut out the noise: the overpriced coffee, fancy watches, the status games that drain your wallet. Humility is good for your soul and your stack. I have a buddy who has been stacking since 2015. Never talks about it unless you ask. Lives in a decent place, drives an old truck, and just keeps stacking. He is not chasing clout, he is chasing freedom. That is the vibe: less ego, more sats, all grounded in life. **The Big Picture** Stack those sats. Do it quietly, do it consistently, and do not let the green days puff you up or the red days break you down. Humility is the secret sauce, it keeps you grounded while the world spins wild. In a decade, when you look back and smile, it will not be because you shouted the loudest. It will be because you stayed the course, one sat at a time. \ \ Stay Humble and Stack Sats. 🫡
@ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-07 00:26:37There is something quietly rebellious about stacking sats. In a world obsessed with instant gratification, choosing to patiently accumulate Bitcoin, one sat at a time, feels like a middle finger to the hype machine. But to do it right, you have got to stay humble. Stack too hard with your head in the clouds, and you will trip over your own ego before the next halving even hits. **Small Wins** Stacking sats is not glamorous. Discipline. Stacking every day, week, or month, no matter the price, and letting time do the heavy lifting. Humility lives in that consistency. You are not trying to outsmart the market or prove you are the next "crypto" prophet. Just a regular person, betting on a system you believe in, one humble stack at a time. Folks get rekt chasing the highs. They ape into some shitcoin pump, shout about it online, then go silent when they inevitably get rekt. The ones who last? They stack. Just keep showing up. Consistency. Humility in action. Know the game is long, and you are not bigger than it. **Ego is Volatile** Bitcoin’s swings can mess with your head. One day you are up 20%, feeling like a genius and the next down 30%, questioning everything. Ego will have you panic selling at the bottom or over leveraging the top. Staying humble means patience, a true bitcoin zen. Do not try to "beat” Bitcoin. Ride it. Stack what you can afford, live your life, and let compounding work its magic. **Simplicity** There is a beauty in how stacking sats forces you to rethink value. A sat is worth less than a penny today, but every time you grab a few thousand, you plant a seed. It is not about flaunting wealth but rather building it, quietly, without fanfare. That mindset spills over. Cut out the noise: the overpriced coffee, fancy watches, the status games that drain your wallet. Humility is good for your soul and your stack. I have a buddy who has been stacking since 2015. Never talks about it unless you ask. Lives in a decent place, drives an old truck, and just keeps stacking. He is not chasing clout, he is chasing freedom. That is the vibe: less ego, more sats, all grounded in life. **The Big Picture** Stack those sats. Do it quietly, do it consistently, and do not let the green days puff you up or the red days break you down. Humility is the secret sauce, it keeps you grounded while the world spins wild. In a decade, when you look back and smile, it will not be because you shouted the loudest. It will be because you stayed the course, one sat at a time. \ \ Stay Humble and Stack Sats. 🫡 -
 @ a58a2663:87bb2918
2025-03-05 12:41:36After two years of using Standard Notes as my main note-taking app, I’m switching to Obsidian. The $100 that Standard Notes charges for basic editing capabilities is difficult to justify, especially for someone paying in Brazilian Real and striving to make a living from writing. However, I will certainly miss its simplicity and cleaner interface. It’s my impression that the developers are missing an opportunity to create a privacy-focused note-taking app tailored to the specific needs of writers, rather than general users. Substack, for example, achieved such success because it targeted the distribution and monetization of writers’ work. But we need more tools focused not on distribution or monetization, but on the actual process—indeed, the various phases of the process—of creating texts. This is especially true for complex, long-form texts with different levels of argumentation, numerous written and multimedia sources, and cross-references to other works by the author. It’s crucial that an app like this doesn’t feel overly complex, like Notion or Evernote, or so all-purpose, like Obsidian. And, of course, I’m not talking about a new full-fledged text editor like Scrivener. Just a thought. Take note.
@ a58a2663:87bb2918
2025-03-05 12:41:36After two years of using Standard Notes as my main note-taking app, I’m switching to Obsidian. The $100 that Standard Notes charges for basic editing capabilities is difficult to justify, especially for someone paying in Brazilian Real and striving to make a living from writing. However, I will certainly miss its simplicity and cleaner interface. It’s my impression that the developers are missing an opportunity to create a privacy-focused note-taking app tailored to the specific needs of writers, rather than general users. Substack, for example, achieved such success because it targeted the distribution and monetization of writers’ work. But we need more tools focused not on distribution or monetization, but on the actual process—indeed, the various phases of the process—of creating texts. This is especially true for complex, long-form texts with different levels of argumentation, numerous written and multimedia sources, and cross-references to other works by the author. It’s crucial that an app like this doesn’t feel overly complex, like Notion or Evernote, or so all-purpose, like Obsidian. And, of course, I’m not talking about a new full-fledged text editor like Scrivener. Just a thought. Take note. -
 @ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-04 17:00:18This piece is the first in a series that will focus on things I think are a priority if your focus is similar to mine: building a strong family and safeguarding their future. --- Choosing the ideal place to raise a family is one of the most significant decisions you will ever make. For simplicity sake I will break down my thought process into key factors: strong property rights, the ability to grow your own food, access to fresh water, the freedom to own and train with guns, and a dependable community. **A Jurisdiction with Strong Property Rights** Strong property rights are essential and allow you to build on a solid foundation that is less likely to break underneath you. Regions with a history of limited government and clear legal protections for landowners are ideal. Personally I think the US is the single best option globally, but within the US there is a wide difference between which state you choose. Choose carefully and thoughtfully, think long term. Obviously if you are not American this is not a realistic option for you, there are other solid options available especially if your family has mobility. I understand many do not have this capability to easily move, consider that your first priority, making movement and jurisdiction choice possible in the first place. **Abundant Access to Fresh Water** Water is life. I cannot overstate the importance of living somewhere with reliable, clean, and abundant freshwater. Some regions face water scarcity or heavy regulations on usage, so prioritizing a place where water is plentiful and your rights to it are protected is critical. Ideally you should have well access so you are not tied to municipal water supplies. In times of crisis or chaos well water cannot be easily shutoff or disrupted. If you live in an area that is drought prone, you are one drought away from societal chaos. Not enough people appreciate this simple fact. **Grow Your Own Food** A location with fertile soil, a favorable climate, and enough space for a small homestead or at the very least a garden is key. In stable times, a small homestead provides good food and important education for your family. In times of chaos your family being able to grow and raise healthy food provides a level of self sufficiency that many others will lack. Look for areas with minimal restrictions, good weather, and a culture that supports local farming. **Guns** The ability to defend your family is fundamental. A location where you can legally and easily own guns is a must. Look for places with a strong gun culture and a political history of protecting those rights. Owning one or two guns is not enough and without proper training they will be a liability rather than a benefit. Get comfortable and proficient. Never stop improving your skills. If the time comes that you must use a gun to defend your family, the skills must be instinct. Practice. Practice. Practice. **A Strong Community You Can Depend On** No one thrives alone. A ride or die community that rallies together in tough times is invaluable. Seek out a place where people know their neighbors, share similar values, and are quick to lend a hand. Lead by example and become a good neighbor, people will naturally respond in kind. Small towns are ideal, if possible, but living outside of a major city can be a solid balance in terms of work opportunities and family security. --- Let me know if you found this helpful. My plan is to break down how I think about these five key subjects in future posts.
@ 04c915da:3dfbecc9
2025-03-04 17:00:18This piece is the first in a series that will focus on things I think are a priority if your focus is similar to mine: building a strong family and safeguarding their future. --- Choosing the ideal place to raise a family is one of the most significant decisions you will ever make. For simplicity sake I will break down my thought process into key factors: strong property rights, the ability to grow your own food, access to fresh water, the freedom to own and train with guns, and a dependable community. **A Jurisdiction with Strong Property Rights** Strong property rights are essential and allow you to build on a solid foundation that is less likely to break underneath you. Regions with a history of limited government and clear legal protections for landowners are ideal. Personally I think the US is the single best option globally, but within the US there is a wide difference between which state you choose. Choose carefully and thoughtfully, think long term. Obviously if you are not American this is not a realistic option for you, there are other solid options available especially if your family has mobility. I understand many do not have this capability to easily move, consider that your first priority, making movement and jurisdiction choice possible in the first place. **Abundant Access to Fresh Water** Water is life. I cannot overstate the importance of living somewhere with reliable, clean, and abundant freshwater. Some regions face water scarcity or heavy regulations on usage, so prioritizing a place where water is plentiful and your rights to it are protected is critical. Ideally you should have well access so you are not tied to municipal water supplies. In times of crisis or chaos well water cannot be easily shutoff or disrupted. If you live in an area that is drought prone, you are one drought away from societal chaos. Not enough people appreciate this simple fact. **Grow Your Own Food** A location with fertile soil, a favorable climate, and enough space for a small homestead or at the very least a garden is key. In stable times, a small homestead provides good food and important education for your family. In times of chaos your family being able to grow and raise healthy food provides a level of self sufficiency that many others will lack. Look for areas with minimal restrictions, good weather, and a culture that supports local farming. **Guns** The ability to defend your family is fundamental. A location where you can legally and easily own guns is a must. Look for places with a strong gun culture and a political history of protecting those rights. Owning one or two guns is not enough and without proper training they will be a liability rather than a benefit. Get comfortable and proficient. Never stop improving your skills. If the time comes that you must use a gun to defend your family, the skills must be instinct. Practice. Practice. Practice. **A Strong Community You Can Depend On** No one thrives alone. A ride or die community that rallies together in tough times is invaluable. Seek out a place where people know their neighbors, share similar values, and are quick to lend a hand. Lead by example and become a good neighbor, people will naturally respond in kind. Small towns are ideal, if possible, but living outside of a major city can be a solid balance in terms of work opportunities and family security. --- Let me know if you found this helpful. My plan is to break down how I think about these five key subjects in future posts.